An Overview of NBFC Registration
NBFC or Non-Banking Financial Company is a Company registered under the Companies Act, 2013 involved in the business of loans & advances, acquisition of bonds or securities or shares or bonds or stocks issued by the Government or Local Authority or other marketable securities like leasing, insurance business, hire-purchase, chit business. NBFCs in India doesn’t possess proper banking Licenses such as Commercial Banks (after obtaining NBFC License from RBI) provide a variety of very supportive & helpful services to public depositors, borrowers & investors in some selected areas of Business.
Following are some conditions that should be fulfilled to continue NBFC License:
- Total Assets comprise more than 50% of Financial Assets;
- More than 50% of the gross income must be generated from Financial Assets.
Restricted Activities:
- Industrial Activity;
- Agricultural Activity;
- Sale or Purchase of Goods & Services;
- Sale or Purchase of Construction of Immovable Property.
Note: Another way of commencing a Finance Business in India is to take over an existing NBFC; however, it is advisable to go for New NBFC Registration.
Market Size of NBFC
In India, there are a number of banks. However, certain areas are still untouched & no banking facilities are available there; this consequently has resulted into the increased demand for getting loans from NBFC &eventually, more no. of NBFC Registrations. In the last few years, the NBFC Registration has taken a boom and played an essential role in the growth of the financial sector. The main reason behind this is providing customised loan product, user friendly loan policy and, faster processing loans and the use of advanced technology & digital reach.
In India, MBFC has managed to attract a significant stake of the market in banking & banking-related services. Non-Banking Financial Companies are involved in the business identical to a bank but don’t cover everything that a bank is engaged into. In our opinion, the NBFC sector will continuously grow because of advanced technologies used by financial companies.
Role and Functions of an NBFC
The role and functions of an NBFC in India can be summarised as follows:
- To develop sectors like Infrastructure, Education and MSMEs;
- To assist in wealth creation;
- To generate substantial employment;
- To provide financial assistance to the economically weaker section of society;
- Faster processing loan;
- A digital platform to offer loans using advanced technology;
- To assist in the economic development of the country;
- To contribute to the state exchequer;
- To provide specialised credit;
- To help in the growth of the financial market.
Different Types of NBFCs in India
Basically, NBFCs are categorised into two different parts and you can check the same below:
- On the Basis of Liabilities:
- All NBFCs-ND whose asset size is Rs. 500 crores and more as per the last audited balance sheet is deemed as Systemically Important NBFC (NBFC-ND-SI);
- The asset size of the group companies to be clubbed;
- NBFC-ND-SI has to follow the policies suggested by the Reserve Bank of India mandatorily & exempt from Credit Concentration Norms;
- NBFC-ND- Non-Systemically Important is exempt from observing Prudential Norms, 2015 (except Annual Certificate).
- On the Basis of Activities:
- NBFC- Investment and Credit Company (ICC): ICC is one common License for all types of financing business in India. Earlier, there were three different licenses, namely Loan Company, Asset Finance Company and Investment Company. Now, after the merger into one single License defined as ICC (Investment & Credit Company), it allows the license holder to engage in various kinds of wholesale, retail loans and Investment business. The ETA for the NBFC ICC License is estimated to be 120 days.
- NBFC-Microfinance Companies (MFIs): NBFC-MFI is mainly formed to provide credit to economically disadvantaged groups.
- NBFC-Factors: It is concerned with the acquisition of receivables of an assignor/extending loans against the security of the receivables at a discount.
- NBFC-Peer to Peer Lending (P2P): It provides an online or digital platform to being lenders & borrowers together to help mobilise funds.
- NBFC-Account Aggregators: Collecting & facilitating detaiuls of customer’s financial assets in a consolidated, organised & retrievable manner to the customer/others as specified by the customer.
- Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC): This type of NBFC deploys at least 75 per cent of its total assets in infrastructure loans.
- NBFC-Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC-ND-SI): It’s mainly involved in investment in equity shares, preference shares, debt or loans of group companies.
- NBFC-NOFHC (Non-Operative Financial Holding Company): Facilitation of promoter groups or promoters in establishing new banks.
- MGC (Mortgage Guarantee Company): Undertaking of mortgage guarantee business.
- NBFC-IDF (Infrastructure Debt Fund): The activities of this NBFC are mainly concerned with the facilitation of the flow of long-term debt into infrastructure projects.
