Difference between Public Issue and Private Placement

Dashmeet Kaur | Updated: Apr 18, 2020 | Category: SEBI Advisory
The barter system may have ended a long time back, but in the modern arena, companies have adopted a new method of offering their securities in exchange for cash. Such activities are executed in a primary market that deals with the new issue of securities. In the market, companies raise funding by selling their company’s shares to the investors. The process of selling shares to investors is known as underwriting, while the sale itself is called initial public offer or listing. Companies have these choices to access funds, i.e., a Public Issue and Private Placement.
A shortage of funds is inevitable in the business; hence companies generate sufficient funds from the public and issue of shares. The fund generated from the issue of shares is a boon as the company does not have to pay any interest, unlike the case of loans. Businesses only need to distribute dividends based upon the profits.
There are multiple ways of issuing shares, and as an investor, you should have adequate knowledge about their types. This write-up will highlight the differences between Public Issue and Private Placement for a better understanding of both the offerings.
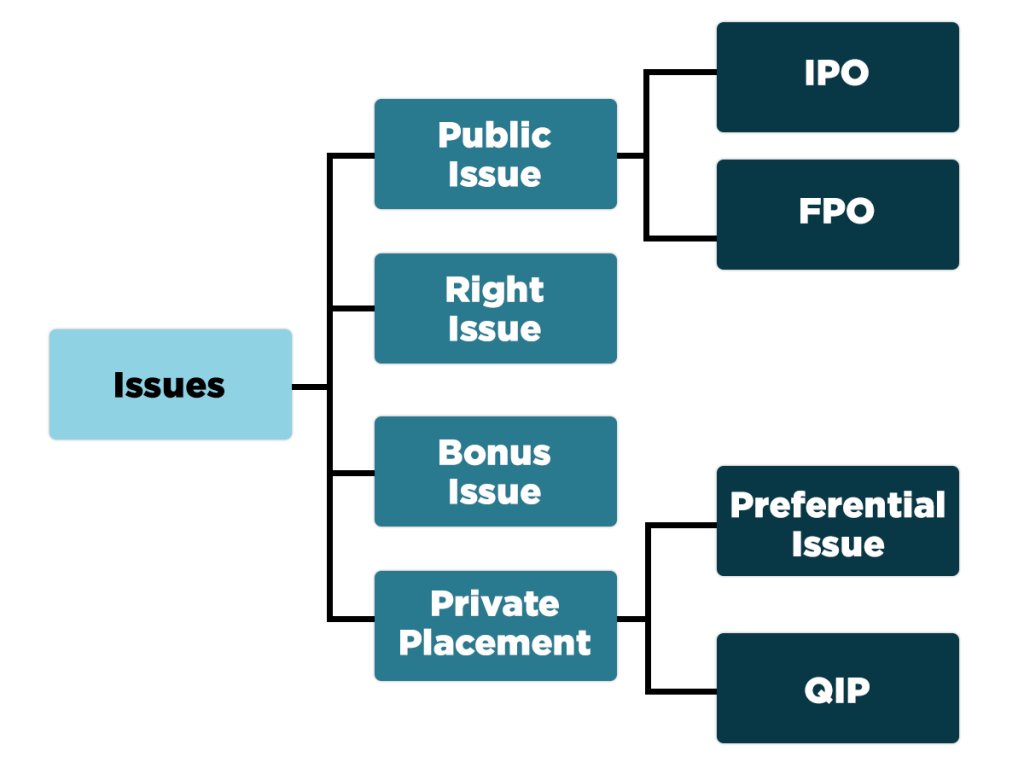
Table of Contents
What does it mean by a Public Issue?
Public Issue or public offering is the method of issuing convertible securities or shares in the primary market by the promoters to drive new investors for subscription. In the public offering, companies issue a prospectus for inviting the general public and offer shares in return of funds. Thereby, the investors who strive to subscribe for the shares file an application to the concerned company, which then allows shares to them. The company that issues its share or securities is named as an Issuer.
It is the most popular form of raising capital from a large group of people. Such type of issue is commenced in a public market instead of being privately funded by the company’s promoters. By issuing shares publically, companies get access to ample capital to start, produce, or sustain their business. It enables the public to own a portion of the company, besides there is no controlling factor involved.
Provision that regulates the Public Issue
Public offerings are regulated under the following statutory provisions:
- Chapter 3, part 1 of the Companies Act, 2013;
- Securities Contract (Regulation) Act, 1956, RBI Regulations, and other regulatory frameworks;
- SEBI Rules and Regulation 2009, along with SEBI Listing Regulation 2015.
Types of Public Offers
The Securities and Exchange Board of India governs the Public Issue of shares and revise its guidelines on regular intervals to safeguard the interest of investors. Let’s look at the various categories of public offers:
- Initial Public Offer: An Initial Public Offer abbreviated as IPO is a process of listing the shares or securities of an unlisted company on the stock exchange. It is a gateway for all the unlisted companies or budding start-ups to lists their shares in a recognized stock exchange and reach out to the public for raising funds. The central objective of an IPO is to expand and enlarge the business activities. Many established organizations make IPO to help owners sell some or all of their ownership to the public. It is a significant source of fund-raising for those companies that just entered into the corporate world. However, Initial Public Offerings are riskier than the Further Public Offering as the companies make offering for the first time.
- Further Public Offer: Also known as Follow-on Public Offer, it is the issuance of a company’s shares, which is already listed on the stock exchange. Such a company has successfully complied with all the procedures & requirements of IPO. Therefore, the investors are familiarized with the company’s performance, which makes it less risky in contrast to the Initial Public Offer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Public Issue
Before drawing any conclusions by comparing Public Issue and Private Placement, it is indispensable to perceive the pros & cons of a Public Issue:
Pros of Public Issue
- Access to an abundance of capital: When a company approaches the public, it can raise a prolific sum of money and satiate its business needs.
