Trademark Classes: A Guide on Trademark Classification

Shivani Jain | Updated: Aug 18, 2020 | Category: Trademark
The term “Trademark Classifications” or “Trademark Classes” denotes the categories under which an owner or a service provider can obtain Trademark Registration in India. These classes are made on the basis of ICGS (International Certification of Goods and Services)[1], also known as NICE Classification.
In this blog, we will discuss the concept of Trademark Classes and how they play a significant role in obtaining TM Registration in India.
Table of Contents
Know the Concept of Trademark in India
The term “Trademark” signifies protection available for specific names, devices, labels, symbols, words, and colour combinations.
The main benefit of a TM Registration is that it facilitates differentiation between the goods of the registered owner with other available in the market.
Therefore, Trademark registration provides the owner with the authority to maintain the individuality and uniqueness of his/her goods and services. In the case of Trademark Infringement, it allows the owner with the power to sue the third person as well.
Further, the symbol “R” will apply to the concerned good or service after successful Trademark Registration. It will be valid for a period of 10 years and is eligible for Trademark Renewal as well.
Governing Force for Trademarks
The Controller General of Patents Designs and Trademarks (CGPDT) acts as the regulatory force for Trademarks, whereas, the Trademarks Act 1999, serves as the governing law for Trademarks in India.
Concept of Trademark Classes

The categories under which an owner or a service provider can obtain Trademark Registration are known as Trademark Classes. These classes are based on the classes specified by the NICE Classifications. Further, in total, there are 45 trademark classifications available, out of which 34 classes are known as TM Classes for Goods, and the remaining 11 are termed as TM Classes for Services.
At present, there are around 8000 products and services covered under the ambit of Trademark Classifications.
Significance of Trademark Classes
The significance of Trademark Classes can be summarised as:
- Provides Guideline for Registering Trademarks in India;
- Helps in Identifying the Trademark Infringers in India;
Concept of Trademark Search in India
The procedure for determining a correct Trademark Class for obtaining TM Registration is known as Trademark Search or Trademark Public Search. Further, for doing the TM Search, an applicant can use the Indian Trademark Registry Database (ITRD).
The main purpose of TM Public Search is to ascertain whether a specific goods or service falls under the ambit of Trademark Classification or not.
Concept of Trademark Description
The term “Trademark Description” denotes the general indications appearing on different class of goods and services. It basically depicts the field from which a product or service belongs.
Concept of NICE Classification
The term “NICE Classifications” denotes a mechanism on which the trademark classes are based on. It was formed on 15.06.1957, by way of an agreement signed at the NICE Diplomatic Conference. However, the said classification was revised in the year 1967 at the Stockholm Conference and again in 1977 at the Geneva Conference.
Further, India signed the NICE Agreement on 07.09.2019, i.e., the ITO (Indian Trademark Office) are using the updated version for the classification of goods and services.
Furthermore, the NICE Classification provides a broad heading named as “Class Header”. A class header gives a clear explanation about the goods and services covered under each class.
Tools Available for Trademark Classification
The different tools available for Trademark Classification are as follows:
NICE Classification
This Tool was provided by the World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO);
TM Classification
This Tool was provided by the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO);
Further, in our opinion, TM Classification is a better tool than NICE Classification. The reason for the same is that this tool highlights the goods and services that are not eligible for TM Registration as per the TMO (Trademark Office).
Procedure to Choose a Valid Trademark Class
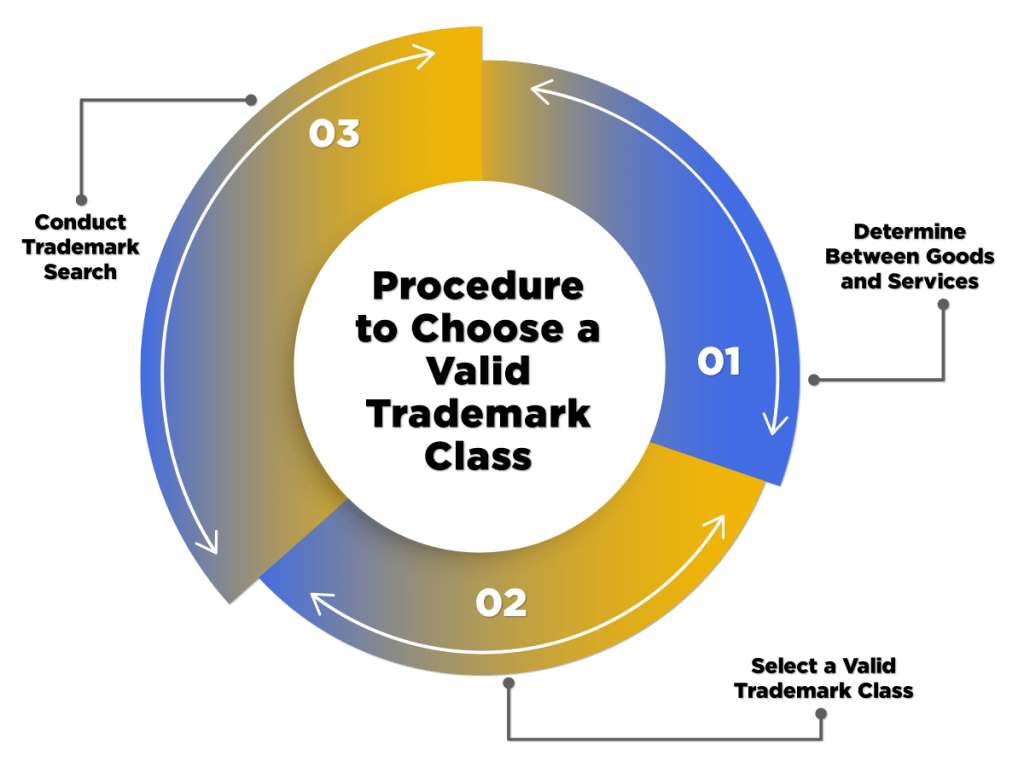
The steps included in the Procedure to Choose a Correct Trademark Class are as follows:
Determine Between Goods and Services
The first step is to check whether the applicant provides goods or services. Further, one can also apply the Trademark Registration for both goods and services.
