A Complete Summary of NBFC Compliance under FEMA
Japsanjam Kaur Wadhera | Updated: Dec 21, 2020 | Category: NBFC
Non- Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 2013. NBFC is involved in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of stocks, shares, debentures, securities and bonds issued by govt or local authority or other marketable securities, but it does not include any institution whose business includes the industrial, agricultural or sale or purchase of immovable property (other than securities). NBFC has to act in accruing to the RBI guidelines to engage in the activities relating to the financial sector. This article will provide you with a complete summary of NBFC compliance under the FEMA.
While borrowing credit from foreign countries, it is necessary for NBFC to comply with the regulations of the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
Table of Contents
Two Routes of Foreign Investment
The foreign investment has two routes for NBFC compliance under FEMA. These are:-
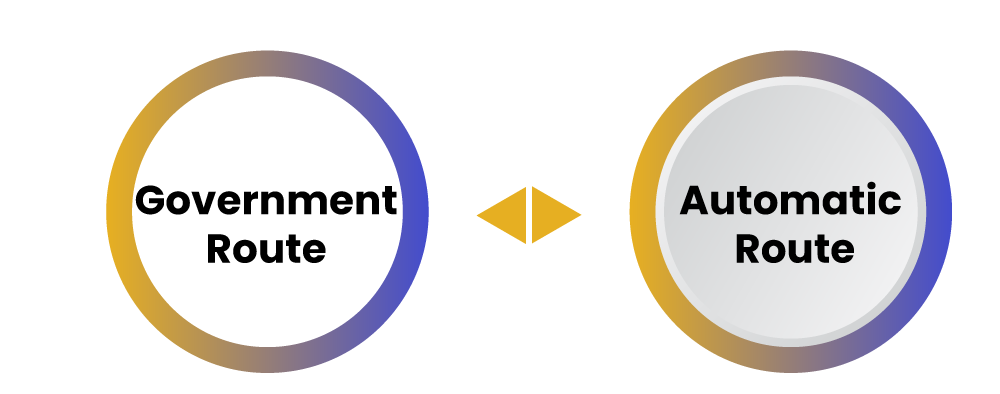
- Government Route
- Automatic Route
The foreign countries entities are allowed to invest their funds in NBFC sector under the automatic route. All the activities related to foreign investment is regulated under the automatic route. Therefore, it is not required to take permission from the Reserve Bank of India. There is no limitation levied on the foreign investors in relation to the investment of funds under the automatic route. The parties engaged in it are not required to face any legal formalities for such type of investment. The funds can be put in the NBFC sector regardless of the scale of investment and without any form of approval from the government.
What are the purposes for which NBFC compliance is mandatory under FEMA?
The main reasons for which NBFC compliance under FEMA is mandatory are: –
- To receive investment from foreign investors
- To help increase the growth and development of NBFC
- Since the NBFC activities carried out is based on rural development, the foreign investors invest more money in NBFC.
Do FEMA and RBI mandate the NBFC compliance?
It is necessary for Non – Banking Financial Companies (NBFC) to take permission from RBI for its establishment. In order to form an NBFC, it is necessary to start a private company which has minimum capital requirements. And the formation of the company must be in accordance with the rules of company law. And in similar ways, it is also necessary for NBFC to be compliant with the laws under FEMA in relation to all the activities related to foreign investment. Therefore, NBFC compliance under FEMA and RBI is mandatory.
The amendment in 2016 of Foreign Exchange Management (Borrowing and Lending in Foreign Exchange) Regulation, 2000 by RBI, it allowed foreign investors to invest in NBFC.
Requirements for Foreign Investment in NBFC before 2016 Amendment
Prior to the amendment in 2016, the following requirements regarding capitalization were imposed on foreign investment in an NBFC. The previous norms under the regulatory authority are mentioned in the following list: –
- USD 0.5 million for foreign capital up to 51% to be brought upfront.
- USD $ 5 million for foreign capital more than 51% and up to 75% to be brought upfront.
- 50 million for foreign capital more than 75% out of which $7.5 million to be brought upfront and the balance in 24 months.
- The Non- Banking Financial Companies (NBFC) having foreign direct investment (FDI) more than 75% and up to 100% and with a minimum capitalization of $50 million, can set up subsidiaries below them for specific NBFC private lender activities, without any constraint on the number of operating subsidiaries and without getting additional capital. There is no particular constraint for the number of subsidiaries that are formed under this.