New Scale-Based Regulations of NBFC
According to the revised framework, the Reserve Bank of India has notified 4 scale-based layers to regulate NBFCs, namely, the Base layer, upper layer, middle layer, and top layer. Below is the table that categories NBFCs into different layers:
|
Layers |
Types of NBFCs |
|
Base Layer |
|
|
Middle Layer |
Note: Except for IDF & SPDs, all these NBFCs can be shifted to the upper layer. |
|
Upper Layer |
|
|
Top Layer |
|
Revised Regulatory Framework for NBFCs – 2021
On October 22, 2021, the RBI introduced a scale-based revised regulatory framework for NBFCs with a view to having a tight oversight of the sector. According to this revised framework, there will be more categorised of NBFCs as per their activity with strict rules.
The key highlights of the revised regulatory framework for NBFCs:
- There will be a ceiling of Rs. 1 crore per borrower for financing subscription to IPO;
- The regulatory structure of the Non-Banking Financial Companies will comprise y layers, as we discussed above.
- The NOF requirement will be hiked for all NBFCs to 10 crores with certain exceptions and you can check the table below:
|
NBFCs |
Present NOF |
By Mar 2025 |
By Mar 2027 |
|
NBFC-ICC |
Rs. 2 crores |
Rs. 5 crores |
Rs. 10 crores |
|
NBFC-MFI |
Rs. 5 crores |
Rs. 7 crores |
Rs. 10 crores |
|
NBFC-Factors |
Rs. 5 crores |
Rs. 7 crores |
Rs. 10 crores |
- In the case of NBFC-AA, P2P, and NBFC without any public funds & no customer interface, the NOF will be Rs. 2 crores;
- NBFCs will be required to identify loans overdue for more than 90 days as NPAs by March 2026 & over 150 days by March, 2024.
Current and Revised NOF Requirements for Different NBFCs
|
Type of NBFC |
Current NOF Requirements (INR) |
Revised NOF Requirements (INR) |
|
NBFC P2P |
2 crores |
No Revision |
|
NBFC-AA |
2 crores |
No Revision |
|
NBFC-ICC without public funds & without customer interface |
2 crores |
No Revision |
|
NBFC-Factor |
5 crores |
10 crores |
|
HFC (Housing Finance Company) |
20 crores |
No Revision |
|
SPDs undertaking core Activities |
150 crores |
No Revision |
|
SPDs undertaking non-core Activities |
250 crores |
No Revision |
|
NBFC-IDF |
300 crores |
No Revision |
|
NBFC-IFC |
300 crores |
No Revision |
|
Other NBFC-ICC |
2 crores |
10 crores |
|
NBFC-MFI |
5 crores |
10 crores |
|
NBFC-MGC |
100 crores |
No Revision |
Advantages of NBFC Registration in India
In India, the advantages of an NBFC Registration are:
- Saves Time and Cost: In contrast to small banks, the process of incorporating an NBFC is much simpler. Opening a bank involves a large amount of capital, time and cost, whereas the same is not in the case of an NBFC. One just needs the assistance of a good NBFC consultant with prior experience to obtain NBFC Registration in India.
- Easy Recovery of Loan: NBFCs work systematically and offer customised loan products with achievable repayments. It becomes a convenient process for the borrowers as they can repay the loan amount quickly within the prescribed time period.
- Economic Growth: Businesses and individuals are looking for an easy and reliable source of credit for their financial requirements. NBFCs provide affordable and secure credit facilities to an unserved market for their personal and business-related credit requirements. Therefore, NBFCs have contributed to the country's economic growth by providing financial freedom to MSMEs, self-employed professionals and individuals.
- Trading Money Market: NBFCs serve the benefits of trading in money market instruments.
- Provide Multiple Choices: Due to technological advancement, NBFCs are providing multiple choices to reach a huge audience at a quicker step. Non-Banking Financial Company covers both the large businessperson & small sectors by providing them multiple choices to avail themselves the credit facilities.
- Allowed FDI: Under NBFC, up to 100%, FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) is also an amazing advantage of NBFC Registration. Non-Banking Financial Companies are the largest propellants of starting finance in the country. Also, the financing process is faster & easier compared to Banks.
- Give Loans to Poor Credit Scorers: Generally, banks check the credit score first and in case of a poor credit score, the bank rejects the loan application. However, NBFCs provides loan to people having less credit score.
