Authorised Money Changer Activities: How Money Changers Work

Shivi Gupta | Updated: Jun 20, 2020 | Category: FFMC
The business of foreign exchange or foreign securities can only be undertaken by Authorised Money Changers, who have obtained the Full-Fledged Money Changer License from the RBI. In this guide, we’ll talk about how money changers work and the different kinds of activities that can be undertaken by them.
Table of Contents
Concept of Authorised Money Changers
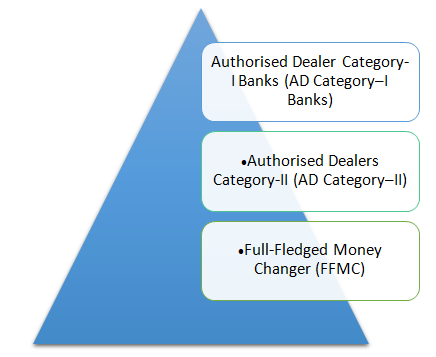
Authorised Money Changers are the authorised dealers, money changers, off-shore banking units or any such persons who have the authority to deal in foreign exchange or foreign securities under Section 10(1) of the Foreign Exchange Management Act. There are three kinds of authorised money changers in India:
An entity wishing to operate as a money changer in India must obtain the Authorised Money Changer License, or commonly known as Full-Fledged Money Changer License (FFMC License). The FFMC license can be obtained by filing an application with the Reserve Bank of India. The RBI is the regulatory authority that issues the guidelines as to how money changers work; the activities permitted and their compliance obligations.
The particulars relating to registration, renewal, cancellation, etc. of the FFMC license are provided under FEMA- the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
How Money Changers Work: Activities Allowed By the RBI
As per the RBI/FED/2015-16/17, FED Master Direction No.3/2015-16 updated as on March 29, 2019, Authorised Money Changers need to carry out their activities in accordance with the Section V and VI of the Master Directions. Section 5 lays down in details of how money changers work and how they must conduct their activities. Let’s have a look at the activities of authorised money changers in India:
Movement of Foreign Exchange
Foreign exchange can be brought into India in any form without restrictions or limit if it is stated on the Currency Declaration Form (CDF) to the Customs Authorities upon its arrival. When foreign exchange brought is not more than USD 10,000 or its equivalent in the form of currency notes or travellers’ cheques, or the value of foreign currency notes is up to USD 5,000 or its equivalent, such declaration to the CDF is not required by the authorities mandatorily.
No one can take out any kind of foreign exchange unless it is obtained from an authorised dealer or a money changer. However, the only exception to this condition is when a general or special permission is obtained from the Reserve Bank. Non-residents in India automatically have general permission to take out an amount not exceeding the amount originally brought in by them.
Purchase of Foreign Currency from Public
Authorised Persons and their franchisees are allowed to purchase foreign currency notes, coins and travellers’ cheques from residents as well as non-residents. If the foreign currency is brought through a declaration on form CDF, the tenderer must produce the same.
Requests for cash payment in Indian National Rupees can be made to resident customers for their purchase of foreign currency notes or Travellers’ Cheques up to the extent of only USD 1000 or its equivalent per transaction.
Requests for cash payment can be made to foreign visitors or Non-Resident Indians up to the extent of only USD 3000 or equal to the amount per transaction.
Authorised Money Changers may sell Indian Rupees to foreign tourists or visitors against International Credit Cards or International Debit Cards and take vigilant measures to obtain reimbursement.
At the time of making payments in Indian Rupees to resident customers for their purchase of foreign currency notes or traveller’s cheques, payment can be made in cash, through account payee cheque, demand draft or loading in INR debit cards or electronic funds transfer through net banking in accordance with the set limits.
Encashment Certificate
Authorised Money Changers in India are also allowed to issue a certificate of encashment purchases of foreign currency notes, coins and travellers’ cheques from residents as well as non-residents. These certificates must bear the authorised signatures and must be issued on the letterhead of the money changer. Additionally, proper records must be maintained for the same.
When the encashment certificate is not issued, the customers must be informed about that the unspent local currency held by non-residents becomes eligible to be converted into foreign currency only against production of a valid encashment certificate.
Purchases from other FFMCs and Authorised Dealers
A Full-Fledged Money Changer or a Non-Bank AD Category II can purchase any foreign currency notes, coins and encashed traveller’s cheques from other FFMCs and Authorised Dealers. Indian National Rupees which is equal to the amount of foreign exchange purchased must be paid only through crossed account payee cheque, demand draft, banker’s cheque, pay order or electronic funds transfer through banks.
