An Overview of Biotechnology Patents in India

Karan Singh | Updated: Jun 08, 2021 | Category: Patent
The inventions regarding biotechnology are essential for the development or advancement of human beings. The biotechnology inventions have branched out to different fields & resolved several problems. The Patent Office issues guidelines concerning biotechnology Patents in India intending to set up identical and consistent practices for the examination of biotechnology Patents applications. The guidelines linked with the biotechnology Patent were planned to aid the examiners & controllers of the Patent Office to achieve consistency in issue Patent Registration to the candidates. The guidelines set by the Patent Office are subject to time to time modification based on the explanations by a Court of Law, legal alterations, and valuable concepts from the investors.
Table of Contents
What are the Biotechnology Patents?
Biotechnology inventions are a wide area of biology concerning living organisms & systems, or derivatives thereof, to amend or make products or processes for particular uses. The main behind the first Act of the Patent, Thomas Jefferson, doesn’t have any concept that life forms can also become a subject matter for protection under Patent.
In the case of Diamond v Anand Chakrabarty, a biochemist at General Electric (GE) developed a genetically altered organism that has the ability to decompose crude oil. Firstly, the application of the Patent of the inventor was refused. However, later on, an appeal was made, and the court granted the Patent to the inventor with an order expressing that the inventor claim is not to up till now unknown natural phenomenon; however, a non-naturally occurring composition or manufacture of matter a product of human resourcefulness.
History of the Biotechnology Patents in India
The Patent act in India was approved in the year 1856. Since then, the Patent Act was altered and changed many times. In 1970, one significant modification came into action which fulfilled the international norms of patentability of an invention covering originality, industrial application, and inventive step. However, the altered version of the Patent Act, 1970[1], doesn’t comprise anything particular regarding the invention concerning biotechnology and the protection of such biotechnology inventions.
Simultaneously, the EU and US Patent office & courts were observing an increase in the number of biotechnology inventions & applications of Patent for the same. Therefore, a massive demand for an amendment concerning the Biotechnology Patents in Indian came into effect in 2002 to clearly comprise microbiological, biotechnological, and biochemical processes within the meaning of potentially patentable methods.
Provisions Concerning Biotechnology Patents in India
The sections of the Patents Act, 1970, which are emphasised for the inspection of applications concerning biotechnology Patents in Indian and related fields, are as follows:
- Section 2 (1) (a): This provision concerning inventive steps, originality, and industrial applicability of processes or products.
- Section 3 (b): This provision is related to inventions contrary to morality or which cause serious prejudice to the animal, human, or plant life or environment or health.
- Section 3 (c): This provision is concerning the discovery of any non-living or living substance occurring in nature.
- Section 3 (d): This provision is concerning to mere discovery of a new form of a known substance which doesn’t outcome in the improvement of known efficiency or mere discovery of any new property or new use for a well-known substance.
- Section 3 (e): This provision concerning mere admixture results only in the properties aggregation.
- Section 3 (h): This provision concerning the agriculture and horticulture method.
- Section 3 (i): This provision concerning the method of diagnosis & treatment.
- Section 3 (j): This provision concerning plants & animals in overall or any part thereof other than micro-organisms; however, comprising seeds, species and varieties, crucially biological processes.
- Section 3 (k): This provision is concerning computer programs per se and algorithms, mathematical methods.
- Section 3 (p): This provision concerns the inventions that are, in effect, conventional knowledge.
- Section 10 (4): This provision is concerning the competence of disclosure and the best method of performing the invention.
- Section 10 (5): This provision is concerning the unity of invention & clarity, succinctness & claims support.
What are the Requirements for Procuring Biotechnology Patents in India?
Following are some basic requirements for Procuring Biotechnology Patents in India:
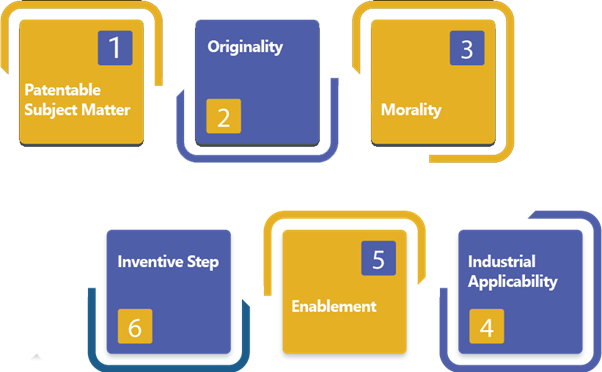
- Patentable Subject Matter: The extent of the qualified subject matters is very extensive broad in India. In India, any product or any process, despite the technology, is a patentable matter. But, the Patents Act, 1970 furnishes a long list of inventions that are mislaid from being a patentable subject matter, which also comprises some type of biotechnology inventions.
