An Overview of ESIC Registration
The Employee State Insurance (ESI) is social security and self-financing scheme which benefits the employees by providing them with various health benefits. ESI Scheme gives benefits to both employees and their families. The benefits provided by the ESI scheme include sickness benefits, disablement benefits, medical benefits, reimbursement of funeral expenses, and several other benefits. However, to benefit from the ESI scheme's benefits, the Employer with an employee count of more than ten employees (in some states, the prescribed limit is extended to twenty employees) earns a maximum salary of Rs. 21,000 p.m., are required to obtain ESIC Registration.
The Employee State Insurance (ESI) Act of 1948 works as the governing law for the ESI scheme. Hence, the ESI scheme is governed and regulated by the provisions of the ESIC Act, 1948. The Employee State Insurance Corporation is an autonomous body formulated by the Ministry of Labour and Employment. In India, all the activities concerning to ESI scheme are regulated by this independent body.
ESIC Registration is mandatory for those employers who have employee strength of more than ten employees and are earning a maximum salary of Rs. 21,000 p.m. By obtaining ESI Registration, the workers or the employees working are provided with several monetary, medical, and other benefits by the Employer.
What is an ESI Scheme?
The term ESI Scheme refers to a social security scheme designed to provide social protection to the employees working in the organized sector. Social protection refers to protection provided against the uncertain events of maternity, sickness, disablement, and death due to any injury caused in the course of employment. This scheme also focuses on providing medical care facilities to both insured employees and their family members (dependents).
What is an ESIC Code Number?
ESIC Code is a 17-digit unique identification number issued to every registered establishment. This code is generated either when the Employer submits the required information on the ESIC Portal or on the receipt of a survey report from the Social Security Officer.
Benefits of ESIC Registration in India
The following listed are benefits of ESIC Registration:
- It provides comprehensive medical benefits.
- It includes dependants.
- ESI Registration can be used easily at different ESI hospitals and dispensaries.
- Any payments made will be compensated or reimbursed.
- It also takes into account the needs of the disabled.
- It provides easy access to medical care in ESI Dispensaries or Hospitals.
- Sickness benefits are offered at the rate of 70 percent of the employee's salary. The same is provided if the sickness continues for more than ninety-one days a year.
- Maternity benefits are given in the form of paid leaves.
- 90% percent of the total salary of the insured person is given to his or her dependents in case of his or her death during employment.
- Funeral expenses are provided to the deceased’s family.
- In the Permanent Disablement case, 90 percent of the insured’s monthly salary is offered as an insurance benefit.
Who are eligible to obtain ESIC Registration?
The entities which are required to obtain ESIC Registration are as follows:
- Shops;
- Hotels or the Restaurants do not have any manufacturing activity but are engaged in providing service;
- Cinemas;
- An establishment engaged in Roadside Motor Transports;
- Newspaper Establishments;
- Private Medical or Educational Institutions.
Who is a Principal Employer as per the ESI Act?
A principal employer is usually the occupier or the owner of the factory to which the ESI Act applies. In the case of a Factory, either of the listed below can be considered a Principal Employer:
- Occupier.
- Owner.
- Managing Agent of the Occupier or Owner.
- Legal Representatives of the Deceased Occupier or Owner.
- Factory Manager.
- If the establishments belong to the Government of India.
However, in the case of any government-owned department, the head of the said department will be considered the Principal Employer. And, in all the other establishments, the person in charge of the Supervision and Control is called the Principal Employer.
Who is an Immediate Employer as per the ESI Act?
Immediate Employer can be either of those mentioned below:
- One who executes or completes any work inside the factory of the Principal Employer.
- One who executes or completes any work outside the premises supervised and managed by the principal Employer.
- One who provides the on-hire services of his employees to the principal Employer of a factory or establishment.
- And a Contractor.
Eligibility for ESIC Registration in India
Any establishment has more than 10 employees (in some other states, it is 20 employees) who have a maximum salary of Rs. 21,000/- has to compulsorily register itself with the ESIC within 15 days from the date of its applicability. Under the ESIC Scheme, the Employer needs to contribute an amount of 3.25% of the monthly salary paid to the employee, whereas the employee must contribute only 0.75% of their monthly salary. The only exemption to the employee in paying their contribution is whose salary is less than Rs. 176 per day.
