Form MGT 14: A Guide on Its Meaning, Fees, and Mode of Filing

Shivani Jain | Updated: Sep 15, 2020 | Category: Compliance
The term “Form MGT 14” denotes an e-form that a company needs for filing Resolutions with the ROC (Registrar of Companies), which are passed by the Directors and Shareholders at Board Meetings. Further, this e-form is available on the official portal of MCA[1] .
In this blog, we will discuss the meaning of Form MGT 14, together with its Fees, Documents, and Mode of Filing.
Table of Contents
Form MGT 14 Meaning
According to Section 117 (3) of the Companies Act 2013, a copy of every Agreement signed and Resolution passed, along with the Explanatory Statement under Section 102, needs to be filed with the Registrar of Companies India.
Further, companies require to file these resolutions within 30 days from passing it under MGT 14 Form with the Fees prescribed.
Therefore, Form MGT-14 was introduced under the Companies Act 2013 for providing a basis to the directors for filing the resolutions passed as at various Board Meetings.
Laws Regulating MGT-14
The laws regulating MGT 14 Form are as follows:
- Section 94(1) of the Companies Act 2013; and
- Section 117 of the Companies Act 2013;
MGT 14 Form Purpose
A Liquidator or Company needs to file some Resolutions and Agreements with the Registrar of Companies, India. The term “Resolutions” denotes the decisions passed in various Meetings by the Shareholder/ Directors/ or Creditors of the Company. The concerned company requires to file the particulars of these resolutions and agreements in this E-form.
Resolutions and Agreements Filed under Section 117 (3)
The Resolutions and Agreements to be filed under Section 117 (3) are as follows:
- Special Resolutions;
- Resolutions Passed by the Shareholders of the Company;
- Resolutions passed by the Board of Directors with respect to Appointment/ Reappointment/ Renewal/ Variation of Terms of Appointment of the MD (Managing Director);
- Resolutions passed by the class or majority of Members;
- Resolutions passed for the Winding up of the Company in accordance with Section 59 of the IBC 2016; and
- Resolutions passed under section 179 (3) of the Companies Act 2013;
Resolutions to be Filed under Form MGT 14
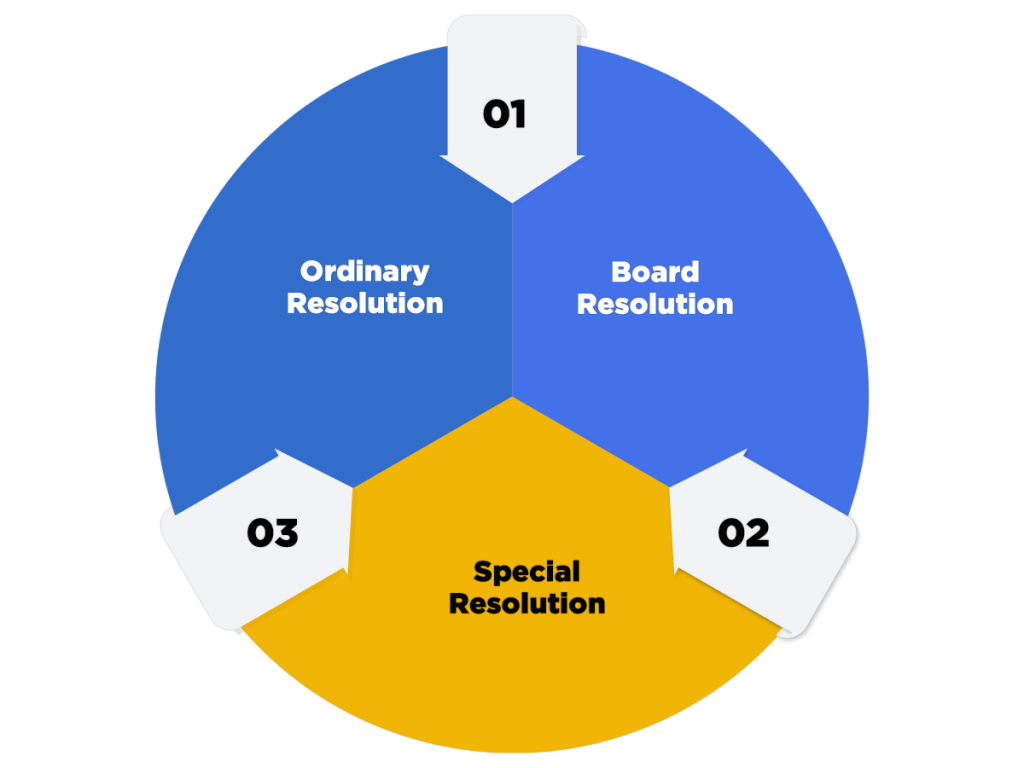
The different types of Resolution filed under Form MGT 14 are as follows:
Board Resolution
For passing a Board Resolution, at least 75% of the Board of Directors needs to give their approval regarding a decision made. Moreover, the same must be signed by the Shareholders as well. Also, all the Resolutions passed by the Board are filed under Annexure A of the MGT 14.