Sale of Foreign Exchange
How Money Changers Work WRT Private Visits
Authorised Money Changers are allowed to sell foreign exchange up to the prescribed ceiling as laid down in Schedule III to the Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transaction) Rules, 2000 during a financial year. Authorised Money Changers can sell foreign exchange to a person resident in India to execute their one or more private visits to any foreign country, except to Nepal and Bhutan.
The exchange for such private visits can be availed via self-declaration basis to the traveller about the amount of foreign exchange availed during any financial year. Foreign nationals [1] who have been permanently resident in India are also eligible to avail this quota for private visits. This can be done when the applicant is not availing the facilities for remittance of his salary, savings, etc., to a foreign country.
Alaso, Read:What is the Regulatory Framework for FFMC License?
Business visits
Authorised Money Changers may sell foreign exchange to a person resident in India for the purposes of business travel or to attend a conference or specialised training, or for maintenance expenses of a patient going abroad for their medical treatment or check-up. Forex can also be sold to a person who is accompanying a patient going abroad for medical treatment or check-up up as their attendant to the limits specified in Schedule III to FEMA (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000.
Forex Prepaid Cards
Authorised Dealers Category-II are allowed to issue forex pre-paid cards to residents travelling on private or business visit abroad. However, the KYC/AML/CFT compliance must be met. Additionally, the settlement for forex pre-paid cards may be made via AD Category-I banks.
The RBI has also explained that the Pre-paid foreign currency cards are a form of foreign currency, just like foreign currency notes or travellers’ cheques. The FFMCs selling pre-paid foreign currency cards for travel purposes must comply with the rigorous standards of due diligence and KYC applied to the sale of foreign currency notes or travellers’ cheques to their customers.
For the issue of travellers’ cheques, the traveller must sign the cheques in the presence of an authorised official. The acknowledgement of the purchaser regarding the receipt of the travellers’ cheques must also be held on record.
Authorised Money Changers can also release foreign exchange for travel purposes as per the declaration submitted by the traveller about the amount of foreign exchange availed of during the financial year.
Authorised Persons also allowed to accept payment in cash for less than INR 50,000 against the sale of foreign exchange for travels to the abroad. If the sale of foreign exchange equal to or above INR 50,000 in a single drawl or multiple drawls for a single journey, the payment must be received only via a crossed cheque which is drawn on the bank account of an applicant; a crossed cheque which is drawn on the bank account of the company which has sponsored the visit of the applicant; electronic funds transfer through banking channel by the applicant or sponsoring public or private company; or banker’s cheque, pay the order, or demand draft. In addition to the payment by Indian National Rupees through crossed cheque, banker’s cheque, pay the order, demand draft or electronic funds transfer, the FFMC holder may also accept the payments made by the traveller through debit cards, credit cards or pre-paid cards for travel abroad. However, the following conditions must be fulfilled before the same can be done:
- KYC/ AML / CFT guidelines must be complied with.
- The sale of foreign currency or issue of foreign currency traveller’s cheques must be within limits prescribed by the bank.
- The purchaser of a foreign currency or foreign currency travellers’ cheque and the credit, debit or pre-paid cardholder must be one person.
Any sale of foreign currency notes and coins within the overall entitlement of foreign exchange cannot be made up to the limits specified by the Reserve Bank of India for the country of the visit of the traveller.
Sales against Reconversion of Indian Currency
Authorised Money Changers are allowed to convert unspent Indian currency held by non-residents at the time of their departure from India into foreign currency if a valid Encashment Certificate is submitted.
Money Changers can convert unspent Indian currency up to a limit of INR 10,000 in possession of non-residents if the person provides sufficient reason for the inability to submit an Encashment Certificate after ensuring that the departure would happen within seven days.
Authorised Money Changers in India can also provide the facility for reconversion Indian National Rupees up to INR 50,000 to foreign tourists but not NRIs, against ATM Receipts. However, the following documents must be submitted:
- Valid Passport and VISA
- Ticket confirming the departure within seven days.
- Original ATM slip, verified with the original debit/ credit card.
How Money Changers Work WRT Cash Memo
Authorised Money Changers can also issue a cash memo upon a query to travellers to whom they sell foreign currency, on their official letterhead. The cash memo may be required to be submitted with the emigration authorities while leaving the country.
Rates of Exchange
Authorised Persons can also put through transactions relating to foreign currency notes and travellers’ cheques at rates of exchange as per the market conditions and in accordance with the ongoing market rates.
