All you need to know about Section 8 Company in India

Khushboo Priya | Updated: Apr 24, 2019 | Category: NGO, Section 8 Company
Section 8 Company is one of the most talked and preferred NGO types. The reason, why you should opt for Section 8 NGO when compared to trust and society, is that it has got several exemptions in terms of tax and others. Besides, in order to start Section 8 NGO, Firstly, you need to obtain company registration under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013 and then proceed further.
In this write-up, we have covered several significant aspects of Section 8 Company such as its definition, features, eligibility, requirements and checklists, registration process, pros & cons, etc. So we recommend you to move on at a steady pace in order to grab every essential detail.
Table of Contents
What is Section 8 Company?
Any company formed with a prime objective of promoting specific fields and with a charitable aim is known as a Section 8 company. Moreover, Section 8 companies are governed under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013.
Since such companies are completely engaged in charitable work, they have several exemptions such as Income Tax return exemption, etc. Furthermore, these companies don’t share the profits earned with any of its members. Rather, profit is used for promoting the company’s object.
In short, Section 8 Companies are Non-Profit Organizations or Non-Governmental Organizations formed with the intention of doing charity work and working towards social welfare.
Objectives of Section 8 Companies
The primary objective of Section 8 Company is to work towards the welfare of society in the following fields: Science, Art, Sports, Education, Research, Social welfare, Protection of the environment, etc.
Further, the aim of establishing this company is to promote all the aforementioned fields while keeping the public interest into consideration.
Features of incorporating a Section 8 Company in India
There are numerous things which make Section 8 Companies distinct from others. Those features are:
- Nobody can treat Section 8 companies as a Small Company.
- Members of the company can’t avail any profit or dividend.
- The members can use any profit or income of the company for the promotion of the company’s object.
- One can’t incorporate Section 8 companies using the Form INC-29.
- As per Section 8 (2) of the Companies Act, 2013, such companies can enjoy all the benefits and shall be subject to all the obligations of other limited companies.
- Section 8 companies receive a special license from the Central Government.
- Such companies don’t require using the suffix ‘Pvt Ltd.’ or ‘Ltd’ with its name.
- The Central Government governs these companies. However, the power of the Central Government is delegated to the Registrar of Companies (ROC). Further, ROC has jurisdiction over the area where the company’s registered office is present. Therefore, the application for company registration must be made to the ROC.
Checklists/Documents required for incorporating Section 8 Company
In order to register your company as Section 8, you should keep the following documents ready in a proper sequence:
- Copy of PAN (Permanent Account Number) of all Directors & Shareholders as an identity proof;
- Copy of a Driving License or Aadhaar Card or Passport or Election ID card, etc., as an address proof;
- Recent passport size photographs of all the Directors and Shareholders;
- The Utility bills of the registered office not older than 2 months;
- Form DIR-2, consent to act as a director;
- Rent agreement, in the case the registered office is on rent;
- NOC (No-Objection Certificate) from the Landlord;
- Details of the Directorship of the directors in any other companies or LLP, if any.
Forms required for registering Section 8 NGO
For registering your company under Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013, you will require the following forms:
| Forms required | Purpose of the form |
| INC 1/RUN | For the reservation of the proposed company name |
| INC 7 | Application for company registration as Section 8 |
| INC 8 | Declaration |
| INC 9 | An affidavit from every subscriber and director |
| INC 12 | Application for grant of license for operating the company as Section 8 |
| INC 13 | MOA (Memorandum of Association) of the company |
| INC 14 | Declaration from a Chartered Account in practice |
| INC 15 | Declaration from every entity filing the application |
| INC 16 | License for company incorporation as Section 8 |
| INC 22 | For Registered Office |
| DIR 2 | Consent to act as a Director |
| DIR 3 | Application to Registrar of Companies (ROC) to obtain DIN (Director Identification Number) |
| DIR 12 | Appointment of Directors |
Section 8 Company Registration Procedure
One can surely opt for section 8 company registration online. However, we suggest you to hire a professional for the registration procedure because it’s quite lengthy and cumbersome. Although we have described the registration process step by step as follows:
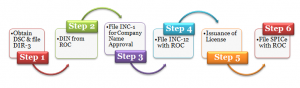
Step1: Obtain DSC and file Form DIR-3
The first step to incorporating Section 8 NGO in India is to obtain a DSC (Digital Signature Certificate) of the proposed directors of the company. After you have received the DSC, you need to file Form DIR-3 with the Registrar of Companies, requesting for a DIN (Director Identification Number).
For DIN, you need to attach documents such as Identity proof and Address proof.
Step2: DIN from ROC
If the ROC finds the form valid and true, it will approve and allow the DIN to the proposed directors.
Step3: File INC-1/RUN for Company Name Approval
Next, you need to file form INC-1/RUN for the company’s name approval with the ROC. You need to propose a total of two names in the order of choice. However, the ROC will allow only one of the names out of two depending upon the availability.
Step 4: File Form INC-12 with the ROC
Once your company’s name is approved, you need to file Form INC-12 with the ROC. Form INC-12 is an application for the grant of license for operating the company as Section 8.