Documents Required for NBFC Registration
The following documents are required for NBFC Registration as follows:
- Certified or original copy MOA (Memorandum of Association), AOA (Articles of Association), COI (Certificate of Incorporation);
- Net worth certificate of Shareholders, Directors, and Company;
- Business profile of Directors and Shareholders;
- Income Tax Returns;
- Educational qualification certificates of the proposed directors;
- KYC details such as PAN of the company, GST Number, and address proof of the company;
- Highest experience certificate;
- Bank account details of the company;
- Format of Board Resolution regarding NBFC Registration;
- IT Returns;
- Loan and Business Structure;
- Credit report of directors and shareholders;
- Last 3 years of the audited balance sheet;
- Related party disclosures;
- Detailed action plan for next 5 years, including Risk Assessment Policy & Fair Practice Code;
- Report of Banker confirming no lien on fixed deposit.
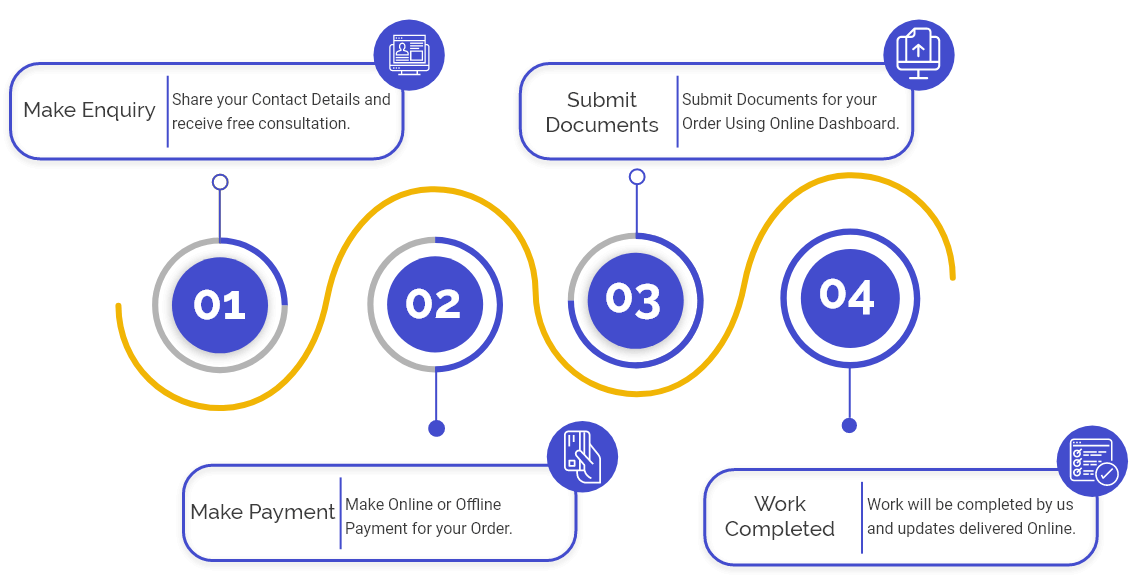
Procedure for NBFC Registration
The steps involved in the process of NBFC Registration are as follows:
- First you need to hire an experienced NBFC Consultant who is having at least 10 years of experience having a team of professionals such as CA, Lawyers, CS, and Senior Banker.
- Then, you need to select a name of the company that must include, Fintech, Finance, Capital, Finserv, Investment, Leasing, etc.;
- Then the applicant need to arrange all the required documents to initiate the NBF Registration process;
- After that, the applicant must file the application with the Authority.
- After submitting the application to the Authority, then they will verify the documents & application to check the accuracy of the submission made by the applicant;
- Once satisfied, the Authority will issue the NBFC Registration Certificate.
Conditions Specified by RBI for NBFC Registration
After filing the application, the RBI will examine the file & issue the License only after fulfilling the below mentioned conditions:
- Ability of NBFC to repay all its dues to investors & Business Plan of the Company must fulfil the larger interest of the Society;
- Earning capability of the proposed Business;
- Proposed NBFC shall comply with RBI regulations;
- Activities shall be carried out in a way that it shall be in the public interest;
- Capability to infuse sufficient capital;
- NBFC activities shall not be damaging any public interest at large;
- Board shall act in the interest of depositors or public.