- Joint Venture operating Non- Banking Financial Companies (NBFC) that have less than 75% or 75% foreign investment can also create subsidiaries for carrying out activities of NBFC, subject to the subsidiaries also in accordance with the minimum capitalization norm mentioned above.
- Non- Fund based activities: the US $0.5 million to be brought up front for all allowed non-fund based NBFC private lenders regardless of the level of overseas investment.
Who regulates the NBFC compliance?
The NBFC compliance is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). NBFC is required to be registered with RBI and has to obtain permission from RBI to execute its business activities. Besides this, the Foreign Exchange Management (Borrowing and Lending in Foreign Exchange) Regulation, 2000 and Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999, regulates the NBFC.
NBFC compliance eligibility criteria
The eligibility criteria for NBFC compliance is: –
- Registering an NBFC compliance/NBFC with the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
- The NBFC must be allowed for securing foreign investment.
For an NBFC, foreign investment is allowed permitted the automatic route in the below mentioned 18 prescribed NBFC activities. The foreign investment is permitted through the automatic route in the following sectors: –
Foreign investment under automatic route
- Underwriting
- Stock broking
- Merchant banking
- Portfolio management services
- Venture capital
- Factoring
- Asset management
- Custodian services
- Housing finance
- Leasing and finance
- Rural credit
- Micro credit
- Credit card business
Non- Fund based Activities
- Financial consultancy
- Investment Advisory Services
- Credit rating agencies
- Forex broking
- Money changing business
What is the procedure for NBFC compliance under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA)?
The following process has to be followed, once the Non- Banking Financial Company is registered with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI): –
- It is necessary that the NBFC has to be in compliance with the foreign exchange laws as directed under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
- Form 83 has to be downloaded from RBI’s website for any form of foreign investment.
- The form must be filled with all the requested details and any additional sheet must be added if required.
- Further, the duplicate of form along with the necessary documents must be submitted by the borrower to the designated Authorised Dealer (AD) for all the specified categories and any amount of external commercial borrowing (ECB).