- No fixed rate of interest: Unlike debentures, there is no fixed cost bearing interest payment in case of a Public Issue.
- Boost value: When the shares of a company are traded on the stock exchange, it reflects that the company intends to maintain a transparent relationship with the investors and the public. Hence, increase the company’s goodwill.
- Easy Transferability: It enables an easy transfer of ownership as the shares are freely transferable.
- Liquidity: Shares are more liquid in nature as compared to other securities.
Cons of Public Offer
There are some drawbacks of public offerings as well; some of them are as follows:
- Lengthy process: The procedure of the Public Issue of shares is time-consuming and lengthy. Thus, it is prudent to seek professional assistance to ease the procedure.
- Costly-affair: Shares are costlier than the low interest-bearing debentures as they involve dividend payments.
- Complex: There are several prerequisites that a company needs to fulfil before pursuing the Public Issue of share. Further, the company gets subject to a penalty in case of non-compliance.
- External control: Companies that issue their shares to the public always has a sense of additional control of the new investors who may intervene in the affairs of the company.
- No privacy: Since the company’s shares are listed in the stock exchange, it minimizes the level of privacy.
An overview of Private Placement
In Private Placement, the company issues its shares directly to a small selected group of investors. In other terms, this is called as a non-public offering. In Private Placements, the investors generally fall under the category of insurance companies, large banks, pension funds, and mutual funds. There are no stringent guidelines for Private Placement, and companies do not have to be registered with the regulatory body of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
A Private Placement is much cheaper than the Initial Public Offer. On the other hand, this mode of raising funds cannot be used for large issues since a small group of investors shall only have a limited risk appetite. Further, these issues are not traded in the secondary market, in contrast to IPO securities, which once listed get traded, which, makes it difficult for investors to liquidate the securities.
Any entity regardless of being a Private or Public Company can make a Private Placement by issuing a (PPOL) “Private Placement Offer Letter”.
Guidelines to make a Private Placement
Follow these guidelines to issue shares and securities through Private Placement:
- A company can issue an offer to subscribe its securities to the number of persons not more than 50 or such a higher number as prescribed in a Financial Year.
- The qualified institutional buyers & employees of the company that is offering the securities under the scheme of employees’ stock option shall not be counted as investors.
- If any listed or unlisted company makes an offer to allot securities or invites subscription of more than the prescribed no. of persons, then the same shall be deemed to be a public offering.
- It won’t result in any change whether a company wants to list its securities on any recognized stock exchange in or outside India, nor will it make any difference if the company has already received any payment or not.
Advantages of using Private Placement
There is an array of benefits of using Private Placements to raise finance for a business:
- Select your own investors– Private Placement gives liberty to issuers for choosing their group of investors. It elevates the prospectus of having investors that align with your company’s objectives and can provide business assistance along with funding.
- Sustain a Private Status– When a Private Company raises funds through Private Placement instead of going for Public Issue, it helps to sustain its stature.
- Flexible- Through Private Placements, companies can pursue any type and amount of funding. For instance, a company can combine bonds & equity capital.
- Return on Investment- It enables issuers to make a return on investment over an extended period of time as the investors are more patient.
- Faster Turnaround- One can avail faster turnaround on raising funds through Private Placements. Therefore, it one of the most secure forms of raising capital for more risky business ventures.
Disadvantages of Private Placements
Let’s not overlook the disadvantages of using Private Placement to raise business finance:
- Limited access due to reduced market- Private Placements happen in a small group of investors, which confines the access to a big market for the issue of bonds. It may have a long-term effect on the value of your business
- Small number of investors- This type of issue of shares not only reduces the market size but also decreases the number of potential investors.
- Discounted Shares- Another drawback of Private Placement is that the companies need to place their shares or bonds at a substantial discount in order to compensate their investors for taking greater risk and granting longer-term returns.
- Mandatory credit rating- To issue shares or securities via Private Placements, it is mandatory for the companies to provide an insight of their credit rating to the investors. This can be time-consuming and add to the cost of the process.
Head to head Comparison between Public Issue and Private Placement
| Sr.No | Public Issue | Private Placement |
| 1 | Public Issue is a method of selling securities to the public where there are a large number of investors | In Private Placement companies sell securities directly to a few numbers of investors or institutions |
| 2 | Usually large scale companies uses Public Issue to raise funds | Generally small scale companies raises funds through Private Placement |
| 3 | For Public Offering, floatation cost is included since there is a requirement of an underwriter | There is no floatation cost included in the Private Placement as there is no underwriter |
| 4 | In the process of Public Issue, the investment backers act as a mediator between the issuers and investors of long-term funds in the capital market. | In the case of Private Placement, there is no involvement of mediators since all the dealings are done directly amidst the issuers and investors. |
Conclusion
In a nutshell, both Public Issue and Private Placement are efficient methods for raising funds for a company. The former method is usually deployed by large size companies that need plenty of funds for their business venture, while the latter one is more suitable for start-ups and small companies that require a little amount to foster the business.
Public Issue and Private Placement have some advantages and disadvantages; it depends on your venture requirements to choose one amongst them. In case you choose Public Issue then you should consider taking the guidance a reputed legal firm as the process is complicated.
A reliable option for you could be Swarit Advisors. We have a proficient team of Chartered Accountants and Lawyers who can assist you in selecting the type of Public Issue that can be a perfect-fit for your business.