An Overview of Copyright Registration
Copyright is a vital part of Intellectual Property (IP), and it is an exclusive right given to authors or creators of artistic works, musical works, producers of cinematography films, sound recordings, etc. Copyright Registration is done as per the Copyright Act, 1957 and with the Registration, you become a legal owner/proprietor of your creative work in respect of music, books, website, paintings, mobile applications, etc. Copyright Registration that the original work of an author cannot be copied or misused. No individual is allowed to use a similar work or creation without the permission of the actual creator or author. The author has the right to fine others for using their work or changing it without the consent of the original author. Copyright Registration protects the creator's rights from Copyright Infringement. It gives official protection by which no other unauthorised person can misuse the work in any way without procuring the owner's permission.
In India, the Copyright Registration gives its owner exclusive individual rights to copy, distribute, reproduce the work or give authorisation to another entity for the same. It provides a bunch of rights; communication to the public, rights of production, reproduction, and translation of work. However, procedures, ideas, methods of operation or mathematical concepts cannot be copyrighted.
Rights of Copyright Owner
The Indian Copyright Act, 1957 protects the legal, social, and economic interests of the Copyright Owner. The Act communicates the exclusive rights of the owner in the following regards:
- Right of Adaptation;
- Right of Paternity & Integrity;
- Right of Reproduction;
- Right of Public Performance;
- Right of Distribution;
- Right of Communication to the Public.
Importance of Copyright Registration
Following is the importance of Copyright Registration:
- Legal Protection
A Registered Copyright acts as prima facie evidence in the eyes of the law. Also, it provides the owner with the right to sue in order to protect his/her work or creation from infringement or duplication.
- Branding or Goodwill
A Registered Copyright is used for creating and building a sense of goodwill regarding the quality in the minds of the customers.
- Protection after Creators' Death
A duly registered copyright protects the right of a creator after his/ her death as well. That means the validity of Copyright is higher than any other intellectual property right. Moreover, registered Copyright remains valid for a period of 60 years after the death of the creator.
- Prima Facie Evidence
Registered copyright acts as prima facie evidence in the eyes of the law and proves beneficial for the creators as well.
- Publicity of Owner
The process of Registration makes a work searchable across the world in the Copyright Registry Database.
- Restricts Unauthorised Reproduction
A duly registered copyright provides an exclusive right to the owner and prevents the illegal reproduction of his/her work.
- Creation of Asset
Registered Copyright denotes one of the pillars of IPR (Intellectual Property Rights), just like Patents & Trademark. Moreover, the same can easily beTraded, Franchised and commercially engaged.
- Establishes Market Creditability
Registered Copyright will establish & increase the market credibility of particular content/work and will safeguard the work from being copied by any other individual as well.
- Global Protection
Copyright registered in India will enjoy the same protection, privileges & benefits in foreign countries as well.
Benefits of Copyright Registration
The benefits of Copyright Registration are as follows:
- Creates Public Record
The process of Copyright Registration assists in creating a Public Record. The term "Public Record" denotes that the owner's work is duly protected, and no one can use it without obtaining prior approval or license from the actual owner.
- Acts a Legal Evidence for Ownership
Registered copyright acts as legal evidence for the author or creator. It prevents the work from duplication and can be used as proof of ownership in front of the court.
- Protects Work from Infringement
A duly registered copyright enables the owner to file a suit for infringement and take legal action against the infringer.For example, a person is selling copies of a work without the prior permission of the owner.
- Permits Author to Change the Form of Work
After obtaining Copyright Registration, only the author or creator has the right to change the form of work. For example: registered Copyright enables the owner to revise, update, or make a sequel of the work.
- Allows Transfer of Rights
A duly registered copyright enables the owner to sell/ pass/ or transfer the right of his/ her work to another person.
Different Types of Works Eligible for Copyright Registration in India
In India, the work eligible for copyright registration must fall in either of the areas as follows:
- Musical Works.
- Cinematography Films.
- Literary Works, such as Manuscripts and Books.
- Fashion designs.
- Performances.
