General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Bill, 2021

Karan Singh | Updated: Aug 25, 2021 | Category: IRDA Advisory
On August 11, the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Bill, 2021, was passed by the Parliament of India. This bill aims to push greater participation in public sector insurers. The bill seeks to remove the necessity that the centre shouldn’t hold less than 51% of the equity capital in such insurers. It will amend the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act, 1972. Let’s understand more about General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment, 2021.
Table of Contents
Why the need for an Amendment?
As per the Government of India, the need arose to address the following cases:
- Increase the level of insurance penetration and thereby social protection;
- Encourage for higher private participation in public section insurance companies or entities;
- Protect the policyholders’ interests in a proper way;
- Contribute to the rapid growth of the Indian Economy.
What is the Meaning of General Insurance Business?
The Act mentions General Insurance Business as a marine or miscellaneous insurance business. It eliminates annuity and capital redemption from the definition. Capital redemption insurance consists of the payment of an amount of money on a particular date by the insurer once the recipient pays the premium regularly. Under the definite annuity insurance, the insurer pays the recipient over time. The General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Bill, 2021, removes this meaning and mentions the importance provided under the Insurance Act, 1938. Under Insurance Act, 1938, capital redemption & annuity specific come under the influence of General Insurance Business.
General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment– An Overview
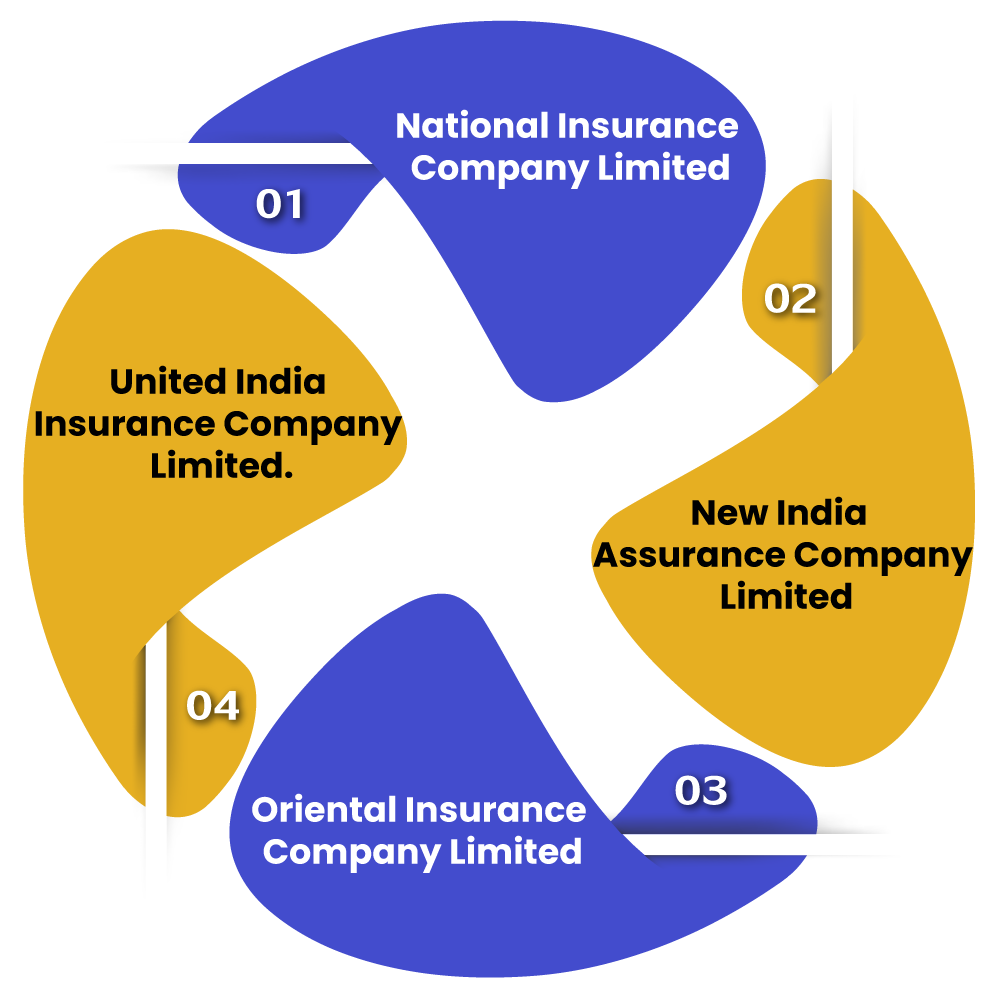
The General Insurance Bill seeks to change the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Act, 1972. This law handles nationalising all private general insurers in the country. Under it, the GIC or General Insurance Corporation of India was established. New India Assurance, Oriental Insurance, National Insurance, and United India became its subsidiaries. The Act was changed in 2002, and the Central Government took over control of the subsidiaries from General Insurance Corporation. The new bill seeks to remove the old Act on the 51% Government holding requirement.