Further, the matters included under Board Resolution are as follows:
- Inspection of the Books of Account and other Records;
- Authorization for making Political Contributions;
- For making an investment or granting Loan/ Guarantee/ Security;
- Related Party Transaction (RPT) concerning Contract or Agreement;
- For Appointing a whole-time KMP (Key Managerial Personnel) of a company;
- Appointment of a person as MD (Managing Director) if he is acting as a Manager or Managing Director of another company;
- Approval of Shelf Prospectus;
- Appointment/ Reappointment/ Renewal/ Variation of Terms of Appointment of the MD (Managing Director)
- For calling of the Unpaid Share Amount from the Shareholders;
- Authorization of Buyback of securities as given under Section 68;
- For issuing securities in India or outside India (including debentures);
- To borrow money;
- For the approval of the Board Report;
- For the approval of the Financial Statements;
- To expand the business of the company;
- To approve Reconstruction, Merger, or Amalgamation;
- For acquiring the controlling stake in another company;
Special Resolution
For passing a Special Resolution, at least 75% of the Board of Directors needs to give their approval regarding a decision made. Further, this resolution is needed for passing special and extraordinary decisions that are not possible to be passed otherwise.
Further, the matters included under Special Resolution are as follows:
- Insertion of the provision of Entrenchment in the AOA (Articles of Association) by companies;
- Change of the Registered Office from One place to another in the same state;
- Alteration of MOA (Memorandum of Association);
- Change in the Object Clause if the money raised is unutilized;
- Alteration of AOA (Articles of Association);
- Variation in the Object of the prospectus and Terms of a Contract;
- Issuance of depository receipts in the Foreign Countries;
- Variation of the Shareholder Rights;
- Issuance of Sweat Equity Shares;
- Issuance of Employee Stock Options;
- Private Offer of Securities;
- Issuance of Debentures or Loans having an option of Conversion;
- Reduction of Share Capital;
- Purchase and Subscription of fully-paid shares for the benefit of Employees;
- Buyback of Shares;
- Keeping of Registers at any place other than the Registered Office;
- Removal of Auditor before the Expiry of the Term;
- Appointment of 15 or more Directors;
- Reappointment of the Independent Director;
- Restricting the number of directorships of a director;
- Selling, leasing, or disposing of the whole or substantially the whole of the undertaking of the company. However, if the company owns more than 1 undertaking, then whole or substantially whole of any of such undertakings;
- For investing in trust securities;
- For borrowing money, where the amount to be borrowed, together with the money already borrowed, will exceed the aggregate paid-up share capital + free reserves of the company;
- Provides time for the repayment of debt remaining from a director;
- Scheme for granting a loan to directors;
- When the Loan and Investment by a company exceeds 60% of the total Paid-up Share Capital, Free Reserves and SPA (Securities Premium Account), or 100% of its Reserves, i.e., (Free Reserves + Securities Premium Account), whichever is more;
- For the appointment of a director who is above the age of 70 years;
- Affairs of the company required to be investigated;
- Application to the ROC for the removal of name from the register;
- Scheme concerning the Amalgamation of Sick Companies with other company;
- Winding-up of a company by the Tribunal;
- Voluntary Winding up of a company;
- For providing sanction to the company, the liquidator needs to exercise certain powers;
- Disposal of the books and paper of the company when the same is completely wound-up and is about to be dissolved;
Ordinary Resolution
For passing an Ordinary Resolution, at least 50% of the Board of Directors needs to give their approval regarding a decision made. Further, a majority of shareholders must agree to pass this resolution as well.