- Artistic works, such as Paintings.
- Website.
- Broadcast on Radio and Television.
- Published Editions.
- Computer Software and other computer programs and compilations, etc.
However, it shall be pertinent to mention that Copyright does not protect names, titles, ideas, concepts, methods, slogans, and short phrases.
Documents Required for Copyright Registration
The documents required for Copyright Registration are as follows:
- Basic Documents
- Address Proof and Identity Proof of the applicant along with the nationality;
- Disclosure of the interest of the applicant in the Copyright; whether the applicant is the author of the work or the legal representative of the author;
- Submit two copies of the original work;
- In case of a company or business, submit an incorporation certificate;
- Details of the work’s nature;
- Work Language;
- Title, class, and description of the work;
- Publication date; publication in magazines or in a research paper (Internal) submitted to a professor doesn’t count as publication;
- Artistic Work
- Submit 2 copies of the work.
- Demand Draft of Rs (as applicable) per work.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the author if in case the applicant is different from the actual author.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the publisher if work is published and the publisher is different from the applicant.
- Search Certificate from the Trade Mark Office, if in case the work is being used on goods or is capable of being used on the goods.
- NOC from the person whose photograph appears on the work.
- If in case the application for Registration is being filed by a copyright expert, then there is a need for a specific Power of Attorney that will be signed by the applicant and accepted by the attorney.
- Cinematograph Film
- Submit 2 Copies of the Work.
- Demand Draft of Rs (as applicable) per work.
- A copy of the Deed of Assignment or NOC from various copyright holders.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the publisher if work is published and the publisher is different from the applicant.
- If in case the application for Registration is being filed by a copyright expert, then there is a need for a specific Power of Attorney that will be signed by the applicant and accepted by the attorney.
- Music
- Submit 2 Copies of Work.
- Demand Draft of Rs (as applicable) per work.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the publisher, if work is published and the publisher is different from the applicant.
- If in case the application for Registration is being filed by a copyright expert, then there is a need for a specific Power of Attorney that will be signed by the applicant and accepted by the attorney.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the author if in case the applicant is different from the actual author.
- Literary and Dramatic Work
- Submit 2 Copies of Work.
- Demand Draft of Rs (as applicable) per work.
- If in case the application for Registration is being filed by a copyright expert, then there is a need for a specific Power of Attorney that will be signed by the applicant and accepted by the attorney.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the author if in case the applicant is different from the actual author.
- Sound Recording
- Submit 2 Copies of the Work.
- Demand Draft of Rs (as applicable) per work.
- A copy of the Deed of Assignment or NOC from various copyright holders.
- If in case the application for Registration is being filed by a copyright expert, then there is a need for a specific Power of Attorney that will be signed by the applicant and accepted by the attorney.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the author if in case the applicant is different from the actual author.
- Software
- Submit 2 Copies of the Work.
- Demand Draft or IPR of Rs (as applicable) as per the work.
- Author’s NOC if the author is dissimilar from the applicant.
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the publisher if the work is published and the publisher is different from the applicant.
- When filling the application via an attorney, an original copy of a Power of Attorney is signed by the applicant and also accepted by the attorney.
- The source code and the object code of the work for due certification.
