Transparent Taxation: PM Decides to Honor Honest Taxpayer

Shivani Jain | Updated: Aug 13, 2020 | Category: Income Tax, News
“Minimum Government and Maximum Governance”
The term “Transparent Taxation” denotes a new tech-driven taxpaying platform unveiled by our Hon’ble Prime Minister, Mr. Narendra Modi, on 13.08.2020, through video conferencing at 11 am in New Delhi. The full name of this online platform is “ Transparent Taxation : Honoring the Honest”[1] .
The main aim of this platform is to infuse transparency, empower taxpayers, minimize government intervention, reduce human interface in the Indian Tax Regime. That means it will work to benefit the honest taxpayers, whose hard earned money stimulates National Progress.
Table of Contents
Key Features of Transparent Taxation
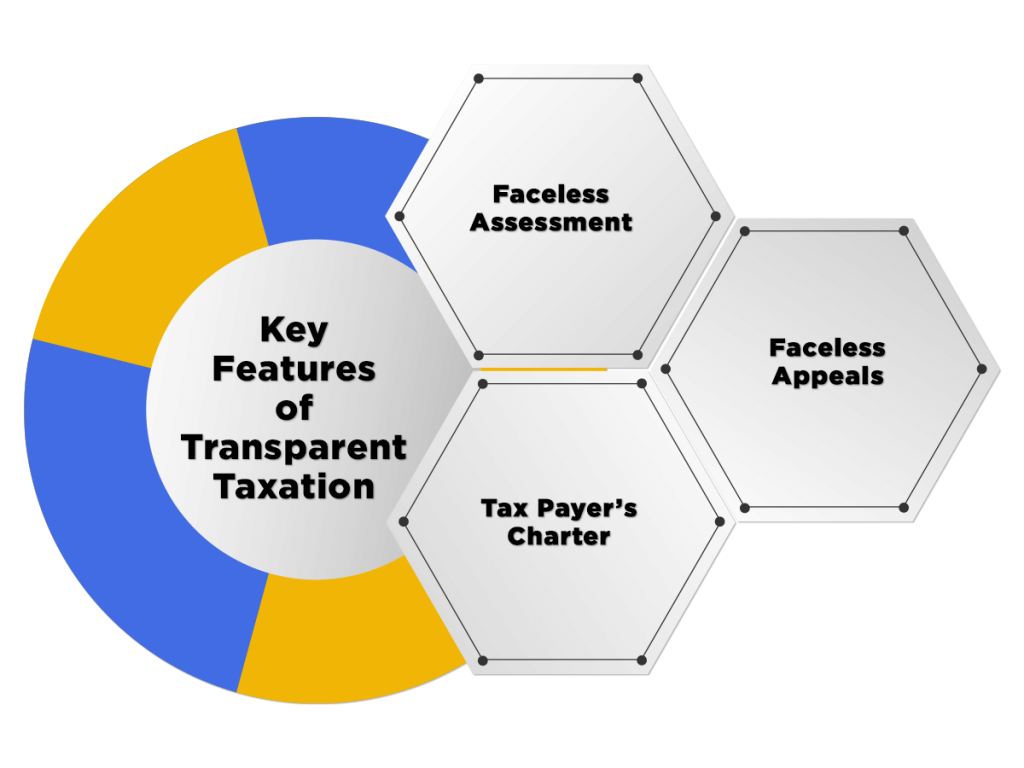
The main features of this technology-driven platform are as follows:
- Faceless Assessment;
- Faceless Appeal;
- Tax Payer’s Charter;
Further, Mr. Narendra Modi[2] , stated that both Faceless Assessment and Tax Payer’s Charter will come into force from today onwards, i.e., 13.08.2020. However, the reform of Faceless Appeal will be going live from 25.09.2020, i.e., on the birth date of Pt. Din Dayal Upadhaya.
He also stated that this mechanism would make the Indian Tax Regime “People Oriented” and “Public Friendly” from “Process and Power Centric”.
