An Overview of Payment Bank License
Demonetization has entirely recast the Indian economic system. Nowadays, people rely more on paperless transactions and prefer using digital payment portals. It has given a sudden boost to E-wallets or Mobile wallets that were outcast earlier. The primary niche of such online gateways is payment banks. To start any payment gateway in India, one needs to acquire a Payment Bank License in India.
What is the Meaning of Payment Bank?
Payments bank refers to a new bank model that got conceptualised by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 2014. Such banks can accept a restricted deposit of up to a maximum limit of ₹100,000 per customer, which shall increase further. Though payment banks are a new addition to the banking sector, it does not avail of the issuance of loans and credit card facilities. While payment banks render an array of other services like debit cards, ATM cards, mobile banking, net banking, etc. Moreover, by procuring Payment Bank License, a bank can operate both current and saving accounts.
As per the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, a payment bank or differentiated bank has the permit to establish new outlets, such as Automated Teller Machines (ATMs), and Business Correspondents (BCs), but cannot commence the activities of banks. Also, the minimum paid-up capital of the payment bank should be 100 crores or more.
The legal provisions regulating the payment banks in India are as follows:
- Companies Act, 2013;
- Banking Regulation Act, 1949;
- Reserve Bank of India, 1934;
- Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999;
- Payment and Settlement System Act, 2007;
- Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961.
Primary Objective of the Payment Banks in India
The central objective of the payments bank is to enlarge the Payment and financial services to all low-income households, small businesses, and migrant labour workforce in a secured, technology-driven environment. The Reserve Bank of India seeks to penetrate the financial support to all the remote areas of India by underpinning payment banks. It aims to redefine the Indian economy with a secure payment gateway for all transactions.
Key features of a Payments Bank
Payments banks are generally variant from the traditional banks. Before you apply for a payment bank license, it's essential to perceive its fundamental characteristics:
- Offers Deposits up to 1 lakh
Payments banks can only accept deposits up to a limit of 1 lakh. The customers have to abide by the prescribed limit, and nobody can exceed that limit at any point in time. One can choose to deposit an amount either fully or partially. RBI has set that limit to protect customer interest and in regards to the relatively new nature of such banks.
- Virtual Debit Card Facility
Another peculiar aspect of the payments bank is that it offers both physical and virtual debit cards. The debit cards give an edge to the users to utilise all ATMs in the domestic boundaries as well as in abroad. The virtual debit cards do not demand any extra charges on cash withdrawal. Also, the physical debit cards are accompanied by an annual fee only.
- Smooth Transactions via an Online Portal
Unlike the traditional banks, payment banks streamline the process of making and receiving money through digital platforms. It facilitates online fund transfer services like NIFT, IMPS and many others to the customers.
- Feasible mode of Making Payment
Regardless of where you live, you can easily access the services of payment banks as it runs digitally. Payments Banks eliminates the need to visit a physical bank for depositing or withdrawing cash. Anybody can start with payments bank business online without having a physical outlet by merely attaining a payment bank license.
Who is Eligible to Acquire a Payment Bank License?
Have a look at the list of applicants who fits well in the eligibility criteria of acquiring Payment Bank license:
- Individuals/professionals
- Mobile telephone companies
- Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFCs)
- Real sector cooperatives
- Supermarket chains
- Public sector entities
- A promoter or group of promoters who have a joint venture with an existing scheduled commercial bank
- Existing non-bank prepaid payment instrument under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- Corporate Business Correspondence
- Public companies
Capital Requirements to Obtain a Payment Bank License in India
In India, the Capital Requirements to obtain a Payment Bank License are:
- A Payment Bank must have a minimum of Rs 100 crore as Paid-up Equity Capital;
- The Payment Bank in India shall be required to invest at least 75% of its demand deposit balances in securities issued by the Government or Treasury Bill having maturity up to 1 year that is recognised by the Reserve Bank of India as eligible securities for maintenance of SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio);
- Maintain at least 25% in current & time deposits with other scheduled commercial banks for its operations & also for the management of liquidity;
- The FDI Policy for private banks shall be the guiding policy for foreign shareholding;
- A Capital Adequacy Ratio of minimum of 15% of its risk-weighted assets & a leverage ratio of not less than 3% shall be maintained;
- As the payment bank may face operational/liquidity risk, they must be required to follow the guidelines prescribed by the RBI concerning liquidity risk management.