The expelled subject matters are as follows:
- Finding of living things occurring in nature;
- Medical treatment methods;
- The animals & plants overall or any part thereof comprising seeds; species, varieties, and mostly the biological processes for production or propagation of the animals & plants;
- Embryonic stem cells & humans;
- Genetically altered multi-cellular organisms comprising humans, plants, animals, and their parts.
Other than this, the micro-organisms & micro-biological procedures are a patentable subject matter under Biotechnology Patents in India. Gene and DNA sequences having disclosed functions are considered the patentable matter in India.
- Originality: The Patent Act doesn’t have any apparent provisions concerning the uniqueness of biotechnology inventions in India. The majority of creations concerning biotechnology are products or goods of nature essentially present in the living organisms. Therefore, such products can be clarified as discoveries and are not patentable according to the Patent Laws of India. The Manual of Patent Practice and Procedure furnishes that some biological substances like recombinant DNA, plasmids, and manufacturing processes such substances are entitled to being patentable in India, furnished that these substances are produced by substantive intervention for human beings.
- Morality: Under the provisions of Section 3(b) of the Patent Act, 1970 furnishes that when the primary use of an invention of differing to public morality or can also cause severe prejudice to the animal, human, and plant health & life or the environment, so such an invention will not be permitted to obtain Patent Registration in India. The Manual of Patent Office Procedure & Practise furnishes that nay biological material and the method of making the same which is competent of causing severe prejudice to the human, animal, or plant lives & health and also the use of such invention would be contrary to the public morality & order will not be permitted to get patented in India.
- Industrial Applicability: It is vital to be proven that the inventor’s invention can be made, can be used in at least one ground of activity and can be reproduced with the indistinguishable characteristics as many times as needed for an invention to be industrially applicable in India. Since the Patent Act doesn’t deliver any particular mention concerning the applicability of industry of Biotechnology Patents in India, it is sensible to apply the general standards of industrial applicability to the inventions concerning biotechnology.
If any inventions of biotechnology can be prepared and used in an industry and can also be duplicated as many time as needed, such inventions, therefore, fulfil the necessities of industrial applicability in India. The guidelines in the Manual Patent Procedure and Practise deliver for examining biotechnology. The guidelines concerning gene & DNA sequences furnish if the functions of such sequences are not disclosed. These sequences don’t fulfil the industrial applicability necessity for Biotechnology Patent in India.
- Enablement: For biotechnology inventions in India, which tells biological substance or material in the full specification, the law delivers for the provisions for the statement of such biological materials or substances at a well-known depository in India. The Manual of Patent Practice & Procedure needs the invention to be mentioned entirely in the specification by the inventor. Such specifications have to be submitted by the inventor to enable any individual skilled in similar art to be able to accomplish the invention by reading the full specification.
- Inventive Step: The Manual of Patent Practices & Procedures has established certain guidelines for the assessment of the inventive step of the invention in Chapter 8, Para 08.03.03. An inventor’s invention should hold an inventive step so as to be entitled to Patent protection.
According to the Act, an invention will have a creative step that involves the following:
- Technically advanced as compared to present knowledge;
- Having economic importance;
- Both.
What is not Patentable under Biotechnology Patents?
The following things are not patentable in India:
- The inventor’s invention is against the public morality or order, damaging to the plants, animals, or humans life or environment as per Patents Act (Section 3 (b));
- The invention concerning the finding of living things or non-living substances or materials in nature as per Section 3 (c) of the Act;
- The invention concerning particular methods of horticulture or agriculture as per Section 3 (h) of the Act;
- The invention concerning the animals & plants in whole or any parts thereof other than the micro-organisms however comprising seeds, varieties, and species as per section 3 of the Act;
- The invention regarding any fundamentally biological processes for the propagation of plants and animals as per Section 3 (j) of the Act;
- The invention comprises conventional knowledge as per Section 3 (p) of the Act.
Conclusion
In the current time, patenting of biotechnology inventions is a noteworthy factor because of its investment & research-intensive nature. The current case laws clearly conclude that the biological materials or substances which are designed in labs & were earlier not available in the natural environment have earned some patentability right. Therefore, for the safety of the inventor’s right and interest of patentability, the biotechnology Patents in India was introduced. The filing process for the approval of the biotechnology Patents in India is complex and lengthy. You can also contact an expert who will guide you in Patent Registration in India.
Read our article:Patent Infringement Letter- An Overview