What are NBFC Annual Compliance Checklist

Shivani Jain | Updated: Mar 06, 2019 | Category: Compliance, NBFC
NBFC is one of the most common forms of financial institutions in India which contributes an outstanding percentage of GDP rise to the country’s economy. As important as it is to obtain NBFC license for commencing a Non-Banking Financial Company, it is equally important to follow-up with the NBFC annual compliance checklist.
However, in case, you don’t follow up with the NBFC compliance; you would have to pay hefty penalties. Even it could lead to the company’s closure or cancellation of NBFC license.
Therefore, if you’re operating an NBFC, then make sure that you have the valid NBFC annual compliance checklist. The checklist will help you to file returns on time. Hence, we have brought a complete list of NBFC annual compliance so that you can save yourself from penalties and file returns before the due date.
Table of Contents
Definition of NBFC Annual compliance checklist
NBFC annual compliance checklist defines the due date of the NBFC compliances and returns that every NBFC has to file. The list is made as per the guidelines and master directions of RBI.
As per the Non-Banking Financial Company Returns (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2016, every Non-Banking Financial Company needs to comply with the compliances described later in this blog.
Types of NBFCs on the basis of activities and liabilities
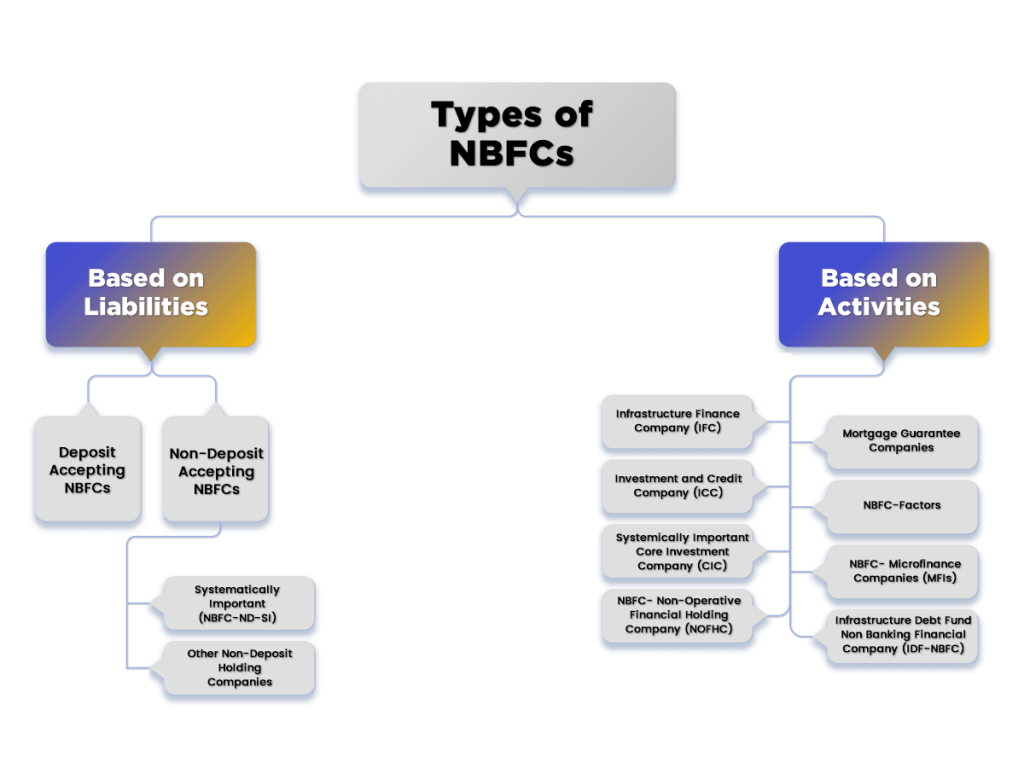
The types of NBFC on the basis of Activities and Liabilities are as follows:
Based on Liabilities
- Deposit Accepting NBFCs;
- Non-Deposit Accepting NBFCs;
- Systematically Important (NBFC-ND-SI);
- Other Non-Deposit Holding Companies;
Based on Activities
- Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC);
- Investment and Credit Company (ICC);
- Systemically Important Core Investment Company (CIC);
- NBFC- Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC);
- Mortgage Guarantee Companies;