Documents Required for ESIC Registration
The documents needed for obtaining ESIC Registration are as follows:
- In the case of a company, a Certificate of Incorporation is required;
- In the case of a Partnership Firm, Partnership Deed is required;
- GST Registration Certificate of the establishment;
- MoA (Memorandum of Association) and AoA (Articles of Association) of the company;
- Address proof of the establishment such as:
- Latest utility bills like electricity bill, gas connection bill or telephone bill of the establishment not exceeding 3 months;
- Rental Agreement of the area or land on which the establishment is situated;
- Property tax receipts of the land where the establishment is situated.
- A cancelled cheque of the company’s bank account;
- List of all the directors of the company;
- A register containing the employees’ attendance;
- List of all the company’s shareholders;
- The compensation details of all the company’s employees;
- PAN Card of the establishment and all the employees working in the establishment;
- A detailed list of all the employees working in the business establishment.
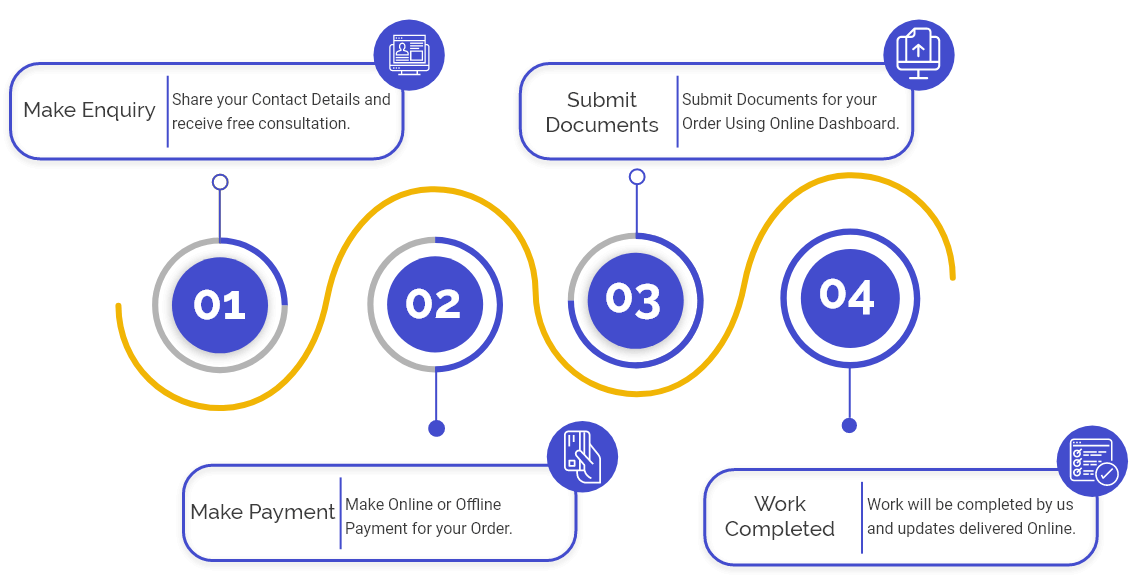
Procedure for ESIC Registration
The steps involved in the procedure for obtaining ESIC Registration are enumerated below:
Step 1: Visit the Official Website: For applying for ESIC registration, the applicant is required to visit the official ESIC website.
Step 2: Login Credentials: The said applicant can sign up by making his password and username. These login credentials can further be used for the purpose of filing returns or doing other similar nature activities.
Step 3: Confirmation Mail: Now, in the next step, a confirmation mail will be sent to the applicant’s registered E-mail ID and also on the registered mobile number.
Step 4: Enter the Login Details: Now, the applicant is required to login into his account by using the already provided username and password.
Step 5: Fill in the Application Form: In the fifth step, the applicant is asked to complete all the necessary details of the application form.
Step 6: Payment of Fees: Once the application form is duly completed by the applicant, he or she is required to finally submit it by paying the prescribed fee. The fee prescribed is paid online and the same Act as an advance contribution for the coming six months.
