An Overview of Payment Gateway License
An organisation that offers payment gateway services in accordance with all relevant laws is granted a licence by the competent authorities. It is a necessity for businesses that want to take electronic payments through different payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and net banking. A difficult application process that involves adhering to numerous legislative standards is necessary to obtain a payment gateway licence. Swarit Advisors provides thorough assistance to people and companies looking to licence a payment gateway.
The application process is handled efficiently, quickly, and by all legal standards by our team of legal experts. We strive to make the procedure as simple as possible for our clients because we are aware of the importance of a payment gateway licence for businesses. Businesses may quickly and easily acquire a payment gateway licence with our end-to-end support, allowing them to accept electronic payments and expand their online business.
Payment Gateway
An online payment gateway serves as an intermediary to move money from one bank account to another. A payment gateway is a piece of software that enables users to make payments online using a variety of methods. Net banking, Credit cards, debit cards, UPI, and other current online wallets are a few of the payment methods. In simple, a payment gateway acts as a link to safely move your funds from your bank account to the merchant’s payment portal.
Eligibility Criteria for Payment Gateway License
The following requirements must be met by businesses in order to qualify for a payment gateway licence:
- According to the Companies Act of 2013 or any other relevant law, the company must be registered.
- The business needs a dedicated office with the proper equipment for payment gateway services.
- The business must have a strong technology foundation to provide safe and secure payment processing.
- The business must abide by all policies and guidelines announced by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and other pertinent authorities.
- The company's pricing strategy for its services must be clear and transparent.
- The organisation needs to have sufficient safeguards in place to stop money laundering and other financial crimes.
- To identify and reduce potential risks related to payment processing, the organisation needs a solid risk management strategy.
- For resolving client grievances and disputes pertaining to payment processing, the business must have well-defined dispute resolution policies.
- A payment gateway licence must be obtained by meeting certain eligibility conditions, and Swarit Advisors can assist businesses in navigating the challenging application procedure and fulfilling all requirements.
Essential Elements of a Payment Gateway License
Merchant Agreement - The agreement known as the “Merchant Agreement” is made between businesses and payment service providers. The obligations and guidelines that have been outlined in the agreement with regard to payment, authorisation, settlement, and processing serve as a guide for the parties participating in online transactions.
Secure Electronic Transactions (SET) - The main electronic transaction providers, including Visa and Master Card, provide secure electronic transactions. Because SET enables merchants to validate payment information without actually seeing it. As a result, clients are safeguarded. For the purpose of verification, the issuer obtains the information directly from the cardholder.
Benefits of a Licence for a Payment Gateway
Businesses that want to take electronic payments can profit from getting a payment gateway licence in a number of ways. These advantages consist of:
Enhanced Credibility: A licence for a payment gateway demonstrates to clients that a business is reputable, dependable, and trustworthy. Customer confidence may rise. As a result, it leads to more sales and income.
Expanded Customer Base: By providing electronic payment options, businesses can attract clients from all over the world and increase their customer base. Potential sales and earnings may rise as a result.
Streamlined Payment Processing: A payment gateway licence enables companies to quickly, safely, and effectively accept electronic payments. By doing away with manual payment processing, processing times and mistake rates are decreased.
Improved Cash Flow: Since electronic payments are frequently handled rapidly, firms can access their funds more quickly, which improves cash flow and financial management.
Regulation Compliance: Having a licence for a payment gateway makes sure that companies follow all rules and laws that are relevant, which lowers their chance of facing penalties and other consequences.
Reduced Fraud and Chargebacks: A payment gateway licence often comes with fraud prevention features that can lower the risk of unauthorised transactions and chargebacks, preventing financial losses for businesses.
Documentation Needed for Payment Gateway Licence
The following documents must be submitted by firms in order to receive a payment gateway licence:
- Company Registration:In accordance with the Companies Act of 2013 or any other applicable law, the company must be registered.
- Articles of Association and Memorandum: It is necessary to submit the company's Memorandum and Articles of Association (MOA and AOA).
- Certificate of Incorporation: A copy of the company's certificate of incorporation must be submitted.
- Bank Records: Bank statements from the previous six months must be submitted to show the company's financial stability.
- Infrastructure Information:Information on the office space, such as ownership or lease documents, must be submitted. This information must also include information about the infrastructure required to offer payment gateway services.