- NBFC-Factors;
- NBFC- Microfinance Companies (MFIs);
- Infrastructure Debt Fund Non Banking Financial Company (IDF-NBFC)
Essential NBFC Compliance Checklist for Non-Deposit & Deposit-taking Company
Below we have made an NBFC annual compliance checklist for both Non-Deposit and Deposit-taking Company. Have a look below:
| S. No | Particulars | Time Limit |
| Annual Compliances | ||
| 1. | Unaudited March Monthly return/NBS-7 | On or before 30th June |
| 2. | Statutory Auditors certificate on Income & Assets | On or before 30th June |
| 3. | Information about Companies having FDI/Foreign Funds | On or before 30th June |
| 4. | Audited March Monthly return/NBS-7 | Upon completion |
| 5. | File audited annual balance sheet and P&L Account | One month from the date of signoff |
| 6. | Resolution of Non-Acceptance of Public Deposit | Before the commencement of the new Financial year |
| 7. | Declaration of Auditors to Act as Auditors of the Company | Annual basis |
| Monthly Compliance | ||
| 1. | Monthly Return | By 7th of every month |
| 2. | Upload Monthly Return | By 7th of every month |
| Periodical Compliances | ||
| 1. | Appointment of Director (Annexure III) | Within 30 days of appointment |
| 2. | Resignation of Director (DIR-12 + Challan report) | Within 30 days of appointment |
| 3. | Adoption of any notification in the ensuing Board Meeting and filing the certified copy with RBI |
Returns and Compliances of NBFCs registered with RBI
With reference to Master Direction[1] – NBFC-NDs-SI and NBFC-SI deposit-taking company must file the following returns as described below:
Deposit-taking NBFCs are required to submit the following returns:
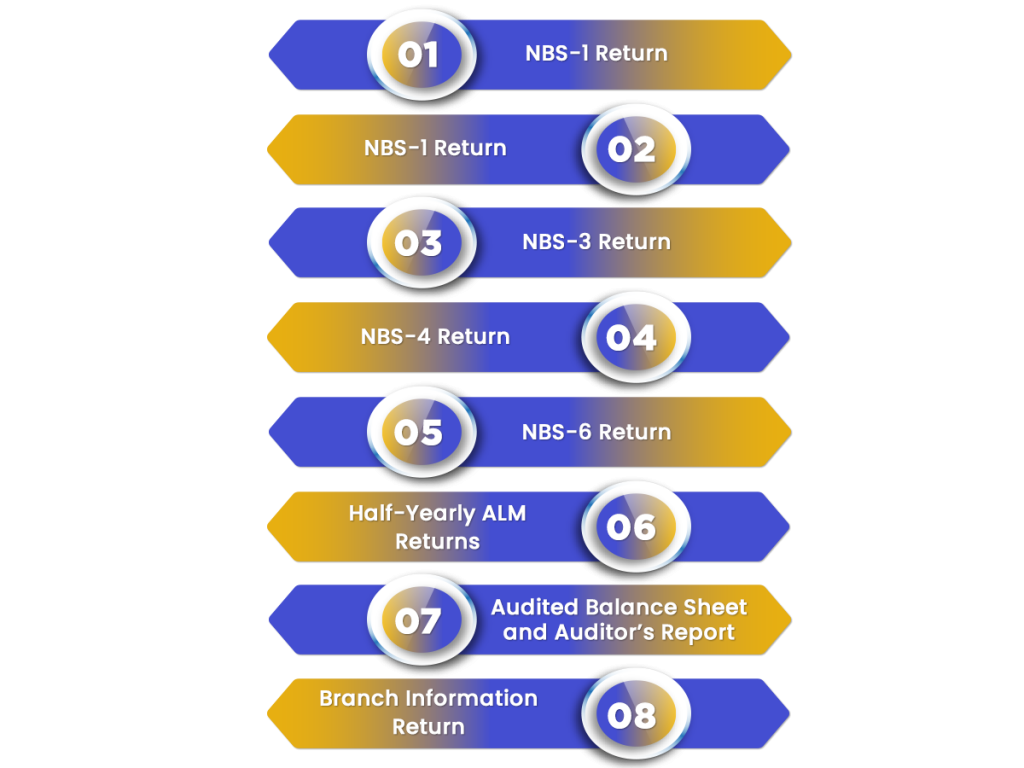
- NBS-1 Return: Every NBFC that accepts or holds public deposits should submit NBS-1 return on a quarterly basis. The purpose of filing this return is to capture financial details such as Profit and Loss account, Components of Assets and Liabilities, Exposure to sensitive sectors, etc.
