Designations in a Private Company: A Hierarchical Guide
Shivani Jain | Updated: Jul 21, 2020 | Category: Private Limited Company
The success mantra behind any company is its organizational structure. That means every company, whether developed or Start-ups, needs to ensure that they have an accurate managerial structure. Further, the term “Managerial Structure” includes executives, investors, officers, and supervisors. In this Blog, we will talk about the Designations in a Private Company and the roles they play.
Table of Contents
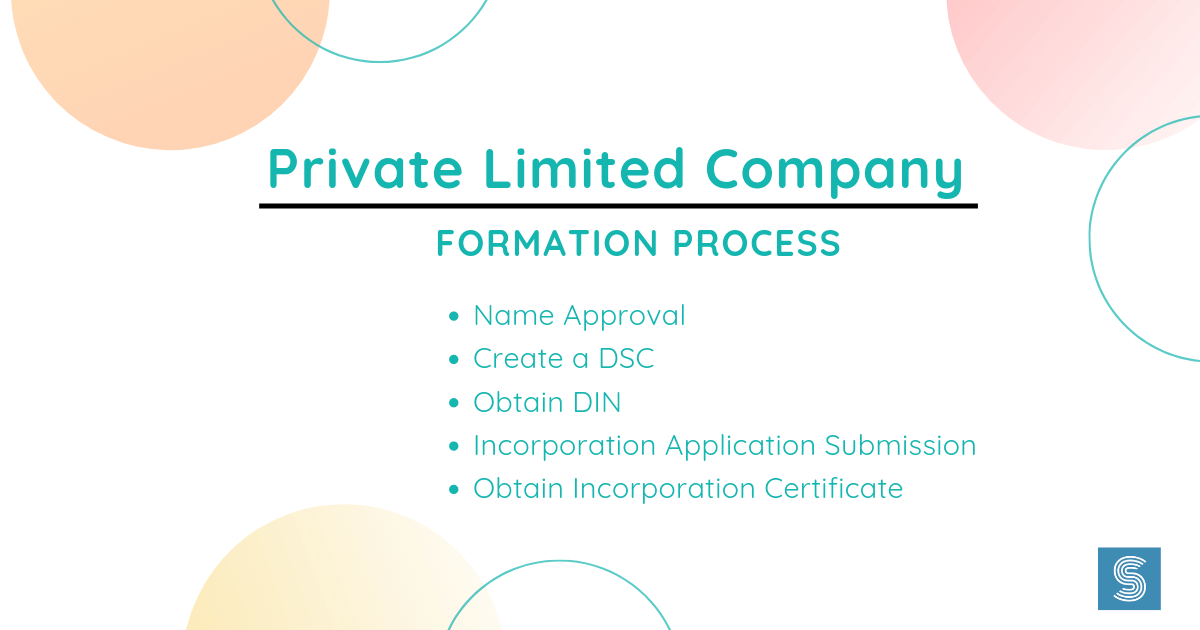
Concept of Designations in a Private Company
The Corporate or Business Titles given to the officials working in an organisation are known as Designations. These titles must relate to the role and duties offered to a concerned official. Therefore, the organisational structure plays a significant role in the performance and sustainability of a private company.

Further, the titles of the executives working in the Top-level Management of a company usually begin with the word “Chief”. The standard three such executives are CEO (Chief Executive Officer), COO (Chief Operating Officers), and CFO (Chief Financial Officer).
The organisational structure is also known as the “Chain of Command” because it sketches out where decision-makers reside. Moreover, the Chain of Command of a large and developed company will be more complex and multifaceted than a small, start-up, or developing company.