NBFC Registration with RBI
The RBI has two separate departments to regulate & supervise the functioning of NBFCs in India:
- Department of Non-Banking Regulation (DNBR): This is responsible for conducting the new or fresh NBFC Registration and it is responsible for preparing the policies & regulations for the NBFCs. The DNBR has a transparent & innovative assessment process for NBFC application. The Department of Non-Banking Regulation will send you an email & a formal notice if they require any extra documents at the time of the NBFC Registration process. The Reserve Bank of India expects your submission or response to the given notice within 7 or 15 or 30 days as per the NBFC Regulations.
- Investigation of Shareholders or Directors' profiles;
- Regulates & administers NBFC Business;
- Publish Circular, Order, and Notifications for NBFC;
- Assessment of application submitted for NBFC License (all categories of NBFC);
- Communication with applicant company in the pre-registration process;
- The communicated final decision to the company with the Approval of RBI (Executive Director Office).
- Department of Non-Banking Supervision (DNBS):
- It is responsible for complying with the NBFC Rules &Regulations issued by the Reserve Bank of India;
- Cancel or suspend NBFC License in case of Non-Compliance with the laws;
- After approval, DNBR collects the Net Owned Certificate and bankers report before they issue you the original NBFC License;
- It is responsible for complying with the NBFC Rules & Regulations issued by the Reserve Bank of India;
- On-site inspection or conduct audit from time to time;
- Conduct & educate a seminar for the general awareness regarding the NBFC Compliance, Business, and Regulations.
Cancellation of NBFC Registration or License
- The business plan is not up to the mark;
- NBFC consultants are not experienced;
- It can be cancelled in case of insufficient financial experience;
- Shareholder and Directors business profile is not satisfactory;
- The area of carrying NBFC operations is not promising;
- Capital is arranged from a prohibited source.
NBFC Compliance After Getting NBFC License from RBI
- Formalities Before Commencement of Business: After obtaining Registration but prior to the commencement of business, there are different types of compliances which should be followed for further operations. NBFCs must apply for the following:
- Central KYC;
- Adoption of FPC (Fair Practice Code);
- Adoption of Anti-Money Laundering Policy and IT Policy;
- CERSAI Registration;
- Registration with 4 credit rating agencies such as CIBIL, Equifax, ICRA, and Experian;
- FIU-IND Registration;
- Submission of financial information to information utilities;
- National e-governance registration.
- Annual Compliances:
- Filing of Annual Return with the RBI;
- Tax filing – ITR & GST Returns;
- Statutory compliances with the ROCs (Registrar of Companies) Annual Return Filing, Filing of Financial Statements.
Penalties for Non-compliance with RBI Regulation
In India, the RBI has the power to impose a penalty on an NBFC for violating the provisions of the RBI Act. These penalties include:
- If a company carries out its operations without obtaining NBFC License, the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) can impose a fine of not less than Rs 1 Lakh, which can go up to Rs 5 Lakh or twice the amount involved in such a violation, whichever is more;
- If a company carries out its operation without obtaining NBFC License, the directors of the company are punishable with imprisonment up to one year;
- In case of non-compliance with RBI directions, then the defaulter will be liable for imprisonment of up to 3 years;
- Failure to produce documentation/answer queries: Fine, which may extend to Rs. 2000/- per offence and in case of continuous non-compliance, an additional fine up to Rs. 100/- per day is charged from the first offence;
- Acceptance of Deposits: Imprisonment or jail up to 3 years & a fine of twice the amount received.
FDI in NBFC
100% FBI is allowed for Non-Banking Financial Companies under automatic route if NBFC is involved in the following subject to the minimum capitalization requirements:
- Merchant Banking;
- Underwriting;
- Portfolio Management Services;
- Investment Advisory Services;
- Financial Consultancy;
- Stock Broking;
- Asset Management;
- Venture Capital;
- Custodian Services;
- Factoring;
- Credit Rating Agencies;
- Licensing and Finance (Financial Leases only);
- Housing Finance;;
- Forex Banking;
- Credit Card Business;
- Money Changing Business;
- Micro Credit;
- Rural Credit.
Some Benefits of Fintech-Based NBFC Business Model
- Facility of online loan;
- Use of AI, Big data & Machine Learning tools to minimise the fraud;
- Working on financial inclusion app;
- Addressing client problems using technology;
- Creating space for the alternative online banking system, intruding conventional business model facing vital legal problems.