What are the Details That Should be Provided to RBI?
In India, the details to be provided to the RBI for obtaining Payment Bank License can be summarised as:
Details of the Individual Partner
- Name of the Promoter;
- Date of Birth;
- Residential Status;
- Parent’s Name;
- PAN (Permanent Account Number) No;
- Branch and the Bank Account Details, together with the Credit Facilities;
- Experience of the Individual Promoter;
- Areas of Expertise;
- Track Record of the Business and Financial Worth.
Details the Entity Promoting the Bank:
- Shareholder Pattern of the promoter entity;
- Memorandum of Association (MOA) and Articles of Association (AOA) of the promoter entity;
- Financial statements for the last five years of the promoter entity;
- Income Tax Returns (ITRs) for the previous three financial years.
Details of the Individuals and Entities in the Promoter Group:
- Names of the Individuals and Entities in the Promoter Group;
- Details of the Shareholding Pattern;
- Details of the Management;
- Pictorial Organogram;
- Total Assets of the Entities;
- Annual Report for the last five years of all the group entities;
- Details of Listing Shares in the Recognised Stock Exchanges;
- PAN(Permanent Account Number);
- TAN (Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number);
- CIN (Company Identification Number);
- Bank Account and Branch Details.
Business Plan Requirements of a Payment Bank in India
The business plan requirements of a payment bank in India include:
- The applicants for a Payment Bank licences need to furnish their project reports and business plans along with their applications;
- The business plan must address how the bank proposes to accomplish the objectives and purposes of setting up Payment Banks;
- The business plan submitted by the applicant must be accurate and practical. Further, first preference will be given to those applicants who offer to set up their Payment Banks with access points mainly in the underdeveloped states or districts in the Central, East and North-East regions of the country;
- A Payment Bank must ensure a widespread network of access points predominantly to remote areas, either through BCs (Business Correspondents), or their own branch network or by way of networks provided by others;
- A Payment Bank is expected to adopt technological solutions to extend its network and lower costs;
If a Payment Bank deviates from the stated business plan after the issuance of the licence, the Apex Bank may consider limiting the bank from expansion, effecting change in the management and can also impose other penal measures as it may deem fit.
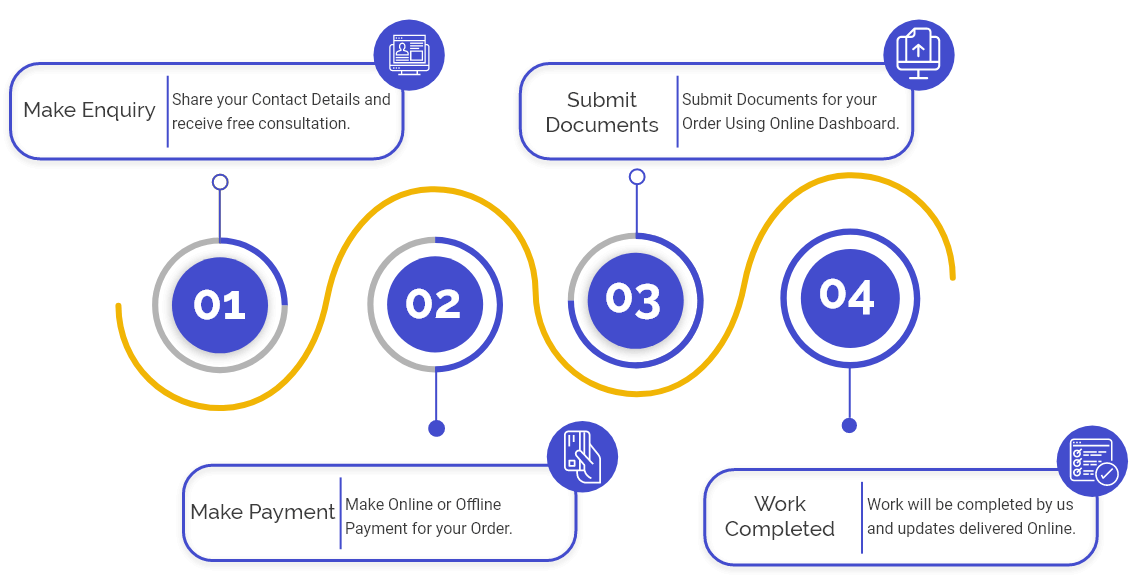
Procedure for Payment Bank License
Now that you have perceived a comprehensive knowledge about the payments banks, you must be eager to set one. So follow these steps to get Payment Bank License:
Step-1: Firstly, as per RBI regulations, the applicant has to incorporate a Public Limited Company under the Companies Act, 2013, wherein the main objective should remain to act as a payments bank.