- After the conformity with the guidelines of the ECB, the authorized dealer will provide the requisite details of the form in Part F and then forward the one copy for allotment of Loan Registration Number (LRN) within 7 days from the date of signing the loan agreement between the lender and the borrower, to be submitted in duplicate by the borrower to the authorized dealer (AD) designated for all specified categories and any amount of external commercial borrowing (ECB).
- The form must be submitted to the mentioned address: the Director Balance of Payments Statistic Division Department of Statistics and Information Management (DSIM) Reserve bank of India C-8-9 Bandra- Kurla Complex Mumbai – 400051
- Once the form is verified by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) the loan registration number shall be issued to the borrower.
What are the documents that are required for NBFC compliance under FEMA?
The documents that are required for the NBFC compliance under FEMA are:
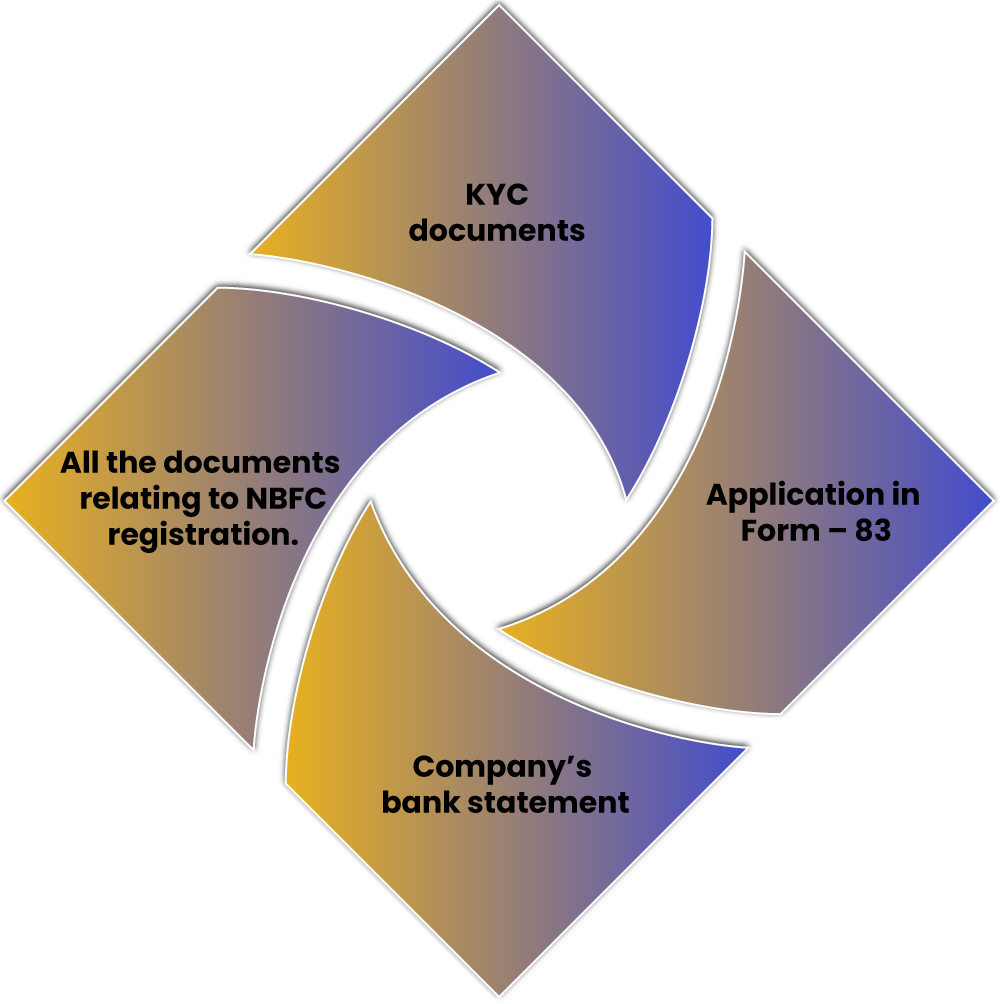
- KYC documents
- Application in Form – 83
- Company’s bank statement
- All the documents relating to NBFC registration.
What happens when Reserve Bank of India approves a loan to the borrower?
When the Reserve Bank of India approves a loan to the borrow it required the below mentioned requirements to be followed: –
- NBFC compliance under FEMA Act, 1999[1] and meeting with rules and regulations of RBI is necessary.
- Copy of the application in Form – 83 should be provided to the Authorized Dealer (AD) for any amount of external commercial borrowings.
- After the conformity with the regulations under the external commercial borrowing, the Authorized Dealer (AD) will submit required information in Part F of the form and forward a copy for the allotment of Loan Registration Number (LRN).
- The borrower has to provide the duplicate of the same to the Authorized Dealer (AD) regardless of the amount of external commercial borrowing. And this must be submitted to the Reserve Bank of India’s office located in Mumbai.
- A credit can be obtained after the loan registration number (LNR) is availed.
How is NBFC different from banks?
NBFC’s performs similar function as that to the banks. However, there are some differences between the banks and NBFCs such as: –
- Demand deposits cannot be accepted by NBFCs.
- NBFCs cannot issue cheques drawn on itself and also do not involve payment and settlement system.
- The depositors of NBFCs cannot avail the deposit insurance facility of the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation, unlike in banks.