For Example, Starbucks has a registered trademark for both its products and services. The reason for the same is that it not only offers a variety of coffees but sells ground coffee, branded coffee beans, coffee mugs as well.
Select a Valid Trademark Class
In the next step, the applicant needs to choose a valid Trade Mark Class from the classification of the finalized Goods and Services.
If in case the functions of a good or service are not provided in the class heading of the Trademark Classes. The applicant can choose the class based on the description of the said good or service.
Further, an applicant can file a Trademark Application only for a single class of goods or services. That means the applicant needs to file multiple trademark applications if in case he/she wants to register a trademark in more than one classification.
Conduct Trademark Search
In the last step, the applicant needs to conduct the process of trademark search based on the nature of the goods and services and not on the basis of components.
However, this process needs professional assistance, because in case the applicant chooses a wrong step, he/she will need to start the process of classification again.
For example, in case an applicant searches for Photography, then Chemicals under Class 1, Computer and Scientific Devices under Class 9, and Education and Entertainment Services under Class 31 are represented as relevant. Therefore, there is a need for an applicant to consult IPR experts.
Basics for the Trademark Classification of Goods
The things to consider for the Trademark Classification of Goods are as follows:
- Normally, a product is categorized based on its usage and functions. However, if in case the usage or functions of a good are not specified by any class, the owner will classify the product based on the similarities with other finished goods available in the alphabetical list.
- If in case the applicant is not able to find any similarity, he/she can categorize the product based on the mode of operation or material used as the Subsidiary Criteria.
- In case a good serve multiple objectives, the same will be categorised in all the classes relating to its functions. However, if in case the functions are not explicitly mentioned, the criteria mentioned in (b) will be used.
- All the Raw Materials, whether unworked or semi-worked, are classified based on their components.
- In case a product intends to form part of some other product, the same is classified in the class in which the product it intends to form a part is classified.
- In case a product is a blend of several raw materials, the same will be classified according to the predominating raw material.
Basics for the Trademark Classification of Services
The things to consider for the Trademark Classification of Services are as follows:
- Normally, the services are categorised based on the branches of activities specified in the Heading and Explanatory Notes of the Service Class.
- If in case, the branches of activities are not specified for a service, the same will be classified based on the similarities with other services available in the alphabetical list.
- Rental Services are categorised in the class in which the services offered using rental objects are classified.
- Services that include consultation, advice, or providing information are classified in the class, which resembles the subject matter of said consultation, advice, and information.
Consequences of Choosing an Incorrect Trademark Class
The consequences of choosing an Incorrect Trademark Class are as follows:
- Authorities will reject the application for trademark registration;
- No refund of the Registration Fees;
- The individual will be infringing the rights of a registered trademark holder;
- In case the applicant has obtained the trademark registration in the wrong class, he/she cannot switch over to the correct class. That means the applicant will have to start a fresh registration process.
- Cannot sue the third party in the case of Trademark Infringement.
Conclusion
After discussing thoroughly, it is absolutely clear that Trademark Classes play a vital role in the process of Trademark Registration. Therefore, it is always advised to take professional assistance in both the process of trademark public search and trademark classification, as one wrong step can lead the application for registration to rejection.
At Swarit Advisors, we have a team of competent IPR experts, who rank high in providing on-time Trademark Registration and other services, such as Trademark Search, Trademark Renewal, Trademark Objection, and Trademark Assignment.
Also, Read:Trademark Class 3: Cosmetics, Perfumes & Cleaning Substances