Furthermore, the chart which is given below explains the different designations in a Private Company:
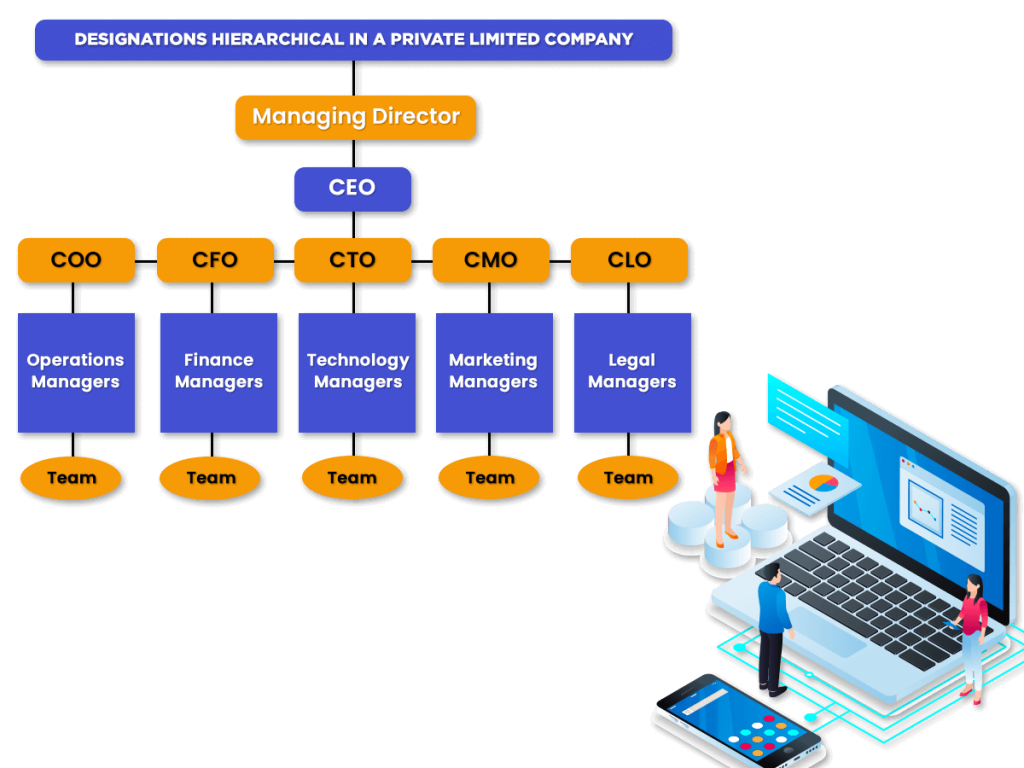
Managing Director (MD)
The definition of a Managing Director is given under section 2(54) of the Companies Act, 2013[1] . As per this definition, a Managing Director means a person who is appointed either by passing a resolution at the Company’s General Meeting or by virtue of the Articles of Association. Further, the Board of Directors of the company can also appoint an MD for the company.
An MD represents the top-level management of a company. He/she is entrusted with substantial power regarding the management and affairs of the company.
Moreover, a Managing Director, together with other directors, can appoint managers and officers. He/she also has the authority to assign duties and roles to these managers and officers.
Role of Officers in a Private Company
The Board of Directors has the authority to appoint Officers of a company. These officers hold several top-level roles and duties within the company.
Further, there is no statutory obligation for the appointment of officers in a private company. However, directors are required compulsorily to be appointed for all company by the shareholders.
Some prominent types of officers in a company are as follows:
- Chief Executive Officer;
- Chief Operating Officer;
- Chief Financial Officer;
- Chief Technology Officer;
- Chief Legal Officer;
- Chief Marketing Officer.
Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
The definition of a Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is given under section 2(18) of the Companies Act, 2013. A CEO is the topmost executive of a corporate entity. He/she is responsible for making the managerial decisions and overall success of a private company. The BOD (Board of Directors) of a company has the power to appoint a CEO.
Further, a CEO is in charge of designing and implementing the policies and strategies for the organisation. He/she also guide the subordinates to complete the objectives of the company.
Moreover, a Chief Executive Officer is a public face for the company and acts as a bridge between the BOD (Board of Directors) and Operational Managers.
Chief Operating Officer (COO)
In the “Chain of Command” or “Designations in a Private Company”, Chief Operating Officer holds the second position. In some corporate entities, COO is also known as “Chief Operations Director” or “Chief Operations Officer”.
A COO acts as the focal point for executing business plans. He/she not only assists the company to work effectively but also ensure its financial strength. In total, COO is both the leader and supervisor of the company, who confirms that employees and organisations are executing the Plans of the CEO.
Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
The definition of a Chief Financial Officer (CFO) is given under section 2(19) of the Companies Act, 2013. In a corporate structure, a CFO is responsible for financial planning, monitoring the cash flow and other financial activities. He/she is similar to a controller or treasurer of a company. He/she also checks the accuracy of the financial statements and reports of the company.