- NBS-2 Return: NBFC which accepts public deposits are required to submit a quarterly return on Prudential Norms. The intent behind filing this return is to capture compliances related to several prudential norms such as Asset Classification, Capital Adequacy, NOF, Provisioning, etc.
- NBS-3 Return: Again, it’s a quarterly return that every deposit-taking NBFC needs to file on a quarterly basis. Besides, the objective behind introducing this return is to capture information about Statutory Investments in the Liquid States. Moreover, the statutory investments include Fixed Deposits in Schedules Commercial Bank, Central or State Government Securities, etc.
- NBS-4 Return: It’s a kind of annual return of critical parameters. The return must be filed by a rejected company holding public deposits. Earlier, NBS-5 was filed. However, now NBS-5 stands withdrawn as NBS-1 is filed quarterly. The objective of filing NBS-4 is to find the repayment status of the rejected NBFCs accepting public deposits.
- NBS-6 Return: It’s a monthly return on exposure to capital market by NBFC taking deposits with total assets equal to or more than Rs. 100 crores.
- Half-Yearly ALM Returns by NBFC accepting public deposits of more than Rs. 20 crores or asset size of above Rs.100 crores.
- Audited Balance Sheet and Auditor’s Report by Non-Banking Financial Companies accepting public deposits.
- Branch Information Return: It’s a quarterly return that every NBFC which accepts or holds public deposits needs to submit.
NBFCs-ND-SI is required to submit the following returns:
- NBS-7: It’s a quarterly statement of capital funds, risk asset ratio, risk-weighted assets, etc., for NBFC-ND-SI. Therefore, you need to file it on a quarterly basis.
- Monthly returns on Necessary Financial Parameters of NBFCs-ND-SI must be submitted on a monthly basis.
- ALM returns: ALM (Asset-Liability Management) Returns refer to multiple returns that are supposed to be submitted by NBFCs-ND-SI at several intervals as described below:
- Statement of short term dynamic liquidity ALM [NBS-ALM1]: Monthly;
- Structural liquidity in format ALM [NBS-ALM2] statement: Half Yearly;
- Interest Rate Sensitivity in format ALM – [NBS-ALM3] statement: Half Yearly;
- Assets Liability Mismatch [ALM-YRLY] statement: Annually.
- Branch Information Return: Every NBFCs-ND-SI must submit the branch information return on a quarterly basis.
Quarterly return on important financial parameters of non-deposit taking NBFCs holding assets of above Rs. 50 crores and higher but below Rs. 100 crores.
Non-deposit taking NBFCs with asset size between Rs. 50 crores and Rs. 100 crores are required to submit the basic details such as the name of the company, address, NOF, and profit/loss during the last three years quarterly.