Types of NBFCs registered with RBI
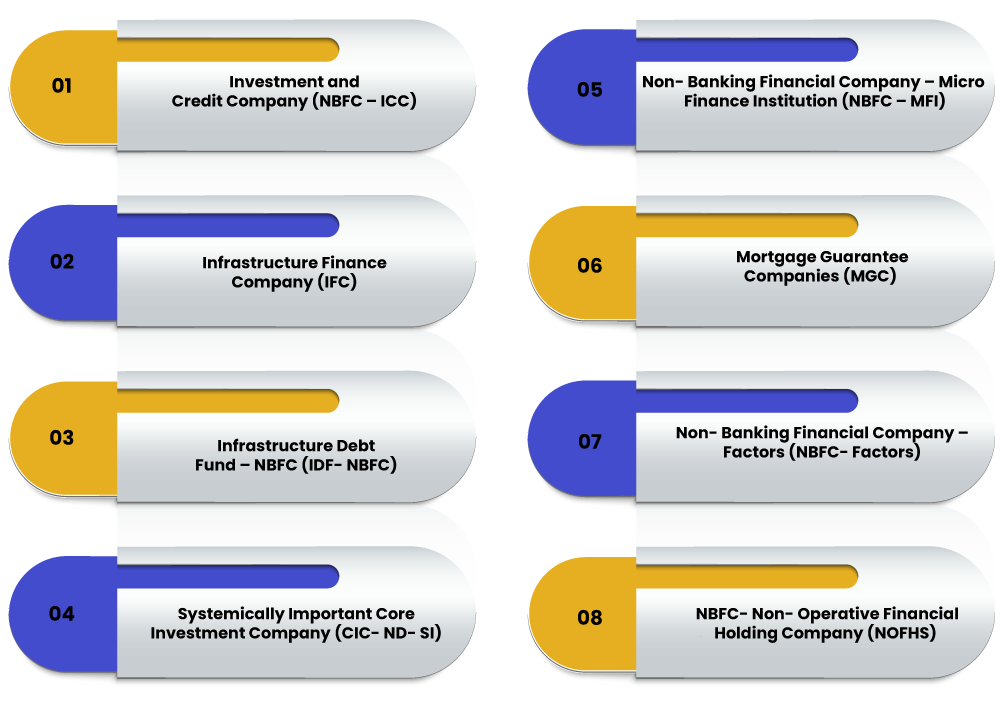
Investment and Credit Company (NBFC – ICC)
It is one of the common licenses for all the types of finance business in India. Earlier, before 2019 there were three different types of licenses, that is, Asset Finance Company, Investment Company and Loan Company. After 2019, these three licenses merged into one single license that is Investment and Credit Company (ICC). It permits the holder of the license to engage or operate in different kinds of wholesale retail loans and investment business. The ETA for NBFC ICC License is estimated to 120 days.
Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC)
It is a Non- Banking Financial Company which utilizes at least 75% of its total assets in infrastructure loans, has a minimum credit rating, net owned funds of Rs. 300 crore and a CRAR of 15%
Infrastructure Debt Fund – NBFC (IDF- NBFC)
It is registered as NBFC to allow the flow of long term debt in infrastructure projects. Rupee or Dollar denominated bonds is issued to raise resources of minimum 5 years of maturity under the IDF- NBFC. It can be sponsored by only infrastructure finance companies (IFC).
Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC- ND- SI)
CIC- ND- SI is an NBFC that is carrying on the business of acquisition of shares and securities on following conditions: –
- Holds 90% of its total assets in preference shares, equity shares, loans or debts in group of companies
- Investment in equity shares is not less than 60% of its total assets in group of companies
- Does not carry out any other financial activity mentioned in Section 451(c) and (f) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- Size of the assets are above 100 crore
- Public funds are accepted
Non- Banking Financial Company – Micro Finance Institution (NBFC – MFI)
NBFC – MFI has at least 85% of its asset in the nature of qualifying assets.
Mortgage Guarantee Companies (MGC)
MGC is a type of NBFC that is carrying on the business of guaranteed mortgage and the gross income is at least 90% from the mortgage guarantee business and Rs 100 crore is the net owned fund.
Non- Banking Financial Company – Factors (NBFC- Factors)
NBFC- Factors carry on its business in factoring and constitutes at least 50% of its total assets. The income is not less than 50% of its gross income.
NBFC- Non- Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHS)
The promoters or the group of promoters are allowed to set up a new bank which is completely owned NOFHS regulated by Reserve Bank of India.
Conclusion
Financial activity is a principle business for many businesses. And giving validity in engaging in financial activities, it is necessary for the financial institutions to register itself with the Reserve Bank of India and comply with its rules and regulations. When a Non- Banking financial institution engages itself in the lending and borrowing of money with the foreign investments, it is mandatory for them to comply with the rules and regulations under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) and RBI. NBFC compliance under FEMA and meeting with regulations and rules of RBI is necessary, for seeking funds from the foreign investors.
The Non- Banking Financial Institutions functions and operates under strict rules and regulations. It is necessary for private lenders to ensure compliance with laws. The Reserve Bank of India has made it easier for the borrowers by simplifying the filing process for them.
Also, Read: How to Avoid Rejections of Trademark Registration?















