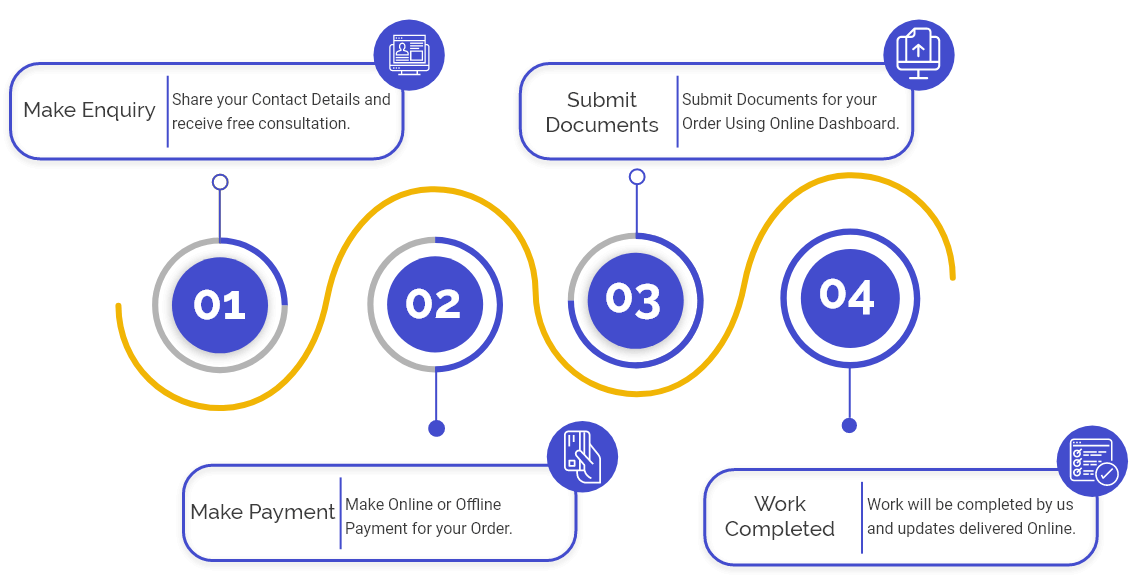
What is Income Tax Return Filing?
Income Tax Return (ITR) is a declaration made by an assessee to the Income Tax Department regarding the income and tax paid thereon. It is a proof showcasing the amount of income and the tax that has been charged on it and duly paid. Income Tax Return is paid for one financial year and the income earned in the particular financial year is shown in it.
In the ITR, it has to be shown from where the assessee is earning income- be it salary, other sources, via investments, etc.
Requirement of Filing Income Tax Return
The following are required to file income tax return:
- An individual below the age of 60 years and annual gross total income exceeding INR 2,50,000.
- An individual between the age of 60 and 80 years with annual gross total income exceeding INR 3,00,000.
- An individual above the age of 80 years (super senior citizen) with an annual gross total income exceeding INR 5,00,000.
- In case of a company or a firm, filing of Income Tax Return is mandatory, irrespective of the fact that the company is running into profits or losses.
- If an individual seeks tax refund for a financial year.
- If an Indian resident act as a signing authority for a foreign account.
- If an Indian resident is in possession of an asset or financial interest that is situated outside of India.
- If an individual holds equity shares or unity oriented mutual funds or units of business trust and has sold the same for an amount more than INR 2,50,000 making tax-exempt long-term capital gain from this sale.
- If an individual receives any income by way of sale of property that was held under political party, educational institution, charitable trust, religious trust or any other body or trust.
- A foreign entity that has been making treaty benefit on any transaction that has been undertaken in India.
- If an individual is an NRI (non-resident Indian) and his/her annual total gross income- earned or accrued in India is over INR 2,50,000.
In case, an individual comes under the above-mentioned categories and fails to file the ITR, he/she can be subjected to penalty by the Income Tax Authorities, for the default.
If any individual does not fall in any of the categories mentioned above but wants to avail a loan, he/she should file an ITR as they serve as valid income proofs and the financial institutions ask for it prior to approving a loan request.
What is the documentation requirement for filing Income Tax Returns?