Step 7: Issuance of the ESIC Code Number: In the last step, the authorities, after verifying all the details and the documents submitted, the authority will issue a registration certificate to the applicant. The authority having the power to issue the certificate of registration is the Employee State Insurance Corporation. This registration certificate also contains the ESIC Code, which is a 17-digit Unique Identification Number.
Post-Registration Compliances under the ESI Act
Once an establishment or a factory is registered under the provisions of the ESI Act, the said establishment is then required to comply with some of the mandatory guidelines prescribed by the Act:
- Maintenance of an attendance register.
- A complete register having the details of the wages paid to the workers.
- Inspection book.
- Monthly return and challan by the 15th of the following month.
- Maintenance of a register having a record of the accidents that took place on the premises.
Post Registration Returns
After the ESIC Registration, the employers have to file ESI Returns half-yearly. The following vital documents are required for the filing of the returns:
- Form 6 – Register;
- Register of wages;
- Monthly challans & returns;
- Register of employees' attendance;
- Register of any accidents or incidents which have happened on the business premises.
Penalty in case of failure to Get ESIC Registration and Returns
In case of any non-compliance by an employer in India, such as failure to get ESIC Registration or not to comply with the ESI Returns, the Employer shall be liable for a fine of Rs. 10,000/-.
FAQs of ESIC Registration
An applicant needs to provide a filled ESI form and photographs of his/her family member to the employer for obtaining ESI Registration. However, the employer must be registered under the ESIC (Employee State Insurance Corporation). Further, the employee will get an ESI Card after registration.
Any company that is employing more than 10 employees, who draw a maximum salary of Rs 15000, needs to obtain ESIC Registration. However, for some states, the employee strength is extended to 20.
Yes, ESI Registration is mandatory for every company that is employing more than 10 people.
The documents needed to obtain ESIC Registration in India include Form 01; details of employees; copy of certified MOA and AOA; a copy of PAN Card; Latest bank account statements; GST Registration; Shop and Establishment Registration; PAN and Aadhar of Employees; Two Passport Size photographs for each employee; Declaration Form for each employee; and the Nominee Details of the person insured.
The term “ESI Return” denotes a return filed by every employer who is registered under the ESIC (Employees’ State Insurance Corporation). Further, the employer needs to file this return twice a year.
An employer needs to file Register of Employee Attendance; Form 6; Inspection Book; Register of Wages; Register of Accidents happened on the Premises, etc. along with the ESI Returns.
For claiming ESI, the employee needs to acquire ESIC Form-9 from the employer.
As per the ESI Act, an employee can claim Medical Benefits only from the ESIC Hospitals and Dispensaries. However, in case of emergency or the non-availability of the ESIC facility in a specific region, an employee can get his/her treatment done from the private hospital as well, but with prior approval from ESIC.
ESIC is a type of medical insurance for the employees who are working below a certain income level. Further, ESI deduction acts as a premium. That means an employee can claim medical reimbursements in the form of cash or medical benefits in case of need. However, they are not qualified to withdraw money from there.
The advantages of ESI Registration include comprehensive medical benefits; definition includes dependants; ease in claiming ESI; reimbursement of payment made; takes into account the needs of a disabled; and easy access to the medical care in ESI Dispensaries or Hospitals.
An ESIC card is valid till the time there is corresponding ESIC benefit available. Further, the eligibility criteria for ESIC benefits depend on the ESIC contribution. That means you can easily claim ESI benefits even after resigning job, provided that the benefit of ESIC is active for that period.
As per the ESI Act, the term “ESI benefits” include cash, medical, disability, maternity, and dependent benefits to the insured persons. Further, the definition of “dependents” includes parents as well.
The trainees are usually not paid a salary but are paid stipend. However, if a trainee satisfies the conditions provided under Section 2(9) of the ESIC Act, he/she will naturally be known as ‘Employee’ and will be covered under ESIC.
With effect from 01.01.2017, all the employees getting salary up to Rs 15000 per month are eligible to obtain ESI Registration.
The employee’s contribution is 0.1% of the wages, rounded off to the next higher rupee. In contrast, the employer’s contribution is 0.4% of the wages payable to every employee, rounded off to the next higher rupee.