The bill has sought three main amendments, and you can check the same below:
- According to the first amendment, it aims to exclude the provision to Section 10B of the Act, 1972, which says that the shareholding of the Central Government in the specified insurers should be a minimum of 51%;
- According to the Second Amendment, it seeks to add a new Section 24B providing ending of the application of the Act to such insurer on and from the date on which Central Government stops to have control over it. Control means the power to assign the majority of directors stated insurer or to have control over its management & policy decisions;
- According to the third amendment, it seeks to add a new Section 31A providing for director’s liability of the stated insurer, not being a full-time director, responsible for an act of error or commission committed with their knowledge & approval.
These amendments were as per Budget Announcement when the Finance Minister announced that they sought to take up the privatisation of two Public Sector Banks & a General Insurance Company in the year 2021-22. Further, she said that it would require legislative amendments and planned to set up the amendments in the session itself.
Which Insurers will be affected?
India has four General Insurers in the public sector, and these are:
What does the Opposition want?
The Government of India has been accused of not following parliamentary rules and bulldozing the legislation. Oppositions demand that the bill be referred to a select committee of the House. As per the Opposition, the amended norms are going to prove damaging to the larger public interest.
Indian Insurance Market
According to the data shown by the insurance regulatory body IRDAI (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India), around 25 General Insurance Companies observed a 10.8% rise in their collective premium in the January month of 2021 to Rs. 16.247 crores as compared with Rs. 14.663 crore in January month last year.
According to the data published by IBEF (India Brand Equity Foundation), insurance penetration in India was observed at 3.76% in the Financial Year 2020. In terms of insurance density, its overall density was seen at 78 US dollars in the Financial Year 2020. It declared that the market share of the private sector companies in the health & general insurance increased from 47.97% in the Financial Year 2019 to 48.03% in the Financial Year 2020.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Bill, 2021
To know the amendments, we need to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of the General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Bill. Following are the advantages & disadvantages of this bill:
Advantages-
- The bill intends to bring more private capital in the General Insurance Business, and it creates a part of the Governments’ strategy to open more & more sectors for private participation & boost efficiency;
- It can help in bringing vital resources;
- It will allow public sector general insurers to design innovative products & services;
- It can include the share of India in the international insurance market.
Disadvantages-
- The bill intends for privatisation, and total privatisation of the General Insurance Companies can cause proprietorship to be with a few capitalists only;
- Another disadvantage to be aware of is that people will have trust issues as they trust public companies more;
- After this bill is implemented, the Government may suffer money loss in the form of dividends considering that the share of the Government will be reduced in the General Insurance Business.
Conclusion
The General Insurance Business (Nationalisation) Amendment Bill, 2021, has been introduced by the parliament, and it changes the General Insurance Business Act 1972[1], which was passed to nationalise private companies or entities undertaking General Insurance Business in India. As we mentioned above, such amendments are in line with the Budget announcement when the Finance Minister of India announced that they sought to privatise two Public Sector Banks and General Insurance companies in the year 2021-22.
Read our article:What are the Key Features of Micro Insurance Companies?