Further, the matters included under Ordinary Resolution are as follows:
- When a company needs to change its name after receiving direction and orders from the ROC. The same is done when the company has submitted false information while applying for the name;
- When a company needs to change its name after receiving direction and orders from the Central Government, if the trademark or name is identical to an existing company or trademark;
- Acceptance of Deposits from the General Public;
- Representation of Corporations at the Board Meeting;
- Representation of Creditors at any meeting;
- Appointing any person as a Statutory Director other than a Retiring Auditor;
- Removal of Director before the expiry of his office tenure;
- Delegation of powers by the board as mentioned under Section 179 (3) clauses (d) to (f);
- Permission to a director for entering into non-cash transactions;
- Appointment of an MD (Managing Director)/ WTD (Whole-time Director)/ Manager;
- Dissolution after analysing the report made by the Company Liquidator;
- For entering into a contract with an RP (Related Party);
Exemption from Filing Form MGT 14
The ones who are exempted from filing MGT 14 MCA are as follows:
- There is no need for a private limited company to file MGT-14 for the matters prescribed under section 179 (3) read with Rule 8 of the Companies (Meetings of Board and its Powers) Rule 2014;
- The provisions of Clause (d) of section 179 (3) are not applicable to the borrowings made by a Banking Company from any other banking company or RBI or from any other bank established;
Documents Required for E-form MGT 14
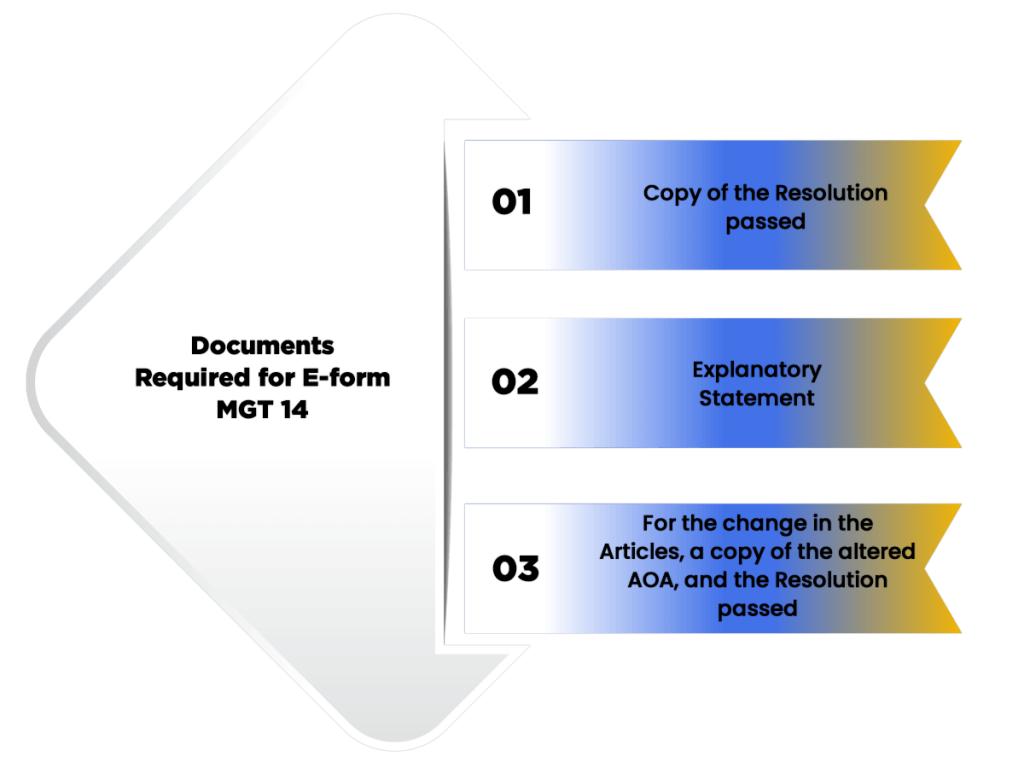
The documents required for filing E-form MGT 14 are as follows:
- Copy of the Resolution passed;
- Explanatory Statement;
- In case the company passes a resolution for the change in the Articles, then the copy of the altered AOA, together with Resolution passed;
Contents of MCA Form MGT 14