The following documents are required for filing the income tax return:
- Aadhaar Card
- Permanent Account Number (PAN Card)
- Details of the Bank Account
- Form 16 (that has been issued by the employer)
- e-filing profile on ITR e-filing portal
- Details of investment (if any)
- Details of loan (if any)
Types of Income Tax Forms
|
Form |
Applicability |
|
ITR 1 (SAHAJ) |
This form is for individuals (not being “not ordinarily resident”, who have an annual total income of up to INR 50 lakhs, the source of income being – salaries, one house property, other sources and agricultural income. |
|
ITR 2 |
This is for individuals and Hindu Undivided Families that do not have profits or gains from business or profession |
|
ITR 3 |
This is for individuals and Hindu Undivided Families that have income from profits and gains of business or profession |
|
ITR 4 |
This is for resident individuals, Hindu Undivided Families and firms (except LLPs) that have annual total income up to INR 50 lakhs and the income is from business and profession as evaluated under Sections 44AD, 44DA or 44AE. |
|
ITR 5 |
This is for persons other than – individuals, company, Hindu Undivided Family or person filing Form ITR-7. |
|
ITR 6 |
This is for companies except the companies that claim exemption under Section 11. |
|
ITR 7 |
This is for persons (inclusive of companies) that are required to file return under Sections – 139(4A), 139(4B), 139(4C) or 139(4D) |
Different modes of Filing the Income Tax Returns
- In paper form
- Electronically, under digital signature
- by transmission of data in the return electronically under electronic verification code
- Electronic transmission of data in the return followed by submission of the verification of return in Form ITR-V.
Note: If the return is filed in iv) mentioned above, without the digital signature, then the taxpayer would be required to make two printed copies of ITR-V, duly signed, one of which would be sent to the Income Tax Department, Bangalore. The other copy can be retained by the taxpayer for his own record.
Due dates for Income Tax Return Filing
|
Taxpayer |
Due Date |
|
A company other than a company that is required to submit report in Form No. 3CEB under Section 92E |
September 30 |
|
A person required to furnish report in Form No. 3CEB as per Section 92E |
November 30 |
|
A person, not being a company, that has to get its accounts audited as per the Income Tax Law or other law |
September 30 |
|
A working partner of a firm that has to get its accounts audited under the Income Tax Act or any other law |
September 30 |
|
Any other Assessee |
July 31 |
Expert Opinion
Filing income tax return forms as a proof that an Assessee has legal income and is fulfilling his/her duties of paying tax. Evaluation of income tax can be a complicated process as there are multiple provisions that can allow deductions and rebates on the income earned by an Assessee. It is important that income tax is calculated correctly so that no complication or penalty gets attracted.
Our team of professional accountants can help you in accurate computation of income tax, savings on tax, etc. For more information on this, contact us.
Income Tax Return Filing FAQs
The term “E-filing Utility” denotes the facility of Generating and Electronically Furnishing the E-Return free of cost on the Official Portal.
The Process of making Electronic Payment of Tax through Net Banking or Debit/Credit card is referred to as E-payment. On the other hand, the Process of Furnishing the Income Tax Return Electronically is E-filing.
If an individual wishes to carry forward the loss that has been sustained in the previous financial year, the taxpayer has to make a claim for loss by filing the return before the due date.
If a person has paid excess tax, the same shall be refunded by making credit in his/her bank account through ECS transfer.
It shall be relevant to note that ITR Filings and TDS Deduction are not the same thing. One needs to file ITR to confirm that all the taxes have been duly paid from his/her side.
An Individual can pay taxes easily by using Net Banking with Challan 280 on the official portal of the Income Tax Department.
The document received by a taxpayer after duly paying his/her taxes is known as ITR V.
After receiving form ITR V, a taxpayer needs to print and sign it and needs to send the same to the Income Tax Department within 120 days.
Yes, a taxpayer can file Form ITR 1, only if in case his/her Agricultural Income is up to Rs 5000.
No, a taxpayer needs to file Form ITR 2 if the Agricultural Income is above Rs 5000.
If in case a taxpayer has paid excess tax, then the Income Tax Department will refund the same through ECS Transfer.
One needs to select a suitable form as per his/ her eligibility. In case a person wants to file his/ her ITR but is confused about ITR to be filed, contact Swarit Advisors.
In case a taxpayer does not have Form 16, he/she can still file Income Tax Return by showing his/her pay slips.