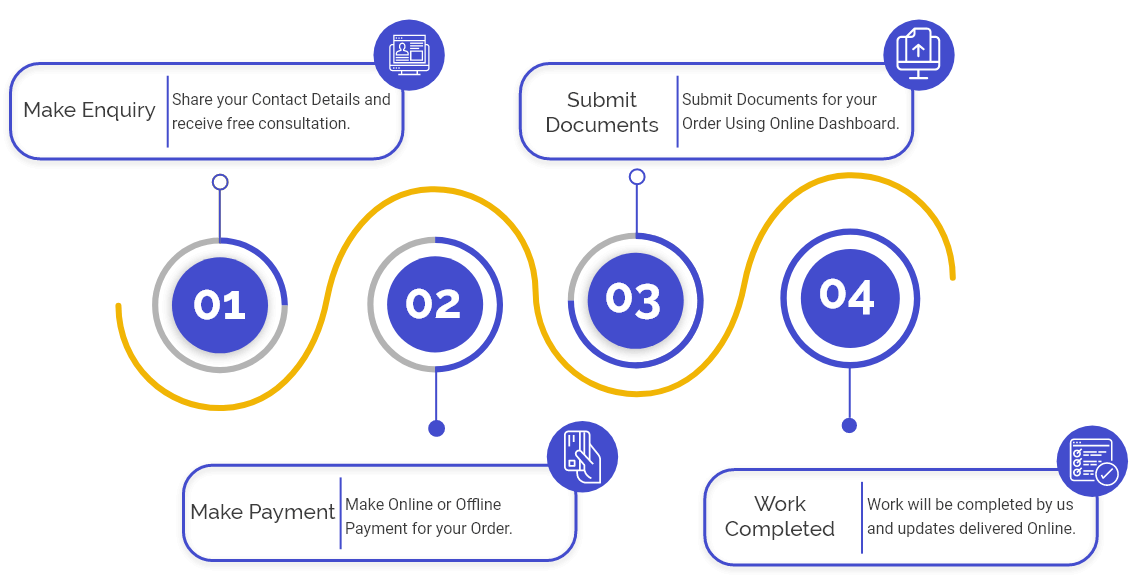
Procedure for Copyright Registration in India
In India, the steps involved in the process for Copyright Registration are as follows:
Step 1: Create the Applicant’s User ID and Password: First, the applicant needs to create the user ID and password for login before applying for the Copyright Registration. For this, the applicant is required to opt for "New User Registration".
Step 2: Filling the Application: An applicant can file the application form for the Registration either manually in the office or via an e-filing facility available on the official website.For the Registration, an application should be filed with the Registrar along with the details of the work. After login, the applicant needs to click on the button "Click for Online Copyright Registration" and fill out the online Registration Form"with all the vital documents. The Registrar will issue a Diary Number to the applicant after filing the Copyright application form.
Step 3: Examination of Copyright Application: After filing the application, the next stage is to examine the application. Once the Diary Number is issued to the applicant, at least thirty days of waiting time are provided where the Copyright examiner can examine the application. Once the examination process is done, the Registration Process gets categorised into two different segments:
- In Case the Objections are Raised
If anyone raises the objection against the applicant, then the letter regarding the objection is sent to both the parties and they are called for a hearing by the Registrar. In case the objection is declined upon hearing, then the applicant can ask for the examination and the inconsistency procedure is followed.
- In Case of No Objections
If any objections are not raised by any party, then the examiner approves to examine and check the application to find any problem. If no discrepancy arises and all the vital documents are delivered with the application, the applicant is permitted to proceed to the next stage or step. But, in case of discrepancies are found, a discrepancy letter is sent to the applicant. The applicant will have to respond to the same and based on the response; a hearing is conducted by the Registrar. Once the difference is resolved, the applicant is permitted to move forward to the next step. In case the difference is not resolved, the application is declined, and a letter is sent to the applicant.
Step 4: Issuance of Registration Certificate: This is the final step of Copyright Registration. The Registrar may ask for extra information and documents. If the Registrar is fully satisfied with the Copyright application made by the applicant, he or she will enter the application details into the Copyright Register and issue a registration certificate.
What is the Validity of Copyright Registration?
- In Case of Published Works: The validity of the copyright works is up to the life of an artist or creator, i.e., 70+ years.
- In the case of Unpublished Works: The Copyright is valid until the work is 1st published to a life span of the artist or creator i.e., 70+ years.
Penalties for Copyright Infringement
- In the case of Copyright Infringement, the minimum punishment is imprisonment for 6 months with a minimum fine of Rs. 50,000/-;
- In case of a second & subsequent conviction, the minimum punishment is imprisonment for 1 year and a fine of Rs. 1 lakh.
The process to Check the Status of Copyright Registration
The steps involved in the process of checking the status of Copyright Registration are as follows:
Step 1: First, the applicant has to visit the official website.