Documents you would require to attach with INC-12 are:
- As per Form INC-13, Memorandum of Association (MOA);
- Articles of Association (AOA);
- As per Form INC-14, Declaration from the Practicing Chartered Accountant;
- As per INC-15, Declaration from every person filing the application;
- Assessed expenditure and income for the next three years.
The subscription pages of the MOA and AOA of the company must contain the signature of every subscriber. Furthermore, it must also their name, address, and occupation. The subscribers must sign the document in the presence of a minimum of one witness who needs to attest the signature and add his name, address, and occupation, along with his signature.
Step5: Issuance of License
The ROC will examine the form. If everything is correct, they will approve the form. Besides, the ROC will issue the license under Section 8 in Form INC-16.
Step6: File SPICe Form INC-32 with the ROC
After you have received the license, you require filing SPICe INC-32 with the Registrar of Companies for company incorporation. Further, you are required to attach the following documents:
- As per INC-9, an affidavit from every director and subscriber;
- KYC of every director;
- Declaration regarding the deposits;
- Consent letter of every director;
- Form DIR-2 with an identity proof and address proof of the directors;
- Utility bills as an address proof of office which must not be older than two months;
- NOC in case the office premise is on rent or lease;
- Interest in other entities of all directors;
- Draft MOA and AOA.
If the ROC finds the form satisfying with every criterion, he will issue a COI (Certification of Incorporation) along with a unique CIN (Corporate Identity Number).
Advantages of Section 8 Company Registration
We have already discussed a few significant features of registering Section 8 companies in India. Now, let’s dig a little deep and find out the advantages of section 8 company over trust and society. They are as follows:
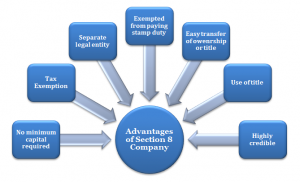
No minimum capital requirement
For section 8 companies, there isn’t any prescribed minimum capital requirement as in the public company registration and others. However, at any stage, there could be alteration in the capital structure as required for the company’s growth. Further, there could be direct funding and donations to Section 8 company.
Tax exemptions
Since section 8 companies are a form of a non-profit organization, they can avail several tax exemptions, especially the donors who contribute to such companies. Hence, under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act, 1961, the donors can claim the tax benefit against the donation they have made to the company.
Separate legal entity
Just like other business entities, a section 8 company is a separate legal entity and stands distinct from its members. Further, the company also has a perpetual existence.
Exempted from paying stamp duty
Section 8 companies have exemptions from paying the stamp duty required for incorporation as applicable in the case of other business entities such as the private and public company.
Transfer of ownership/title is easy
Unlike other business entities, the transfer of title or ownership is easily transferable. Further, the interest and shares of other members of the company are also considered as movable property and easy to transfer. As a result, it’s easy for the members of the company to leave and transfer its ownership to others.
Use of title
Unlike other companies, such as private limited company and public limited company, LLP, etc. where it’s imperative to use the title ‘limited company’ or ‘LLP’ in the end, section 8 companies have got the exemption from the use of the title. Further, such companies can still execute their operations without informing the public of their status as limited liability. However, they need to add a suffix such as foundations, associations, etc.
More credible
Such companies hold more credibility than other non-profit organizations be it a Society or Trust. Since the licensing is done by the Central Government, the rules are stringent when compared to other companies. Hence, changes in MOA (memorandum of Association) and AOA (Articles of Association) aren’t possible in any situation or at any stage. Therefore, due to strict regulations, section 8 companies are more reliable and hold better credibility than others.
Hence, from the above discussion, it’s quite evident why sec 8 company is preferred over NGO and trust.
Disadvantages of registering your company as Section 8
Well, everything has its pros and cons and hence, so does section 8 companies also have. We have observed its benefits; let’s find its disadvantages as well so that you can identify whether it’s suitable for you to go with Section 8 Company or not.
Limitations of Section 8 companies in India are as follows:
- The profits earned should only be used for the promotion of the company or satisfying its objectives of encouraging arts, commerce, science, etc. Apart from this, nobody else can claim the profit of the company be it, director or shareholder.
- Unlike other companies, the members of the company can’t be appointed as the remunerating officer.
- Making changes in the MOA and AOA of the company isn’t possible due to the stringent rules and regulations of the company. This can be counted both in advantages and disadvantages.
- Declaring the dividend or distribution of profit among its member is not allowed.
- Additionally, except the reimbursement of pocket expenses, reasonable rent on the premises or reasonable interest on lent, no benefit or remuneration shall be paid to its members whether servant or officer of the company.
Penalty under Section 8
If a company doesn’t follow the terms and regulations of Section 8, then as per the provisions of sub-section (11) of Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013, the company shall be subject to fraudulent actions and shall be held punishable. Furthermore, the company would have to pay:
- A fine of Rs. 10 lakhs which could further extend to Rs. 1 crore.
- Every director, along with the officer of the company in default shall be punishable. Besides, they would face imprisonment for the terms of three years with a fine not less than Rs. 25,000. However, this fine could extend to Rs. 25 lakh.
- Or the guilty will need to serve both.
In case you have any query regarding Section 8 Company in India, leave a comment below.
Also, Read: How much fees is required for Section 8 Company Registration in India?