Additional Compliances
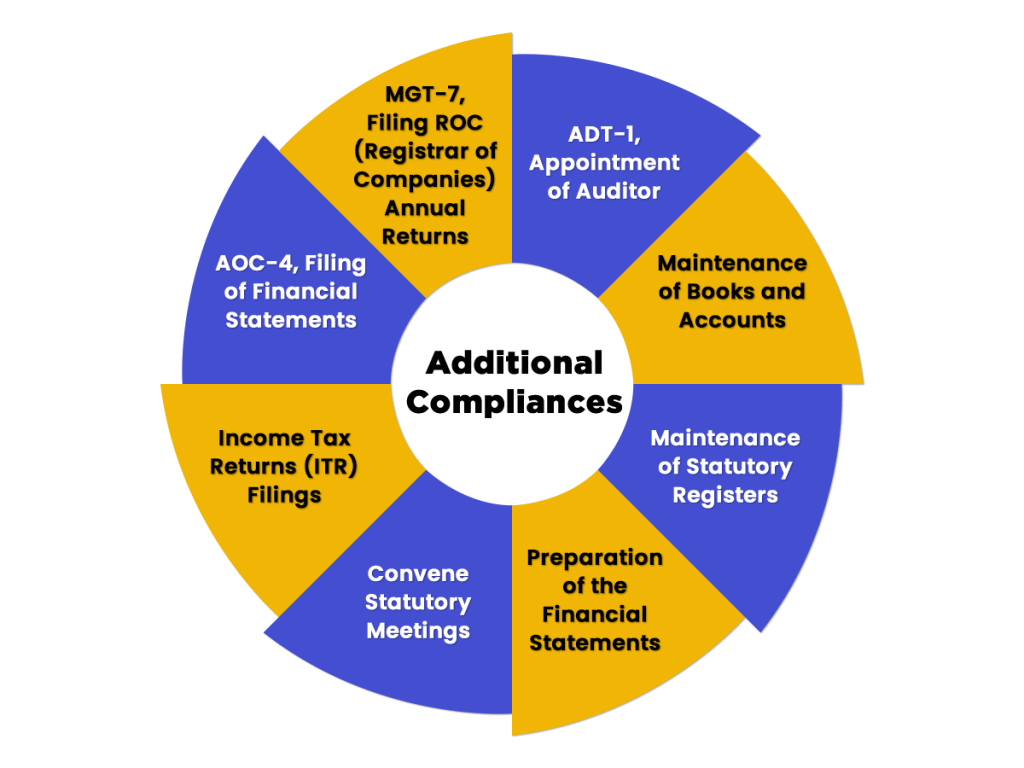
Besides the compliances mentioned above, there are some other compliances under the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013, that all the NBFCs PAN-India must follow, which are as follows:
- ADT-1, Appointment of Auditor;
- Maintenance of Books and Accounts;
- Maintenance of Statutory Registers;
- Preparation of the Financial Statements;
- Convene Statutory Meetings;
- Income Tax Returns (ITR) Filings;
- AOC-4, Filing of Financial Statements;
- MGT-7, Filing ROC (Registrar of Companies) Annual Returns;
RBI Intimations Applicable on NBFCs
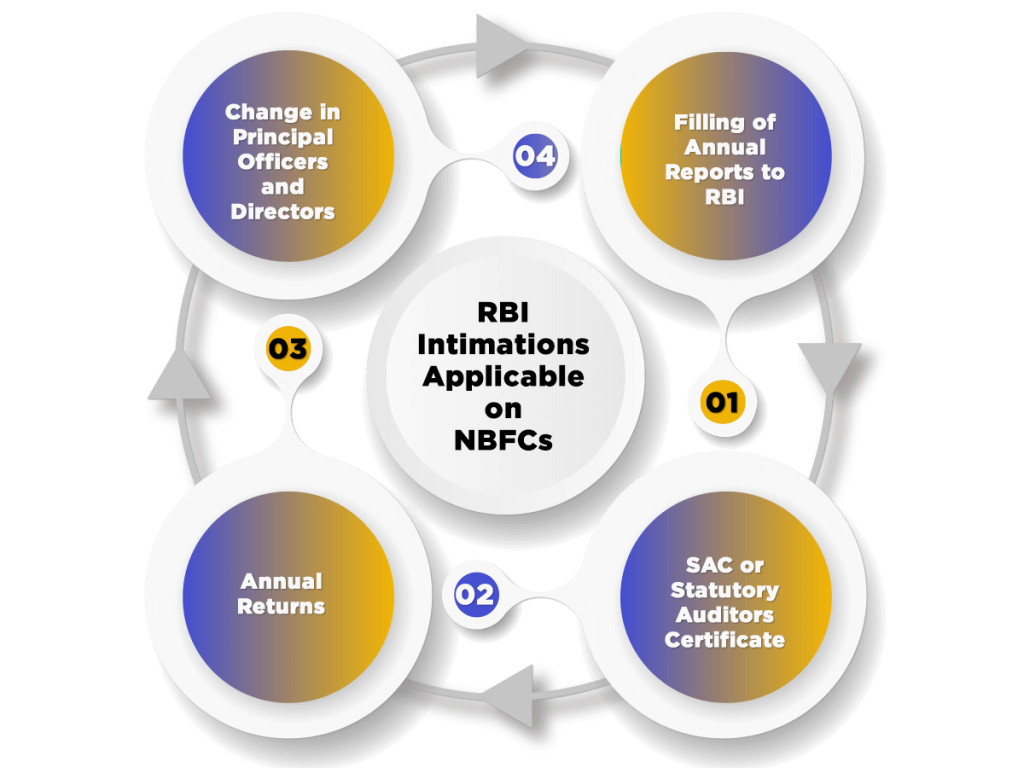
The compliances that are applicable to every NBFC irrespective of the activities are as follows:
- Filling of Annual Reports to RBI: It is compulsory for every NBFC (Non Banking Financial Institution) to submit its Annual Report within a period of 15 days, starting from the date of AGM (Annual General Meeting). Each financial institution should provide its Audited Balance Sheet, together with Audited P&L (Profit and Loss) Statement passed by the company in its Board Meeting. The directors of the company also need to annex a copy of Board Report or Directors Report to the Apex Bank.
- SAC or Statutory Auditors Certificate: All the NBFCs having Registration PAN-India needs to collect a certificate from Statutory Auditors. This certificate will act as a declaration that the said NBFC or Non Banking Financial Company is carrying out the functions of NBFC and is incorporated under section 45-IA of the RBI, Act, 1934. Further, the due date to file this certificate is one month from the date of finalization of the Balance Sheet. However, the period shall not exceed the date of 31st December.
- Annual Returns: Every miscellaneous NBFC that is accepting or holding deposits must submit an annual return containing information in the format prescribed by the Apex Bank of India.
- Change in Principal Officers and Directors: In case an NBFC decides to change its Principal officers or Directors, and then it is compulsory for it to inform the RBI with a time span 1 month, starting from the date of the event. Further, it is compulsory for every non banking financial institution to submit a written statement, including the details as follows:
- Name and the Official Designation of its Principal Officers;
- Name and Residential Address of the Directors of the Company;
- Specimen Signature of the Principal Officer who is authorised to sign on behalf of the Company
Further, any change or amendment made by the Apex Bank in the guidelines provided above shall be informed by the Reserve Bank of India with 1 month from the incidence of such change or amendment.
