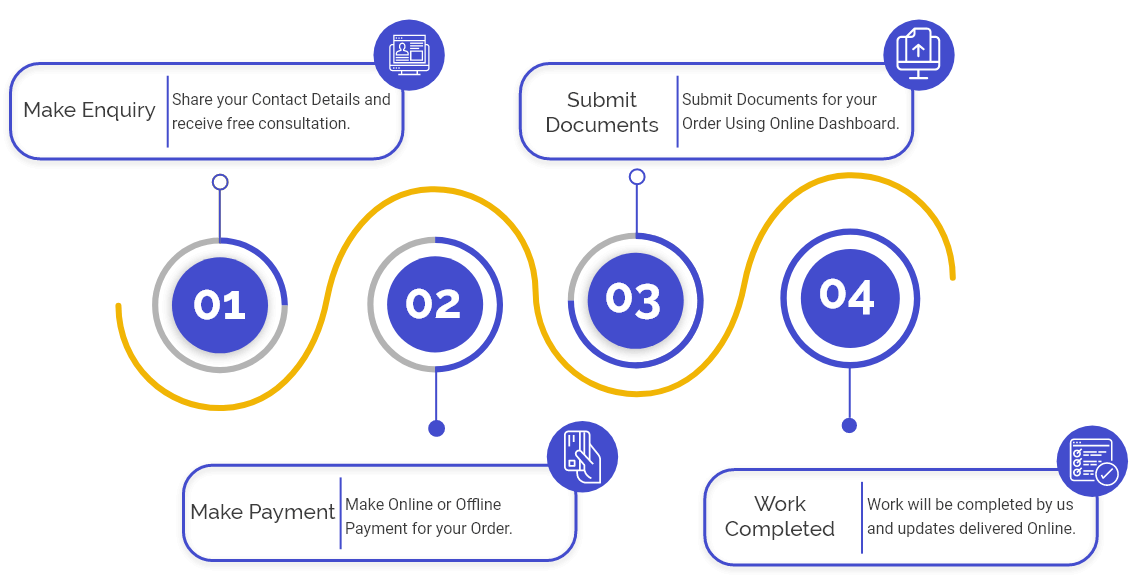
An Overview of Microfinance Company Registration
In India, a Microfinance Company is a financial institution which provides small-scale financial services in the form of loans, credit or savings. These Microfinance companies are introduced to ease the credit system for small businesses as they don't get loans from banks due to their complex process. Such companies offer small loans to various small businesses or households that don’t have access to formal banking channels or are not eligible for loans. The easiest way of Microfinance Company Registration in India is to register a Section 8 Company with MCA without charging any type of marginal money or guaranteeing security. This company can give loans at inexpensive rates directed by the Reserve Bank of India and the Central Government.
Moreover, it shall be noted that a Microfinance Company is a Non-Deposit Taking NBFC and is separate & unique from Section 8 Company. The affairs & operations of a Microfinance Company are regulated & governed by the provisions of the RBI Act, 1934 and the directions issued thereunder.
Benefits of Microfinance Company Registration
The key benefits of Microfinance Company are as follows:
- Does not require Collateral for Lending Funds;
- Facilitates Employment Generation;
- Assists in Rural Development;
- Provides Opportunity to Earn Income;
- No Minimum Capital Requirements;
- Offers better Rate of Repayment;
- Make people Self Sufficient;
Who are Eligible to get a Loan from MFI?
- Agricultural Activities;
- Small Scale Businesses;
- Professional and Transport Trade;
- Artisan Business.
Requirements for Microfinance Company Registration
The basic requirements to start a Microfinance Institution in India are as follows:
- The company should be registered under the Companies Act 2013 or Companies Act 1956;
- Should have Net Owned Funds of Rs 5 crores;
- Can provide loans only between Rs 50,000 to Rs 1.25 lakh;
- Must provide the details of promoters;
- 85% of the total Net Owned Fund needs to be the Qualifying Assets;
- No Minimum Capital Requirement;
Types of Microfinance Institutions
The different types of Microfinance Institution are as follows:
- RBI Registered Microfinance Institutions: To register a Microfinance Company as an NBFC, the applicant needs to incorporate a Private Limited or Public Limited Company under the provisions of the Companies Act 2013. After that, he/ she needs to follow all the steps required for a microfinance company registration, ranging from the minimum capital requirement to the filing of the application at the regional office of the RBI.
- Section 8 Registered Microfinance Institutions: To register a Microfinance Company as a Section 8 Company, the applicant company needs to first apply for DSC (Digital Signature Certificate) and DIN (Directors Identification Number) for all the proposed directors. After that, it needs to file an application for Name Approval in form INC – 1. Further, it needs to draft the Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association for the company and need to file INC – 12, together with the required documents to acquire a license.