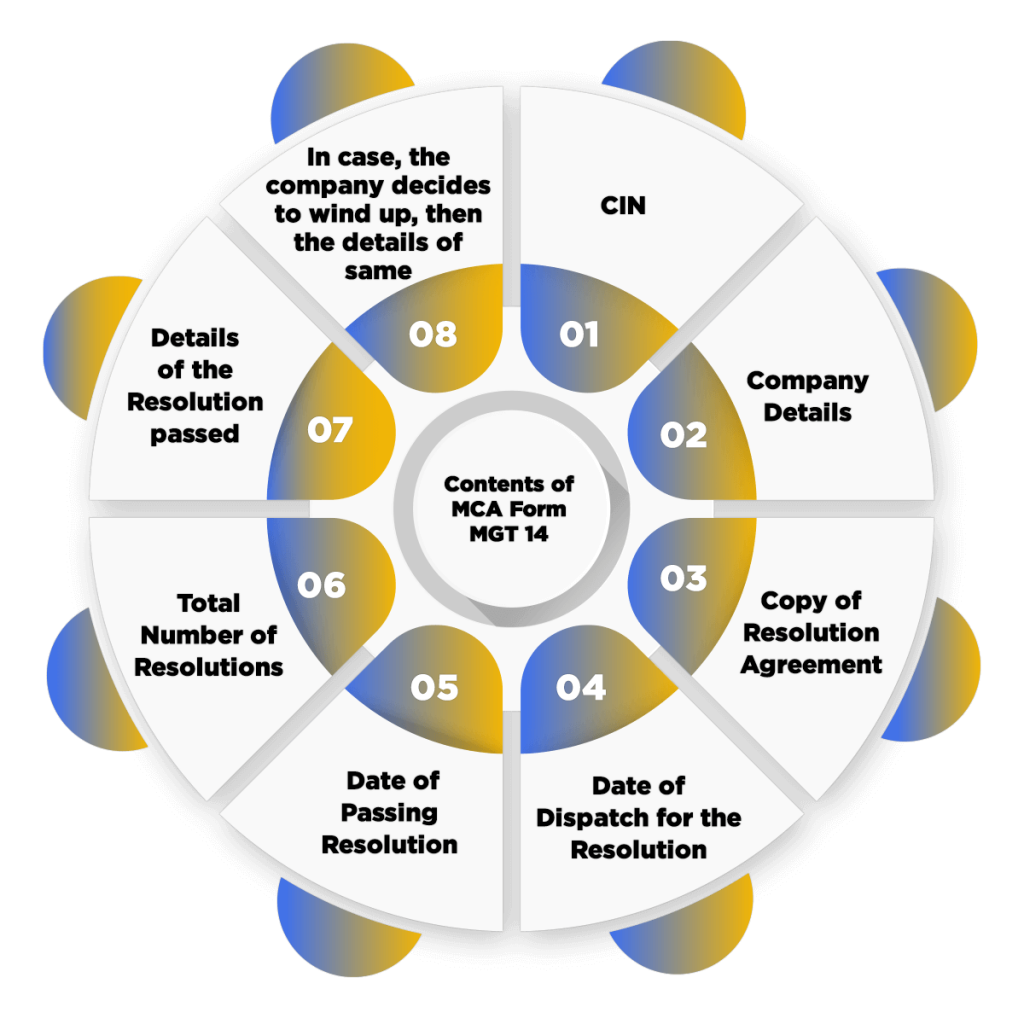
The contents of the MCA form MGT 14 are as follows:
- CIN (Corporate Identification Number);
- Company Details, such as Address of the Office, Name, E-mail ID, and other Contact Details;
- Copy of Resolution Agreement;
- Date of Dispatch for the Resolution;
- Date of Passing Resolution;
- Total Number of Resolutions;
- Details of the Resolution passed, such as purpose, authority, subject matter, etc.;
- In case, the company decides to wind up, then the details of same;
Process of Filing MCA Form MGT-14
Form MGT 14 is processed, approved, and taken on record by using the method of STP (Straight Through Processing). However, there are some situations which do not require the filing of this form, such as:
- Change of Objective;
- Change of Company Name;
- Resolution for the Further Issue of Capital; and
- Conversion of Companies;
Further, the main aim behind the implementation of STP was to facilitate speedy disposal of the E-form MGT 14. The term “Speedy Disposal” denotes that there is no need for any Manual Verification, the details submitted are digitally processed and taken into the record.
Concept of Straight Through Processing
STP or Straight Through Processing is a modern day practice that ensures that the forms uploaded are confirmed, processed, cleared, and settled in a shorter duration, cost-effective manner, and with few errors.
Besides the benefits mentioned above, STP provides Flexible and Cost-effective Infrastructure as well. These benefits not only enable e-business expansion by real time processing but access to enterprise data as well.
Fees for Filing E-form MGT 14
The fees for filing MCA form MGT 14 can be summarised as:
- Rs 200 per document if the Share Capital is below Rs 1 lakh;
- Rs 300 per document if the Share Capital is between Rs 1 lakh to 4.99 lakhs;
- Rs 400 per document if the Share Capital is between Rs 4.99 lakhs to 25.99 lakhs;