- Details of the technology infrastructure:It must be disclosed, including information on the hardware and software utilised for payment processing.
- Pricing Policy: For services involving payment processing, a clear and transparent pricing policy must be offered.
- Framework for Risk Management: To recognise and reduce potential risks related to payment processing, a clear framework for risk management must be offered.
- Process for Resolving Disputes: It is necessary to offer a simple and efficient procedure for resolving client complaints and disputes involving the processing of payments.
- Anti-Money Laundering Measures:Sufficient safeguards must be in place to stop money laundering and other financial crimes.
Capital Requirements for Obtaining a Payment Gateway License in India
The following criteria must be met in order to receive a payment gateway licence in India:
Prepaid payment instruments can only be disseminated by banks and non-bank finance companies that meet the Reserve Bank of India's periodic capital adequacy standards.
Instruments for Prepaid Foreign Exchange: These regulations do not apply to organisations that are permitted by FEMA to provide foreign exchange prepaid payment instruments. The use of such payment instruments must adhere to the Foreign Exchange Management (Current Account Transactions) Rules, 2000, as modified, and be restricted to transactions that are permitted for current accounts.
Types of Payment Gateway Providers After Receiving Payment Gateway License
After obtaining a payment gateway licence, there are various types of payment gateway providers. Two types of payment gateway companies enable businesses to accept payments in Indian National Rupees from domestic and foreign clients using credit or debit cards as well as net banking. The types of payment gateways are:
Second-Party Providers: For start-ups and small organisations, this is an expensive alternative, and such providers will be pricey in the beginning. Although the set-up costs are significant, the transaction discount rate is lower for the specified providers.
Third-Party Providers: Examples of this kind of service provider are CC Avenue, EBS, and PayU, which impose setup and annual fees. For this kind of service, the TDR ranges between 2% and 4%.
How can a Payment Gateway Business be registered?
It is necessary to first register the payment gateway business before applying for a payment gateway registration in India. Many entities can be created in India, but the best way is to create a private limited company in order to obtain a license for a payment gateway. Therefore, in order to create a private limited company, you must meet the following requirements:
- Two shareholders and two directors are required.
- Directors & shareholders can be the same person.
- PAN card of the director.
- Address proof of the company.
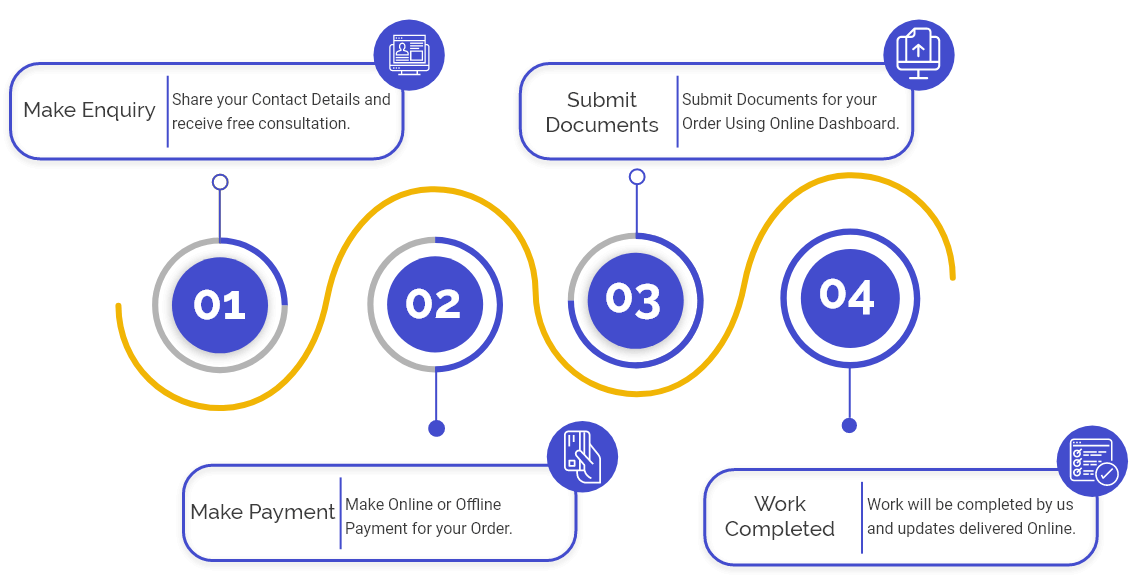
Process of obtaining the Payment Gateway License in India
India has developed the following steps for the payment gateway registration process in order to make it simple to obtain a payment gateway licence:
Step 1 is application Filing: Obtain a licence for a payment gateway. Submit the FORM A payment gateway application to the Chief Manager of the PSS Department.