Display of Exchange Rate Chart
Authorised Persons need to mandatorily display a chart that specifies the rates for purchase or sale of foreign currency notes and travellers’ cheques of foreign currencies and the card rates for any day. The same must be exhibited at a prominent place in or near the public counter and must be updated by 10:30 a.m.
Display of Money Changing Licence
An FFMC or Non-Bank AD Category II must also display a copy of the Money Changer Licence issued by Reserve Bank of India at a prominent place in or near the public counter, at each of its business places.
Foreign Currency Balances
An FFMC or Non-Bank AD Category II must also keep balances in foreign currencies at reasonable levels and avoid build-up of idle balances for speculations on currency movements.
Franchisees must also surrender foreign currency notes, coins and travellers’ cheques purchased to their franchisers within seven working days.
The transactions between authorised dealers and FFMCs must be settled through account payee crossed cheques, demand drafts or electronic funds transfer. However, the settlement must not be made in cash.
Replenishment of Foreign Currency Balances
The Full-Fledged Money Changer or Non-Bank ADs Category II can obtain foreign currency notes from other FFMCs and Authorised Dealers (ADs) holding the FFMC license in India. They can do so against the payment in INR made by way of account payee crossed cheque, demand draft or electronic funds transfer.
When the Authorised Money Changer is unable to replenish its stock in this manner, it can file an application to the Regional Office of the Reserve Bank of India through an AD Category-I to get the permission to import foreign currency into India. The import must take place through the designated AD Category-I through whom the application is made.
Export or Disposal of Surplus Foreign Currency
The Full-Fledged Money Changer or Non-Bank ADs Category II can export surplus foreign currency notes or encashed travellers’ cheques to any overseas bank via the designated Authorised Dealer Category – I in foreign exchange to realise their value through the latter.
Full-Fledged Money Changers may also export surplus foreign currency to private money changers abroad. However, this may be done on the condition that either the realisable value is credited in advance to the AD Category- I bank’s Nostro account or a guarantee is issued by an international bank to cover the full value of the foreign currency notes or coins to be exported.
Write-off of Foreign Currency Notes
When the foreign currency notes purchased are found to be fake or forged, the Full-Fledged Money Changer or Non-Bank ADs Category II may write- off an amount up to USD 2000 in a financial year. This can be done after receiving the approval of the Top Management after exhausting all available options for recovery of the amount.
If any write-off more than the above amount including but not limited to foreign currency notes is found to be fake or forged, it would require the approval of the Regional Office of the Foreign Exchange Department of the Reserve Bank of India.
Temporary Money Changing Facilities
The Full-Fledged Money Changer or Non-Bank ADs Category II are allowed to transact money changer business only at the location mentioned in the Money Changer Licence. If the business plans to provide money changer services on a temporary basis on certain special occasions, a separate application must be made to the Regional Office of the Foreign Exchange Department of the Reserve Bank under whose jurisdiction the temporary money changing facility is proposed to be opened.
Detailed information such as the period for which the exchange counter would be in operation, the volume of business expected, the manner of accounting of the transactions, a letter from organisers to make the venue available for the money changing facilities, etc. must be submitted.
Opening of Foreign Currency Accounts
The Full-Fledged Money Changer or Non-Bank ADs Category II can open Foreign Currency Accounts in India after receiving the approval of the respective Regional Offices of the Foreign Exchange Department. However, the following conditions must be fulfilled:
- Only one account per currency is permitted at a particular centre.
- Only the value of foreign currency notes or encashed TCs exported through the specific bank and realised can be credited to the account.
The balances in the accounts must be utilised only for settlement of liabilities on account of TCs sold by the Full-Fledged Money Changer or Non-Bank ADs Category II and Foreign currency notes acquired by the Full-Fledged Money Changer or Non-Bank ADs Category II from ADs Category-I. However, no idle balance must be maintained in such account.
Nostro Account by Authorised Dealers Category-II
The Authorised Dealers Category-II may open Nostro Accounts after receiving one-time approval from the Regional Office of the Reserve Bank. However, the following conditions must be met:
- Only one Nostro account can be opened for each currency;
- The balance account must be used for the settlement of remittances sent for permissible purposes and not for the settlement in respect of forex pre-paid cards;
- No idle balance must be maintained in such account; and
- The reporting requirements must be adhered to.
Consult Swarit Advisors’ experienced FEMA and RBI experts, who can help you with your Money Changer License Registration, audit requirements, compliance requirements and much more.
Read, Also:Authorised Money Changer Audit: FFMC License Audit Requirements