- Rs 500 per document if the Share Capital is between Rs 25.99 lakhs to 99.99 lakhs;
- Rs 600 per document if the Share Capital is Rs 1 crore or above;
Time Limit for Filing MGT 14 Form
According to section 117 (1) of the Companies Act 2013, a company needs to file Form MGT 14 within 30 days from the passing of resolution or signing of the agreement.
Penalty for Not Filing MCA E-form MGT 14
The penalty for not filing MCA e-form MGT 14 can be summarised as:
| Defaulting Party | Penalty Prescribed |
| In the case of a Company | A minimum of Rs 1 lakh; If in case the failure continues after the first incident, then Rs 500 for each passing day; A maximum of Rs 25 lakhs; |
| In case of the Officer in default (including liquidator) | A minimum of Rs 50000; If in case the failure continues after the first incident, then Rs 500 for each passing day; A maximum of Rs 5 lakhs; |
Consequences of Not Filing MGT 14 Form within 300 Days
The Consequences of Not Filing MGT 14 Form can be summarised as:
- The defaulter company will need to file Form CG 1 with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs;
- The company will need to pay the penalty levied by the MCA;
- After receiving the order and payment of the fine prescribed, the company will need to file a copy of the order passed and penalty receipt with the Registrar of Companies, India in the form INC 28;
Conclusion
Form MGT-14 was introduced under the Companies Act 2013 for providing a basis to the directors for filing the resolutions passed as at various Board Meetings. This form is regulated by section 94 (1) and 117 of the Companies Act 2013.
Further, a company needs to file Form MGT 14 within 30 days from the passing of the resolution or signing of the agreement.
In case of any confusion and dilemma, reach out to Swarit Advisors, our experts will assist you in getting a clear understanding of the concept of MGT 14.
Also, Read:Change of Name of the Company