Step 2 is the payment of the registration fee: Don't forget to include the application fee with the payment gateway registration fee.
Step 3 is the evaluation of the application: RBI will begin its evaluation as soon as you submit an application for a Payment Gateway licence. It will verify the information you provided in your applications.
Step 4 is examining the application: Once RBI determines that you have submitted a valid application, they begin reviewing it based on the following points:
- What technical guidelines were followed in creating the suggested payment system?
- What security measures have you put in place for your payment system's electronic transactions?
- What type of transfer technique does your payment system employ?
- How are the payment instructions given to the user, and how does it change their payment obligations?
- How well-off is the applicant financially?
- What rules and regulations will apply to the interactions between clients and payment providers?
- What financial and credit policies have you put in place?
- How soon after receiving approval can the application begin operating its payment gateway?
Step 5 is the issuance of a certificate: The RBI will issue you the payment gateway certification for operating a payment gateway firm in FORM B once it has approved your application. If there are no problems with the application form, it will take the RBI 6 months to grant the payment gateway certificate after the application is submitted.
Who has the power to grant a Payment Gateway License in India?
According to section 4 of the PSS Act, no one other than the RBI is permitted to start or operate a payment system before the RBI has given its consent. Under section 5 of the PSS Act, a request for authorisation must be made to the RBI.
Validity and Renewal of Payment Gateway License
A payment gateway licence typically has a one-year validity, after which it must be renewed. For the duration of the license's validity, businesses are required to make sure they abide by all applicable laws, rules, and regulations. Otherwise, they risk fines or other legal repercussions. To secure the continuous functioning of the business, Swarit Advisors may help with the payment gateway licence renewal and make sure that all relevant compliance criteria are met.
How Swarit Advisors Help you in getting the Payment Gateway License?
Swarit Advisors offers complete assistance in getting a payment gateway licence for businesses that offer payment gateway services. Our legal staff makes sure that your application is completed quickly and in accordance with all applicable laws. The services included in getting a payment gateway license are:
- With our end-to-end support, businesses may quickly and easily acquire a payment gateway license, allowing them to accept electronic payments and expand their online business.
- Among the services, we provide application drafting and review, application submission, inspection and verification of the payment gateway infrastructure, and legal advice for the entire licence period.
- We strive to make the procedure as simple as possible for our clients because we are aware of the importance of a payment gateway licence for businesses.
- Our goal is to use our knowledge of payment gateway licensing to streamline the procedure and offer hassle-free services to our clients.
- Also, we help you with the payment gateway licence renewal and make sure that all relevant compliance criteria are met.
- Contact us right away to arrange a meeting with one of our legal experts and guarantee efficient and legal business operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
A payment gateway licence is required for any company that offers payment processing services.
The company must have the required technology and infrastructure to provide payment processing services, and it must be registered under the Companies Act of 2013 or any other applicable law.
Documents for company registration, information about the infrastructure and technology, bank statements, a pricing strategy, a framework for risk management, a procedure for resolving disputes, and anti-money laundering measures are all necessary.
A payment gateway licence typically has a one-year validity, after which it should be renewed.
The procedure entails submitting an application to the regulatory body, document verification and inspection, infrastructure inspection will be done, and issue of the licence after all steps are successfully completed.
Swarit Advisors can help with every stage of the procedure, from renewal application, to guaranteeing a simple and hassle-free experience.
The regulatory body, the thoroughness of the application, and the supporting documentation all come to play in processing time.
A licence for a payment gateway allows businesses to legally offer payment processing services to clients, gives them confidence and assurance, and reduces fraud.
To prevent any disruption in the payment processing services, the company must renew the payment gateway licence before it expires.
An RBI-granted authorisation known as a Payment Gateway License enables the applicant to set up and manage a payment gateway. Simply said, a payment gateway is a gate that allows for the completion of electronic transactions. It creates a safe channel between the buyer and the vendor.
An online payment gateway serves as an intermediary to move money from one bank account to another. A payment gateway is a piece of software that enables users to make payments online using a variety of methods.