Prudential Regulations
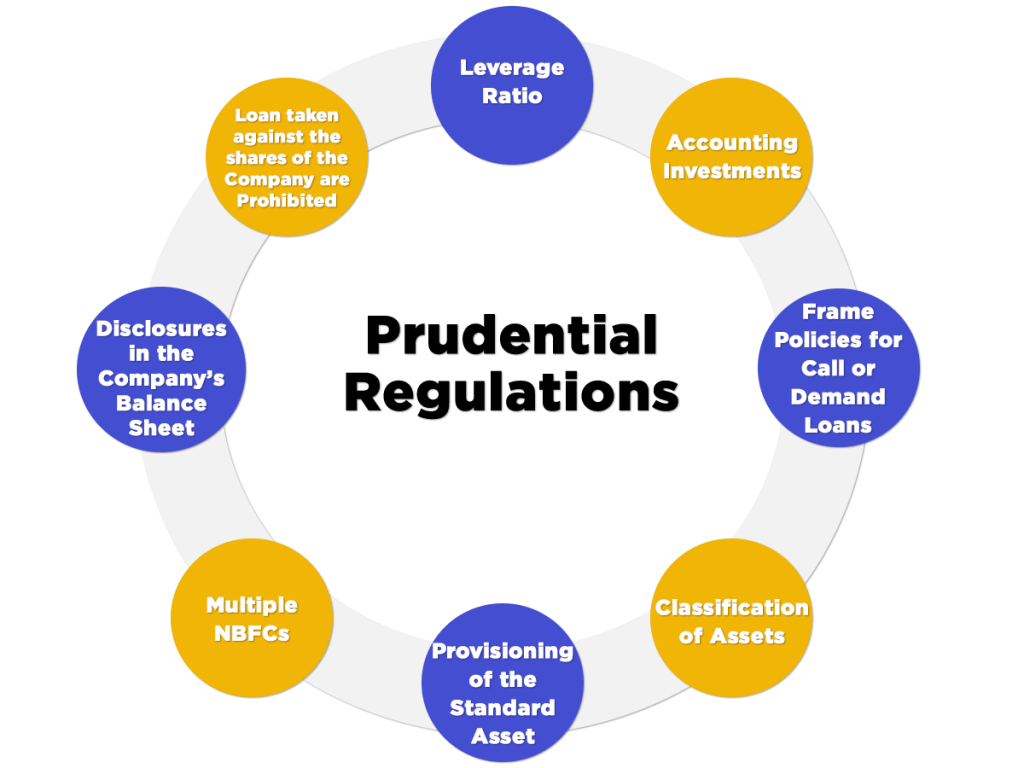
Besides the above mentioned RBI compliance for NBFCs having registration PAN-India, there are some other regulations mentioned under Chapter IV of the Master Director issued by RBI. Such regulations are known as Prudential Regulations. It is again mandatory got every NBFC to abide by the regulations as follows:
- Leverage Ratio: All the NBFCs other than NBFC-IFC (Infrastructure Finance Company) and NBFC-MFI (Micro Finance Institution) must maintain a leverage ratio up to 7 at any course of action.
- Accounting Investments: It is mandatory for the BOD (Board of Directors) of the NBFCs to frame Investment Policies for the company and implement them as well. For example, the criterion to categorise investments into long term and current investments.
- Frame Policies for Call or Demand Loans: The BOD (Board of Directors) of a pertinent NBFC that intends to call or demand loans must frame a policy that will be implemented by the company.
- Classification of Assets: All the NBFCs pertinent under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction must classify their assets in the classes as follows:
- Standard Assets;
- Sub-Standard Assets;
- Doubtful Assets;
- Loss Assets
- Provisioning of the Standard Asset: Every pertinent NBFC is required to make provisions regarding the standard assets at 0.25% of the total outstanding.
- Multiple NBFCs: All the NBFCs relevant under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction will be jointly aggregated for the purpose of checking the threshold of Rs 500 crores asset size.
- Disclosures in the Company’s Balance Sheet: Every NBFC relevant under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction will have separate disclosures provisions for bad or doubtful debts and depreciation in Investments.
- A loan taken against the shares of the Company are Prohibited: No BFCs pertinent under chapter IV of the RBI Master Direction can either take or lend credit against its own shares.
Take away
Therefore, any company willing to carry on the business of non-banking financial institution are imperatively required to obtain an NBFC registration in India with RBI. Moreover, according to Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, 1934, the applicant must have a net owned fund of Rs. 2 crores and it must obtain a certificate of registration from the bank.
In addition, if you have obtained the license, you are strictly required to abide by the NBFC Post Registration Compliances as described above. Furthermore, the consequences of non-compliance will lead to a hefty penalty and even shutting down the company.
However, starting an NBFC can seem complex due to the intricate and complicated licensing requirements. Our experts at Swarit Advisors will provide end-to-end NBFC Registration solutions. We rank high in NBFC Registration and Advisory Services.
Read, Also: How to Takeover NBFC.