Documents required for Microfinance Company Registration
The documents required to obtain the Microfinance Company Registration in India are as follows:
- A copy of the Company’s COI (Certificate of Incorporation);
- PAN Card details of the Directors & Applicant Entity;
- DSC (Digital Signature Certificates) and DIN (Director Identification Number) for all the Directors;
- Latest Passport-sized photographs of all the proposed Directors;
- Address Proof of the place being used as the registered office;
- A copy of the Rental Agreement, in the case of Rented Property;
- A copy of the Ownership Certificate or Sale Deed, in the case of Self Owned Property;
- Certified copy of the MOA (Memorandum of Association) & AOA (Articles of Association);
- Certified Banker’s Report;
- A copy of the Board Resolution;
- Auditors Report showing the minimum Net Owned Funds;
- A Certified copy of the Compliance Certificate from a Chartered Accountant;
- Structured Business Plan of the Entity;
- Latest Financial Report about Directors;
- Income Proof of the KMP (Key Managerial Personnel) and Directors;
- If the proposed director of the company is an Indian National, a copy of the passport is required. However, in the case of Foreign Nationals, notarised or apostil, the passports must be submitted.
Requirements for Microfinance Company Registration as an NBFC and Section 8 Company
|
Requirements |
NBFC |
Section 8 Company |
|
Experience of Director |
At Least 10 years of experience in the Financial Sector. |
No prior experience is required. |
|
Total Number of Members |
For a Public Limited, at least seven members are required, and for a Private Limited Company (Pvt.), a minimum of two members are required. |
Minimum of two members are required. |
|
RBI Approval |
Compulsory |
Not Required |
|
Adhering to Compliances |
It has to adhere to all NBFC compliances. |
Adhere to RBI compliance, but they are less severe as compared to NBFC. |
|
Organisation Status |
Profit organisation |
Non-Profit organisation |
|
Limitation of Loans |
Maximum of 10% of total assets. |
Unsecured loan of Rs. 50000 to small business loans up to Rs. 1.25 lakh to dwelling residence. |
|
Net Owned Funds (NOF) |
Minimum Rs. 5 crores |
No minimum requirements |
|
The difficulty of Microfinance Company Registration |
All processes involved in the company formation have to be executed. |
Relatively simple and easy as it is registered as a Non-Profit Organisation. |
Procedure for Microfinance Company Registration as an NBFC
Following are the steps involved in the Microfinance Company Registration as an NBFC:
- Step 1: Company Registration: To be registered as an NBFC Microfinance Company, the first and essential step is establishing a Public or a Private Company. To form a Public Limited Company or Entity, at least 7 members are required and to start a Private Company, at least 2 members and a capital of Rs. 1 lakh are required.
- Step 2: Raise the Capital: Once you register the company, then the next step is to raise the required minimum NOFs (Net Owned Funds) of Rs. 5 crores. For the north-eastern region, the requirement is Rs. 2 crores.
- Step 3: Capital Deposit: After raising the capital, the next step is to deposit the capital in a traditional bank as a fixed deposit and procure a No Lien Certificate for the same.
- Step 4: Apply for License: At last, the NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Company) must fill out the application form for the NBFC License online and submit the form along with all the verified documents. Submit a hard copy of the application, and the license must also be submitted to the regional office of the RBI. Following are all the crucial documents that should be submitted at the time of NBFC Registration:
- Submit MOA (Memorandum of Association) & AOA (Articles of Association) of the company;
- Submit a copy of the Board Resolution;
- Banker’s report of the company;
- Net-worth Certificate of the directors;
- Company Registration Certificate;
- Any proof of education or professional qualification of the director;
- Structure plan of the organisation;
- Submit a copy of the auditor's report of the fixed deposit receipt;
- Submit income proof & KYC of the director;
- Work experience proof in the financial sector;
- Latest credit report of the directors;
- Banker’s Certificate of No Lien declaring the NOF.
Procedure for Microfinance Company Registration as a Section 8 Company
Another option for the registration of a Microfinance Company is to register the company as a Section 8 Company. Following is the procedure for the same:
- Step 1: Prepare DSC and Name Approval: The first step is to prepare DSC and apply for the name approval as soon as possible through the SPICe+ Form.
- Filing Applications: After getting approval from the regional director, we will proceed to file the application for Section 8 Company Registration with the requisite documents before ROC. Once all clarification along with a CIN (Company Identification Number) and this would be carried out as per the requirements under the SPICe+ form.
- Step 3: File MOA and AOA: After that, the company must draft the MOA (Memorandum of Association) & AOA (Articles of Association) and file it along with vital documents.
- Step 4: PAN, TAN & Bank Account: You must have your PAN, TAN & Bank Account ready while going for Section 8 Company Registration in India.