FAQ of NBFC Registration
Yes, an NBFC or Non Banking Financial Corporation can accept deposits.
The loans offered by NBFCs are Gold Loan, SME Lending, Personal Loans, Loan against Property, Loan against Shares Asset Financing, etc.
The minimum NOF for NBFC registration is Rs 2 crores.
An NBFC shall keep its NOF in the current account of the newly formed company in the form of a Fixed Deposit.
Yes, all the Directors in an NBFC must have financial or banking experience.
An NBFC needs a minimum of 2 directors.
The factors considered by RBI are the Right Team, Clean Capital, Business Plan, and Area of Operation.
An NBFC License remains has lifetime validity. However, the same is liable to be cancelled due to non-compliance with the law.
The new areas that can be explored in the NBFC segment are Fintech based lending, P2P, and NBFC-AA.
The PBC criteria for an NBFC are that out of the total assets, 50% must be financial, and the remaining 50% must be generated from the financing business.
Yes, an Existing NBFC or shareholder can form a new NBFC but with subject to the requirement and convincing business Plan.
Yes, the Directors can be common in 2 or more NBFCs.
Yes, for carrying a loan or investment business in India, one needs to apply for NBFC License.
All the unlicensed lending or financing business is deemed to be illegal.
NBFC with asset size more than Rs 500 crores deemed to systemically important NBFCs.
Yes, higher compliance has been set for NBFC-SI.
No, RBI does not regulate insurance, Chit fund, as all such entities are regulated by SEBI, Nidhi Company, etc.
The main difference between the both is that Public funds include ICD, Loan from Banks. However, Public deposits mainly include the souring of funds from individuals.
Yes, the Interest rate is subject to the business plan submitted by the Applicant Company to the RBI.
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a financial institution registered under the provisions of Companies Act, 2013, that deals in financial services.
NBFCs are registered under the Companies Act, 2013, whereas Banks are registered under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. Further, an NBFC is not allowed to accept all kinds of deposits. However, Banks can easily accept the demand and time-based deposits from their customers.
The two categories of NBFCs are based on Liability and based on Activities.
In India, some of the renowned examples of NBFCs are Muthoot Finance Ltd; HDB Financial Services; Aditya Birla Finance Ltd; L&T Finance Ltd; Tata Capital Financial Services Ltd.
Yes, an NBFC can provide loans to the people in various forms, such as Unsecured Personal Loan, Business Loan, Secured Loan against property, Loan to MSMEs, Loan against Securities, Gold loan, etc.
Yes, an NBFC can list its shares on a recognized stock exchange.
Power Finance Corporation Limited has listed its shares in National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
Any company registered under the Companies Act, 2013, can incorporate an NBFC.
No, the FD in NBFC is not as safe as Bank FD. Although the returns offered on deposits by NBFCs are higher compared to bank FDs, however, the risk factor is higher as well.
In India, NBFCs play a crucial role in promoting inclusive growth by catering to the various financial needs of bank-excluded customers. Moreover, it often takes the lead role in offering innovative financial services to the MSME sector suitable to their diverse business needs.
The term “crisis” denotes that IL&FS scam, after which NBFCs in India faced a severe liquidity crisis.
Type 1 NBFC refers to the Non- Deposit taking NBFCs (NBFC-ND) and Type 2 NBFC refers to the Deposit-taking NBFCs (NBFCs – D).
Type 1 NBFCs denotes the NBFC that do not accept public deposits or have any customer interface.
Type 2 NBFC refers to the Deposit-taking NBFCs (NBFCs – D) that accept public deposits and have customer interface.
RNBC stands for the Residuary Non-Banking Company. It is a type of NBFC in which a company is engaged in the business of receiving deposits.
A minimum of 12 months and a maximum of 60 months period is prescribed for an NBFC to accept deposits.
No, an NBFC cannot accept Demand Deposit or DD.
The working and compliance of an NBFC is regulated by the RBI within the framework of the RBI Act, 1934 (Chapter III-B) and the guidelines issued by it.
The formula for calculating NOF is the Share Capital + Share Premium + Reserves and Surplus - Accumulated Losses.
Yes, it is mandatory to obtain NBFC Registration in India.
The functions of an NBFC are Hire Purchasing, Leasing, Retail Financing, Rural Financing, Venture Capital Services, MSME Financing, and Trade Financing.