Step 2: Once you enter the website, then a home page the website will appear on your computer screen. On the left side, you will see the Online Services section, where you will see the "Status of Application" button.
Step 3: After clicking the button, you have to enter your “Diary Number” and then click on the “View Status” button.
Step 4: After clicking the "View Status" button, then only you will be able to check the status of a Trademark Application.
Different Status of Copyright Registration
The different status of Copyright Registration is as follows:
- Waiting: The term “Waiting” denotes that the Application for Copyright Registration is under a Mandatory Waiting Period.
- Formality Check Failed: The term "Formality Check Failed" denotes that the Documents are not received after Payment.
- Abandoned: The term “Abandoned” means that the documents are not received after the Filing of the Application.
- Scrutiny: The term "Scrutiny" denotes that the application for Copyright Registration is under process.
- Re-Scrutiny: The term "Re-Scrutiny" denotes that the application for Copyright Registration is again under process.
- Hearing: The term “Hearing” denotes the hearing on the objection.
FAQs on Copyright Registration
The term “Copyright” denotes the “right” given by law to the creators. The term “right” includes the right of reproduction, communication to public, adaption, and translation of work.
The Copyright Act, 1957, is the governing law for Copyright Registration in India.
One needs to mention the following, letter "c" in circle ©, or the abbreviation "Copr.", or word "Copyright”; the name of the owner; and year of the first publication.
A Copyright remains valid for the lifetime of creator plus 60 years from his/her death.
No, copyright does not normally apply to the Title and Name.
The term “Copyright Society” denotes a collective administration of societies formed under section 33 of the Copyright Act, 1957.
The term “Copyright Protection” denotes protection to Musical, Dramatic, Literary, and Artistic works from unauthorized use. However, it does not protect Ideas.
No, Mathematical Concepts are not covered under the Copyright Act 1957.
Yes, anyone can submit the application of copyright registration on his/her own.
No, an applicant cannot apply for copyright as a whole; he/she needs to file a separate application for each component.
For Copyright Registration in India, one can choose Swarit Advisors in order to file a proper and correct application for copyright registration. We have a team of IPR experts who will assist in getting registration in a smooth manner.
One can search for copyrights by visiting the official website or copyright office.
One can check by conducting an online search.
One can search by visiting the official website or copyright office.
No, any work without creativity, originality, and uniqueness is not eligible for copyright registration.
Copyright remains valid for the life of the author or creator plus 60 years after the death of the author.
Anything that is in an intangible form, such as ideas, slogans, names, titles, phrases, etc. are not eligible to obtain copyright registration.
The main difference between the two is that copyright gives protection to unique content, whereas, trademark gives protection to the logo, slogan, brand name, colour combination, etc.
No, it is mandatory for the creator to obtain copyright registration, if he/she wants to protect the content from imitation.
Yes, one can use a copyright symbol without obtaining registration, and the symbol has nothing to do with registration.
Usually, a period of 2 to 3 months is needed to obtain Copyright Registration in India.
The symbol of copyright is denoted by the symbol “©”, or by the word “Copyright”.
Initially, a copyright society is granted registration for a period of 5 years.
The term “Work” denotes a wide range of intellectual conceptions from computer applications, novels, to architecture.
No, there is no international registry of copyrighted works.
The term “neighboring” or “related” rights denote a set of copyright type reasons given to the person assisting in making a work available to the public. These mainly include Producers of Phonograms, Performers, and Broadcasting organization.
Yes, any individual who is an original author, rights owner, legal heir, and assignee is eligible to file an application for copyright Registration of work in India.
Yes, a Computer Software or Computer Programme is eligible to be registered as “Literary Work” under the Copyright Act.
The registration fee for Copyright Registration of Literary, Musical, Artistic, and Dramatic work is Rs 500. In contrast, the registration fee for Cinematograph Film and Sound Recording is Rs 5000/- and Rs 2000/- respectively.
All types of Dramatic, Literary, Musical, and Artistic Work, such as Movies, Poetry, Novels, Songs, Computer Software, and Architecture, are eligible for Copyright Registration in India.