Step-2: Now, file an application to the Chief General Manager of RBI to grant the payment bank license.
Step-3: Thereby, the External Advisory Committee (EAC) shall assess the application, and summon the applicant to validate the information given by him.
Step-4: If an applicant successfully meets the eligibility criteria, then RBI shall grant him the license.
Step-5: Subsequent to the previous step, the name of the concerned applicant shall be displayed on the official RBI site.
Step-6: Lastly, after getting the principle approval to operate as a payment bank from the Reserve Bank of India, the bank has to be set up within 18 months.
Mandatory Compliances for Payment Banks in India
The Mandatory Compliances for a Payment Bank in India can be summarised as:
- A Payments Bank is not allowed to accept NRI deposits;
- A Payment Bank needs to have a minimum paid-up capital of Rs. 100 crores;
- A Payment bank can give ATMs or debit cards but is not allowed to offer loan and Visa administrations;
- A Payment Bank is permitted to accept current deposits and Investment Funds Bank deposits from the private ventures up to a specified limit;
- A Payment Bank needs to accept RBI Compliances on Web-Banking, Data Security, Cyber Laws, Electronic Banking and Technology Risk Management;
- A Payments Bank must use the words 'Payments Bank' in its name to differentiate itself from other banks.
Scope of Activities of a Payment Bank in India
The scope of activities of a Payment Bank in India can be summarised as:
- A Payment Bank can accept deposits up to the prescribed limit. The term “deposits” include Current Deposits from Small-level businesses and Saving Bank Deposits from an Individual;
- NRIs are not allowed to make any deposit in the Payment Banks;
- A Payment Bank can issue ATM or Debit Cards;
- Payment Banks are not allowed to indulge in the Lending Activities;
- A Payments Bank must undertake its own KYC (Know Your Customer)/AML (Anti Money Laundering) and CFT (Combating Financial Terrorism) exercise as any other bank;
- A Payment bank can give ATMs or debit cards but is not allowed to offer loan and Visa administrations;
- A Payment Bank can indulge in payments and remittance services through ATMs (Automated Teller Machines) and BCs (Business Correspondent) and mobile banking. The payments or remittance services may include acceptance of funds at one end through various channels such as branches and BCs and payments of cash at the other end, through branches Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) and BCs (Business Correspondent);
- A Payment Bank can issue Prepaid Payment Instruments in accordance with the instructions provided under the Payment and Settlement Instrument Act, 2007;
- A Payment Bank can offer Internet Banking Services;
- A Payments Bank can become a Business Correspondent (BC) of another bank, subject to the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) guidelines on BCs;
- A Payment Bank can work as a channel of accepting remittances from banks under the payment system approved by the Reserve Bank of India, such as RTGS/NEFT/IMPS;
- A Payment Bank is permitted to handle Cross-Border Remittance Transactions in the nature of personal payments or remittances on the current bank account;
- A Payment Bank is not allowed to set up subsidiaries to undertake the activities of an NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Company);
- A Payment Bank can make Payments of utility bills on behalf of its customers and the general public;
- A Payment Bank is allowed to undertake other non-risk sharing simple financial services activities with the prior approval of RBI. It also needs to satisfy all the requirements of the sector regulator for such products.
Future of Payments Banks in India
Before you step into the hassle of documentation and the elongated procedure of Payment Bank License, it is essential to determine the position of payment banks in the upcoming years.
- Payments banks are indeed a robust system that offers a great deal of convenience to their customers. Even though you have an existing account with a traditional bank, a payments bank will enable you to access banking services and carry out transactions.
- Since the traditional bank functions in a particular time frame, one has to stick around the regular banking hours; however, payments banks discard any such limitations and provide seamless transactions at any time.
- Thus, the payment banks eliminate the need to be time-specific while travelling to a branch to make any transactions.
- Another apparent benefit that payments banks provide is cash digitalisation. About 90% of transactions in India were cash-based before demonetisation. Its after-effects have uplifted the growth of payments banks with its emphasis on digitalising transactions.