Unless the Tax Authorities ask, there is no need to file or attach any document with the Income Tax Return.
No, someone else cannot file ITR on behalf of the actual taxpayer due to safety concerns. However, one can take assistance from practicing CAs or Chartered Accountants for the same.
The term “Implication Form” denotes the other name for Income Tax Return.
The time limit to file an ITR varies as per the guidelines issued by the Income Tax Department.
The term Form 16 denotes a Salary TDS Certificate issued by an executive after deducting TDS from the salary.
The term TDS stands for Tax Deducted at Source.
Yes, in the case of companies and business entities, it is necessary to file Nil ITR if the income earned by the company in a financial year is 0.
Yes, it is compulsory to file ITR even if there is a clear loss in the Business Income.
Every individual, sole proprietor, company, limited liability partnership, partnership firm, needs to file an Income Tax Return for the income earned in the financial year.
A Foreign Company needs to pay Income Tax at a rate of 40%.
The term “Amended Income Tax Return” denotes the filing of a new ITR if the ITR previously filed includes wrong calculation or omissions.
Yes, one can file his/ her ITR or Income Tax Return with late fees or interest after the lapse of the Due Dates of Filing.
The benefits of Filing ITR are Sustain Losses, Precise Financial Document, Avoid Interface from Tax Liability, Repayment, Commercial Goodness, Speedy VISA process, High-Risk Protection, and Easy Loan Approval.
Whenever a taxpayer fails to file his/ her Income Tax Return before the Due Date of Filing needs to file a Return known as the Belated Return.
Section 139 (4) of the Income Tax Act 1961 deals with the provisions concerning Belated Return.
The other name for Form ITR 1 is Sahaj.
The other name for Form ITR 4 is Sugam.
The term “Form ITR 3” signifies a Tax Return or ITR that is filed by the HUFs (Hindu Undivided Families) and Individuals who are not generating income from the Profit and Gain from Business or Profession (PGBP).
All the Firms, Limited Liability Partnerships, Association of Person, Body of Individuals, Artificial Judicial Person, and Cooperative Society.
The term “Presumptive Taxation Scheme” denotes a scheme by which the small taxpayers who perform tasks, such as the auditing and maintenance of accounts and ledgers, would receive some sort of relief.
The different types of ITR are Form ITR 1, Form ITR 2, Form ITR 3, Form ITR 4, Form ITR 5, Form ITR 6, Form ITR 7.
Any person who is above the age of 80 years can file his/ her ITR offline.
Yes, an individual who is above the age of 80 years can file his/ her ITR physically.
One can download Form ITR 1 from the official website of the Income Tax Department.
All the Companies that are not claiming exemption under section 11 of the Income Tax Act needs to file Form ITR 6 with the Income Tax Department.
Any company or entity which is not claiming exemption under section 139(4A), 139(4B), 139(4C), and 139(4D) of the Income Tax Act 1961 cannot file Form ITR 7 with the Tax Authorities.
The term “Form ITR 2” means an ITR or Tax Return that is filed by the HUFs (Hindu Undivided Families) and Individuals who are not earning income under the head of Profit and Gain from Business or Profession (PGBP).
The term “Defective Return Notice” denotes the time intimation given by the Income Tax Department to a Taxpayer to re-file his/ her ITR after rectifying all the errors mentioned.
Section 139(9) of the Income Tax Act 1961 deals with the provisions of Defective Return Notice.
A period of 15 days is prescribed under a Defective Return Notice to rectify the errors raised.
The benefits of filing an ITR electronically include ease of filing it from any place, saves time and money, faster processing than the ITRs filed manually.
The term “Revised Return” denotes an ITR filed by the taxpayer in the revision of the original ITR.
Section 139 (5) of the Income Tax Act 1961 deals with the provisions concerning Revised Return.
A Taxpayer needs to file his/ her revised return either before the end of the relevant assessment year or before the completion of the assessment.
A taxpayer can revise his/ her Income Tax Return only before the end of the relevant assessment year or before the completion of the assessment.
The different modes of filing an ITR online are furnishing it in a Physical Paper Format or furnishing a Bar Coded Return.
The legal document in which a taxpayer or assessee informs the government and income tax department about the income earned by him/her in a financial year is known as Income Tax Return.