Mandatory Compliance for Microfinance Institution
The mandatory compliance for Microfinance Institution are as follows:
RBI Compliance: The term RBI Compliance means the guidelines issued for the operating Microfinance Companies. It shall be relevant to state that there is no need for a Microfinance Company to satisfy the RBI requirements, but it needs to adhere to the RBI Rules concerning it.
Companies Act 2013: If in case a Microfinance Company is registered as a Section 8 Company, then, in that case, it needs to comply with the requirements specified under the Companies Act 2013.
FAQs of Micro Finance Company Registration
The term “Microfinance Company” denotes a company that facilitates low income group which are distantly located especially in semi urban as well as rural areas and have no access to banking facilities by providing funds to them.
The main aim of a Microfinance Company is to offer funds to low income people and comes handy for those people who reside in semi urban as well as rural areas.
The key benefits of a Microfinance Company are, it generates employment, facilitates rural development, no need of providing Collateral Security while obtaining a loan.
The term “pre-requisites” include a copy of the Incorporation Certificate, a copy of the Extract of Main Object Clause specified in MOA, a Copy of the Fixed Deposit Receipt, and Banker’s Certificate with respect to NOF and Banker’s Report.
A Microfinance Institution can lend up to Rs 50000 in the first cycle and Rs 1 lakh in the subsequent cycle to people who do not have normal banking facilities.
Normally, the people from low income strata benefit from a Microfinance Company, such as agriculturists, farmers, businessman, etc.
Any borrower who is having a Total Annual Income up to Rs 1.6 lakh in urban and semi-urban areas or Rs 1 lakh in rural areas.
The Minimum Loan Tenure for the Money Borrowed from MFIs is 24 months.
A Micro Finance Company is not eligible to impose more than 1% of the total loan amount as Loan Processing Charge.
A Micro Finance Company is not eligible to levy a high rate of interest than the prescribed limit from its lender. Further, the variation between the two should not exceed 4%.
Yes, a Micro Finance Company can give loans for personal use.
An MFI cannot grant more than 30% of the total loan as loan for personal use.
Yes, it is compulsory for a Micro Finance Institution to become a member of CIBIL.
The steps involved in the process to register a Micro Finance Company are, file an application for Name Approval, Apply for DIN and DSC, Incorporation Certificate, and an Online Application to RBI.
The term “Document” includes a copy of PAN Card, Aadhar Card, Address Proof, Passport Size Photo, Proof of Ownership, Utility Bill, and NOC.
Rs 1190000 is charged as the starting Registration Fee for a Micro Finance Company.
No, a Microfinance Company cannot levy Prepayment Penalty.
Yes, a Microfinance Company can give loans for emergencies.
An MFI cannot grant more than 50% of the total loan as a loan for an emergency.
The term “Net Assets” denotes the Total Assets other than money market devices and cash and bank balances.
The term “Qualifying Assets” denotes the loans disbursed to a borrower who is having an annual household income below Rs1,60,000 in urban and semi-urban areas or Rs 1,00,000 in rural regions.
No, there are no limitations imposed on the remaining 15% of the assets that an MFI holds.
The components considered for calculation are Expenses incurred towards interest payment + Processing Fees + Stamp Duty Charges + DD Charges – Interest Accrued on Security Deposit.
Yes, an NBFC-MFI is allowed to charge a differential rate of interest to its borrowers. However, the variance must not increase by 4%.
It is mandatory for all the NBFC-MFIs to maintain a “Capital Adequacy Ratio” inclusive of Tier I and Tier II Capital. However, the same shall not be below 15% of its aggregate risk weighted assets.
The total value of “Tier II Capital” at any point of time will not exceed 100% of the “Tier I Capital”.
No, the “Credit Concentration Norms” are not applicable to NBFC-MFI.
The term SRO stands for Self-Regulatory Organisation.
No, it is not necessary for an NBFC-MFI to become a member of an SRO. However, it is advisable to become a member of at least one Self-Regulatory Organisation.
The RBI or Reserve Bank of India has made it compulsory for the NBFC-MFI to clearly display in all of its offices and in the directions issued by it and on its official website, the “Effective Rate of Interest” being charged by it.
No, the pricing regulation, including the variance norms, do not apply to the Non-Qualifying Assets.
A borrower needs to pay only three charges for the pricing of loans, which are Interest Charge, Processing Charge, and Insurance Premium.
No, a Micro Finance Institution cannot charge any other component, except the three prescribed for determining the Pricing of Loan.
The Reserve Bank of India or RBI has the authority to regulate and issue directions for the Micro Finance Institutions in India.
Yes, MFIs or Micro Finance Institutions charge more interest than traditional banks.
The reasons are that an MFI offers small and collateral free loan, so it requires intensive assessment for determining the credit worthiness of the client. Moreover, a small loan tends to be expensive in terms of the process than large ones.