Further, a CFO needs to conduct a SWOT analysis[2] of the company on a regular basis. The term “SWOT” stands for “Strength, Weakness, Opportunities, and Threats”. Furthermore, the standard duties of a CFO include Planning, Bookkeeping, Budgeting, Accounting, Fund Raising, Setting up of Internal Controls, and other Financial/Accounting matters.
Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
In the Designations in a Private Company, the next is the Chief Technology Officer (CTO). A CTO is a senior executive in the technology department of a Company. He/she is responsible for managing and supervising technology maintenance and development aspects.
Further, a Chief Financial Officer needs to oversee the technological process, policies, asset maintenance of the company.
Chief Legal Officer (CLO)
In a Corporate Entity, a CLO or Chief Legal Officer acts as a senior legal executive who helps reduce the company’s legal risks. Further, the main function of a CLO is to advise on regulatory and legal concerns to stakeholders or employees of the company. In short, he/she is responsible for reducing litigation risks.
Also, a Chief Legal Officer handles legal matters of a company and acts as the first person of communication with the statutory authorities. Further, there can be more than one manager functioning under the legal departments headed by CLO.
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
A CMO or Chief Marketing Officer is a marketing executive, who is engaged in tasks like managing marketing campaigns, improving brand image, and increasing revenue. Further, a CMO operates directly with marketing, sales, and development departments to combine marketing strategies and policies in every sub-division of the company.
Also, Read our Atricle: Minimum Paid-Up Capital for Private Limited Company
Role of Managers in a Private Company
All the Managers within a private company must report to the officers, senior managers of the divisions. Further, some examples of the role and responsibilities of managers are as follows:
- Operations Manager: An Operations Manager will work under the COO (Chief Operating Officer). His work is to assist the company in obtaining operational effectiveness and efficiency in operational activities.
- Finance Manager: A Finance Manager is responsible for managing the financial operations of the company. He needs to report to the CFO (Chief Financial Officer) of the company. Further, these managers are responsible for Accounting, Bookkeeping, and other Financial Functions.
- Technology Manager: Like every other manager in the designations in a private company, a Technology manager will work as per the direction of the CTO (Chief Technical Officer). Further, he/she will assist in the technological management and development of the organisations.
- Legal Managers: A legal manager will assist the company in handling legal and regulatory matters. Further, he/she will report the Chief Legal Officer of the company.
- Marketing Managers: The CMO (Chief Marketing Officer) will get assistance from the Marketing Managers of the company. These managers are responsible for heading several functions in the marketing department of the company. They also assist in executing marketing strategies and policies of a company.
Other Managers of a Private Company
Apart from the one mentioned above, there are some other managers in the organizational structure of a company. These managers are responsible for executing and heading the functional and administrative activities of the organisation. The designation and role of these managers are as follows:
- Accounts Manager: The main function of an account manager is to maintain books and accounts of the company.
- Recruitment Manager: His/her main function is to set-up interviews and recruits employees for the company.
- Store Manager: Maintenance of raw material and stocks of the company.
- Regional Manager: This manager is required only when a company operates on a regional basis.
- Administrative Manager: An Administrative Manager is responsible for managing and supervising the administrative functions of the organisation.
- Human Resource Manager: A HR Manager leads the employees and their relations with the company. These managers act as a link between the employees and the management.
- Functional Manager: This manager is needed in case the company is divided into different functions. For example, human resources, sales, finance, etc.
- Departmental Manager: This manager is required in case the company is divided into various departments. For example, B2B (Business to Business) retail, online.
- General Manager: These are those managers in an office or factory to whom functional managers report.
Role of Subordinates in a Private Company
In a corporate structure, the subordinates are managed and supervised by the managers of the company. The term “subordinates” refers to the employees who work with the managers to execute and implement several policies and strategies.
These people are responsible for performing the last stage implementation task to achieve the objective set up by top-level management.
Conclusion
In last, we can say that an in-depth knowledge of the Designations in a private company is a must for leading the company towards sustainable growth.
Further, one can reach out to the official website of Swarit Advisors in case of any confusion and to obtain private limited company registration in India. We have a team of experts who can provide customized business solutions as per your needs.
Read, Also:Companies Fresh Start Scheme 2020 and its Provisions