Need for Reforms
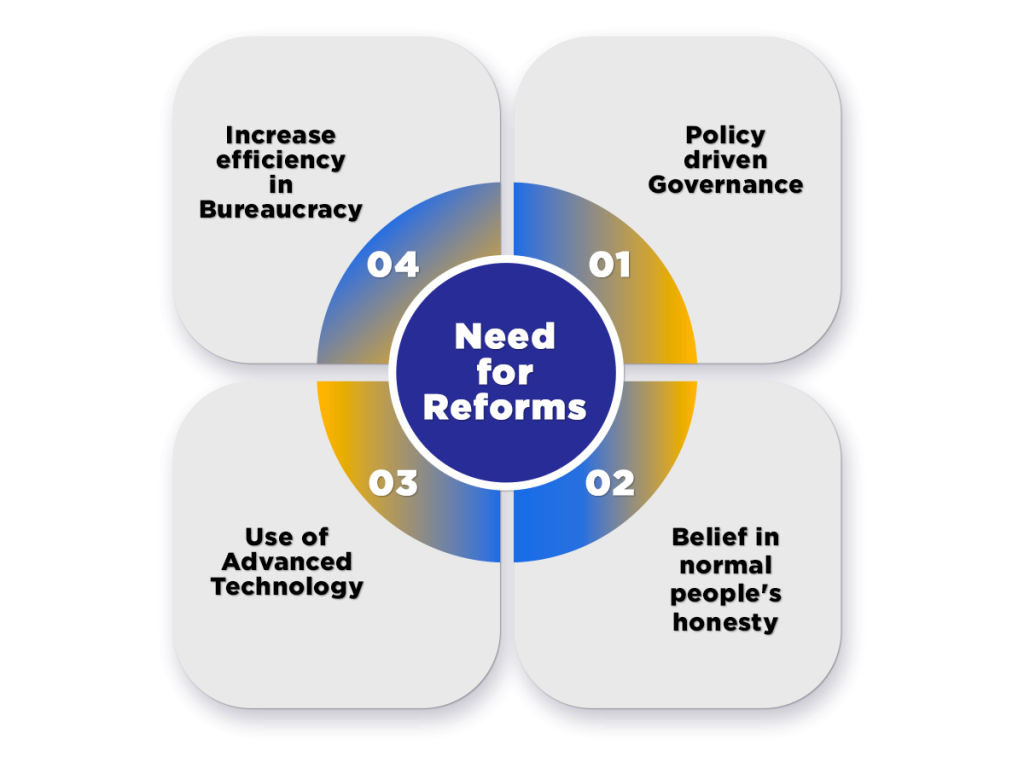
By implementing a new platform for paying taxes, the government aims to make the tax mechanism seamless, painless, and faceless. However, the main reasons for bringing such reforms are as follows:
- Policy-driven Governance;
- Belief in normal people’s honesty;
- Use of Advanced Technology;
- Increase efficiency in Bureaucracy;
Further, our Hon’ble Prime Minister stated that in the last few years, the present government has focused on the following aspects, which has also resulted in the formation of this tech-driven robust tax mechanism:
- Banking the Unbank;
- Securing the Unsecured; and
- Funding the Unfunded;
Concept of Faceless Assessment
The term “Faceless Assessment” denotes a major reform undertaken by the Government that aims to eliminate human interface between the Income Tax Department and Taxpayer.
Under this scheme, the selection of taxpayers is possible only through systems using Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence. That means it eradicates the concept of “Territorial Jurisdiction”.
Further, in this mechanism, a taxpayer will belong to a specific city, but the order for his/her tax assessment, review, and case finalization will take place in another city. That means there is no need for him/her to visit income tax officials, as the case will be allotted on a random basis.
For example, a taxpayer resides in Ghaziabad, but his/her Assessment might take place in Cochin, Review in Ahmedabad, and Case Finalization in Kolkata.
Moreover, any assessment done outside the ambit of Faceless Assessment will be deemed invalid.
Features of Faceless Assessment Mechanism
The key features of the faceless assessment mechanism are as follows:
- Selection of Taxpayer through a system using Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics;
- Eradication of Territorial Jurisdiction;
- Allotment of Cases on Random Basis;
- Central Issuance of Assessment Notice with DIN (Documentation Identification Number);
- No Physical Human Interface;
- No need to Visit Income Tax Officials;
- Team-Based Assessment and Review;
- Draft of assessment order will take place in one city, review in the second city, and lastly, finalization in the third city.
Exceptions of Faceless Assessment
The exceptions to the scheme of Faceless Assessment are as follows:
- Black Money Act and Benami Property;
- International Taxation;
- Cases concerning Tax Evasion, Serious Fraud, and Sensitive and Search Matter;
Concept of Faceless Appeals
The notion behind the concept of Faceless Appeals is similar to Faceless Assessment. The term “Faceless Assessment” denotes that the appeal of a case will be allotted on a random basis to any officer in the country.