The term “wages” includes Basic Pay, City Compensatory Allowance (CCA), Dearness Allowance (DA), Payment of the Day of Rest, Overtime Wages, Attendance Bonus, House Rent Allowance (HRA), Incentive Allowance, Meal Allowance, and Incentive Bonus.
ESI gives a type of social security scheme for the employees working in an organised sector. Employers must contribute some percentage to the ESI fund by deducting the same from employee wages and merging it with the employee’s contribution.
All the details except the name and registration date can be rectified easily if wrongly mentioned earlier. However, the same is possible only after the submission of the relevant documentary evidence. For any change, the employee needs to approach the nearest branch of the ESIC. Moreover, an employee can update his/her details by visiting the online Portal of ESIC.
ESIC Code is a 17-digit unique identification number issued to every registered establishment. This code is generated either when the employer submits the required information on the ESIC Portal or on the receipt of a survey report from the Social Security Officer.
Every employer registered under the ESI Act needs to comply with various compliances. The term “compliances” includes a deposit of monthly contribution, filing of a half-yearly return, and the report to ESIC authorities if there is some change in the business activity, ownership, address, and the maintenance of registers and records, etc.
The ESI Scheme is administered and regulated by a corporate body known as the ESIC (Employees State Insurance Corporation). The members of this corporate body are Employees, Employers, the State Government, the Central Government, Experts from the Medical Profession, and the Parliament. Further, the Director-General of ESIC is the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the ESI Corporation and is also an Ex-officio member of the ESI Corporation.
The ESI scheme acts as a self-financing scheme. The funds are usually built out of the employers and employees contributions and are payable monthly at a fixed percentage of wages paid.
All employees working in an ESI registered unit, whose monthly incomes (excluding the bonus, overtime, and leave encashment) do not exceed the threshold of Rs 15,000 per month, are eligible for the benefits and privileges provided under the Scheme.
An employee who earns a daily wage up to Rs 100 is exempted from the ESIC contribution.
An employer needs to apply in Form 01 for obtaining registration. He/she needs to apply within 15 days after the ESI Act becomes applicable to the establishment.
Swarit Advisors provides ESI Registration services across India in all cities. We have completed ESI registration in Delhi, Mumbai, Gurgaon, Bangalore, Noida, Chennai, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Pune, Surat, Lucknow, Jaipur, Kanpur, Nagpur, and other Indian cities.
An employer needs to submit an Accident Report in Form 12 and Absence Verification Report.
After obtaining the ESI Registration, the employer needs to provide a Temporary Identity Certificate to his/her employees. The Identity Card must have an employee photo and is valid for 3 months.
This Temporary Identity Card act as a proof for both claiming cash benefits at the ESI officer and medical benefit at the dispensary or hospital-affiliated under ESIC.
The term “Medical Benefits” includes complete medical treatment, i.e., from start to finish.
The people included in the definition of “Principal Employer” are Owner, Occupier, Managing Agent of the Occupier or Owner, Legal Representatives of the Deceased Occupier or Owner, Factory Manager, and the establishments belonging to the Government of India.
The term “immediate employer” includes the one who executes or completes any work inside the factory of the Principal Employer; executes or completes any work outside the premises supervised and managed by the principal employer; provide on-hire services to the principal employer of a factory or establishment; and a Contractor.
The term “Sickness benefit” denotes the period of absence. However, the same must be confirmed by the AMO (Authorised Medical Officer).
The term “Disablement” denotes state resulting from an employment injury. This may make an employee incapable of doing his/her work for the time being. Moreover, the state of disablement either leads to a reduction in the employee’s earning capacity or deprives him or her of doing any work (known as the permanent total disability).
An employer needs to pay his/her contribution with 21 days from the last day of the month in which the contribution is due.
The minimum salary needed for availing of the benefits of ESIC is Rs 15000.
Yes, the employer who does not pay the contribution within the set time limit will be liable to pay a simple interest @12% p.a. for each day of the said default or delay.
The definition of an employee does not include Apprentice; an Employee who is earning a salary of more than Rs 15000; and a member of the Indian Armed Forces.
No, the overtime of an employee is not included in his/her wage calculation.
The term “Standard Rate Benefit” denotes the calculation of average wage by dividing the total wages paid throughout the contribution period by the total number of days for which these wages were paid.