Managing Risk in Outsourcing of Financial Services by Co-operative Banks: RBI Guidelines

Karan Singh | Updated: Jul 23, 2021 | Category: RBI Advisory
The RBI (Reserve Bank of India) announced guidelines for co-operative banks to handle risks that will increase from outsourcing of financial services by co-operative banks in India. The RBI said that the CEO (Chief Executive Officer) and the senior management of such banks should be accountable for estimating risks and the applicability of all the present and future outsourcing activities. Scroll down to check the RBI guidelines to control risks in outsourcing of financial services by co-operative banks in India.
Table of Contents
Guidelines for Outsourcing of Financial Services by Co-operative Banks in India – Purpose
The Reserve Bank of India tells that the essential principles behind the issuance of these RBI’s guidelines are that the co-operative banks should make sure that the arrangements for outsourcing neither reduce its ability to satisfy their obligations to clients and the RBI nor obstruct efficient supervision by the National Bank for Agriculture & Development or the Reserve Bank of India. Moreover, these RBI’s guidelines will not apply to technology concerning problems.
Vital Guidelines on Outsourcing of Financial Services by Co-operative Banks in India
The RBI or Reserve Bank of India stated that a bank would maintain definitive control of outsourced activities. Co-operative banks shall have to conduct a self-assessment of their present arrangement for outsourcing now and bring their current arrangements for outsourcing in line with the guidelines announced within six months. The regulator has also stated that such banks will be accountable for all the actions of their service provider, comprising actions of business correspondents and their sub-agents or retail outlets. The method of compliant redressal of co-operative banks shouldn’t be settled on outsourcing accounts.
Co-operative banks are also imperative to put in place a management structure to supervise and regulate outsourcing activities. The suggestive critical risk in outsourcing has to be estimated the following:
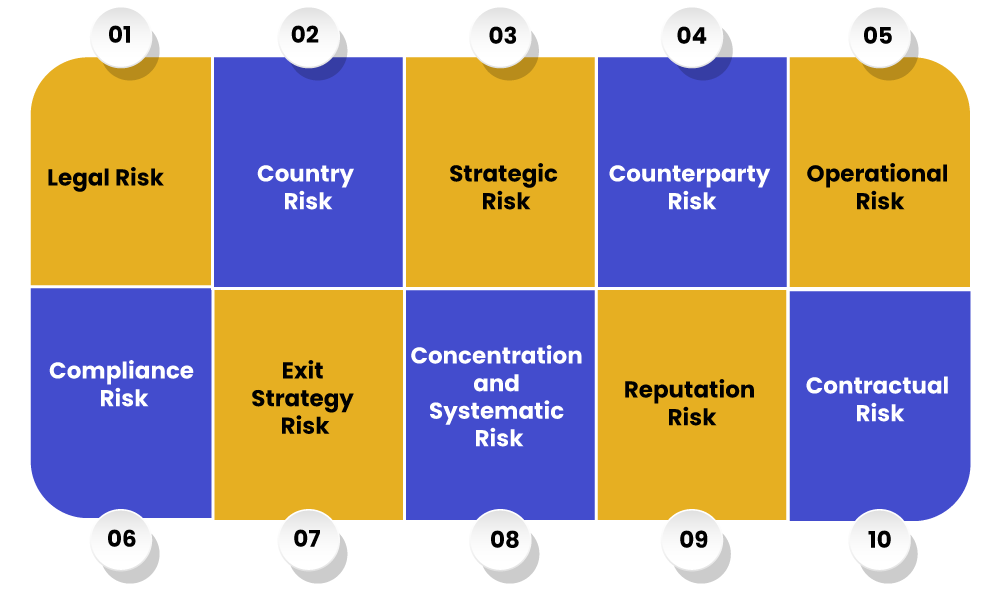
- Legal Risk: It includes but is not restricted to fines, penalising damages or penalties resulting from supervisory actions, and private settlements due to commissions and omissions of the service provider.
- Country Risk: Due to social, legal or political climate creating added risk.
- Strategic Risk: The service provider may perform business on its behalf, which is inconsistent with the complete strategic goals of the bank.
- Counterparty Risk: Due to unsuitable credit assessments or underwriting.
- Operational Risk: Emerging due to failure in technology, error, the insufficient financial capacity to obey obligations or/and deliver remedies.
- Compliance Risk: Client, privacy & prudential laws not sufficiently complied.
- Exit Strategy Risk: This could increase from over-reliance on a single firm the loss of applicable skills in the bank itself preventing it from bringing the doings back in-house and where the bank has listed into contracts wherein quick exits would be unusually expensive.
- Concentration and Systematic Risk: Due to lack of influence of individual banks over a service provider, more so when the banking industry has significant exposure to one service provider.
- Reputation Risk: Poor service from the service provider, its client communication not being reliable with the complete bank’s standard, or failure in protection & preservation of confidential client information.
- Contractual Risk: Emerging from whether or not the bank has the skill to enforce the contract.
A co-operative bank that is looking for outsourcing any of its financial activities will have to place a complete outsourcing policy consented by that Board. In case the bond of the service provider is eliminated prematurely before the finishing of services, IBA (Indian Banks’ Association)[1] will have to be notified with reasons for such elimination. The Association of Indian Banks would be preserving a vigilance list of such service providers for the entire banking industry for sharing among banks.
The RBI (Reserve Bank of India) declared that the board and CEO, as well as senior management, will be eventually accountable for the outsourcing of financial services or operations and to regulate risks inherent in such outsourcing relationships. Moreover, the co-operative banks should undertake reasonable due diligence to assess the capability of the service provider to obey the obligations in the outsourcing agreement.
The RBI (Reserve Bank of India) highlighted that the co-operative banks that make a decision to outsourcing of financial services but shouldn’t outsource core management functions, comprising policy formulation, internal audit and compliance, compliances with the KYC rules, credit sanction and management of the investment portfolio.
But, where required, experts, comprising the previous employees, can be hired on the basis of the contractual subject to the ACB (Audit Committee of Board), Board being assured that such proficiency does not exist within the banks’ audit function.
Any disagreement of interest in such cases will be identified and addressed efficiently. The ownership of audit reports in all cases will rest with standard functionaries of the internal audit function.
At the time of examinations or inspection, the Reserve Bank of India or NABARD (National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development shall re-evaluate the implementation of these RBI guidelines in order to assess the quality of the related risk management systems, especially in respect of material outsourcing.
Conclusion
While releasing the guidelines for managing risk in outsourcing financial services by the co-operative banks, the Reserve Bank of India stated that the lenders could hire experts, comprising previous employees, on the basis of contractual but subject to certain conditions. Outsourcing of financial services is mentioned as the use of a third party to perform activities on a regular basis.
NT642C29DCE69C264AC198E4BDE2C671F7F2-1