The identity of the tax officer deciding the appeal will remain anonymous to the taxpayer.
In this regard, our Hon’ble Prime Minister stated that till now, the authority to decide an appeal was with the IT department of the respective city. However, now the team for deciding appeal will be chosen with the help of technology randomly from any city of the country.
Features of Faceless Appeals Scheme
The features of the Faceless Appeals Scheme are as follows:
- Appeals will be allotted on a random basis to any Tax Officer;
- The Identity of the Tax Officer will not be disclosed;
- No Need to Visit the Tax Officer;
- Appellate Decisions will be Team-based and Reviewed;
Exceptions of Faceless Appeals
The exceptions to the scheme of Faceless Appeals are as follows:
- Black Money Act and Benami Property;
- International Taxation;
- Cases concerning Tax Evasion, Serious Fraud, and Sensitive and Search Matter;
Concept of Tax Payer’s Charter
The term “Tax Payer’s Charter” denotes a two-way document for the tax officer and tax payer. It sets out the rights and benefits given by the government to the taxpayers of India. Further, the terms and conditions of a charter vary from country to country. And after US, Canada, and Australia, India has become the 4th nation to implement it as a law or statute.
Government’s Commitment towards Taxpayers
The government has committed the taxpayers in the following ways:
- To Provide Courteous, Fair, and Reasonable Treatment;
- Treat taxpayers as Honest;
- To Provide Robust Mechanism for Review and Appeal;
- To Provide Accurate and Complete Information;
- To Provide Timely Decisions;
- To Collect the Accurate Amount of Tax;
- To Respect the Privacy of the Taxpayers;
- To Maintain Confidentiality;
- To Hold its Tax Authorities Accountable;
- To Enable Representative of Choice;
- To Provide Robust System to Lodge Complaint;
- To Provide Fair and Just System;
- To Publish Standards for Service and Report Periodically;
- To Reduce Compliance;
Obligations of Taxpayers under Charter
The obligations of Taxpayers mentioned under the Taxpayer’s Charter are as follows:
- To be Honest and Compliant;
- To be Informed and Vigilant;
- To Keep Accurate Records;
- To Know what your Representative or Agent does on your behalf;
- To Respond on Timely Basis;
- To Pay in Time;
Impact of Continuous Tax Reforms in India
The Prime Minister, in his speech, stated that out of all the Income Tax Returns (ITR) filed in the financial year 2012 to 2013, 0.94% underwent Tax Scrutiny. However, the limit came down to almost four times in the year 2018 to 2019, i.e., 0.26%.
Moreover, due to continuous efforts, the count of people filing their ITR (Income Tax Return) has increased to 2.5 crores in the last 6 years. However, the same is microscopic in a country of 130 crore people.
Further, PM mentioned that in the last few years, more than 1500 obsolete laws had been repealed. And earlier, the ranking of India in the “Ease of Doing Business” was 134. However, the same got improved today to 63.
Implementation of Goods and Service Tax (GST) in India has replaced several laws, such as Excise Duty, Value Added Tax, Central Sales Tax, Octroi Duty, Luxury Tax, etc. Now
Other Major Reforms Taken By the Government
Some of the other major tax reforms taken by the Government are as follows:
- Corporate Tax was reduced from 30% to 22%.
- For Manufacturing Units, the Corporate Tax was reduced to 15%;
- DDT (Dividend Distribution of Tax) was abolished;
- The tax scheme “Vishwas se Vivad Tak” aims to effectively reduce the litigation and taxpayer grievance, i.e., effectively settle disputes.
Conclusion
The idea of Compliance is tricky, where there is complexity. That means if a law is clear and simple, then both the citizens and the country are happy. However, the same was not possible in the on-going Direct Tax Regime.
Therefore, In India, there was a need for Fundamental and Structural Reforms to make the tax regime fair and fearless for a taxpayer.
The implementation of Transparent Taxation: Honoring the Honest is a landmark decision in the era of tax administration. It will benefit the taxpayers of India by making the process of paying tax Seamless, Painless, and Faceless.
Also, Read:Online GST Calculator: Easiest Way to Calculate GST Amount