Thus, the payment banks are expected to be a game-changer and revolutionise the current banking system. It will bring banking on a broader scale.
FAQs of Payment Bank License
The main objective of a payment bank is to ensure financial inclusion by offering remittance/payment services to underprivileged sections.
The focus of payments bank revolves around strengthening the migrant labour workforce, opening small savings accounts of small business holders, supporting workers of the unorganized sector and low-income households.
Yes, a payment bank can accept current and saving deposits of up to Rs 1 lakh per customer.
Yes, a Payments Bank can issue ATM Cards or Debit Card.
No, a Payment Bank cannot issue Credit Cards to its Customers.
Yes, a Payments Bank can provide non-risk sharing simple financial products such as Mutual Funds.
Yes, a Payments Bank can provide Insurance Products.
The main difference between a payment bank from a commercial bank is that the commercial banks can accept any amount of money as a deposit per customer. However, payments banks can only accept deposits up to a maximum limit of Rs. 1 lakh per customer.
As per RBI, the minimum capital requirement to open a payment bank is 100 crores.
The promoter needs to contribute at least 40% for the first five years of establishment.
Yes, Foreign Shareholding is allowed in payments banks for the Foreign Direct Investment in private banks in India.
Yes, according to the final RBI guidelines, a Payments Bank needs to invest at least 75% of its Demand Deposits (DD) in (SLR) Statutory Liquidity Ratio for becoming eligible for government securities or treasury bills with maturity up to a year.
Yes, a Payments Bank can invest 25% of their Fixed Deposits (FDs) with other scheduled commercial banks for operational objectives and liquidity management.
The steps involved are incorporate a Private Limited Company; File an Application to the Chief General Manager of RBI; Assessment of Application by External Advisory Committee; and Grant of Payments Bank License.
Some of the renowned examples of Payments Banks are Airtel M Commerce Service Limited; Fino Paytech Limited; National Securities Depository Limited; Reliance Industries Limited; Distribution Services Limited; Vodafone M-Pesa Limited; Department of Posts Aditya Birla Nuvo Limited; and Paytm Payments Bank.
The term “Regulatory Framework” includes Companies Act 2013; Banking Regulation Act 1949; Reserve Bank of India 1934; Foreign Exchange Management Act 1999; Payment and Settlement System Act 2007; and Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act 1961.
The Key Features of a Payments Bank are Offer Deposits up to Rs 1 lakh; Virtual Debit Card Facility; Smooth Transactions via an Online Portal; and Feasible Mode of Making Payment.
As per section 22 of the Banking Regulations Act 1949, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has the authority to issue the Payments Bank License to the applicants.
As per the RBI guidelines, the minimum paid-up capital needed for opening a payments bank and obtaining a Payments Bank License in India is Rs100 Crore.
Yes, existing PPIs can obtain a Payments Bank License in India.
Yes, a Mobile Telecom Company can obtain Payments Bank License in India.
Yes, a PSU or Public Sector Unit can obtain Payments Bank License in India.
Yes, an NBFC is eligible to obtain Payments Bank License in India.
Yes, Real Estate Sector Co-operatives can obtain Payments Bank License in India.
Yes, an individual is eligible to obtain a Payments Bank License in India.
It should include Detailed Information about the persons; details of Foreign Equity Participation; details of the subscriber to more than 5% of the Paid-up share capital; and details regarding the capital source of the proposed investors and bank.
Yes, a Payments Bank can appoint its Parent Company as its Corporate BC on the basis of RBI guideline and Arm Length.
No, the instructions and guidelines issued by RBI to commercial banks will apply to payments banks as well.
A Project report needs to show the Viability, include Bank Business Potential, Business Plan, and the details of the financial services planned to be offered.
No. NRIs or Non Indian Residents are not allowed to make any kind of deposit in the Payment Banks.
Yes, a Payments Bank can embark on its own Combating Financial Terrorism (CFT) exercise like any other bank.
Yes, a Payments Bank can embark on its own Know Your Customer (KYC) like any other bank.
Yes, as per the “payment system approval” by the Apex Bank, a Payments Bank can operate as a medium of accepting “remittances” from banks, such as RTGS/IMPS/NEFT.
Yes, a Payment Bank must agree to take Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Compliances on Technology Risk Management, Web-Banking, Data Security, Cyber Laws, and Electronic Banking.
The application for the Payments Bank License will be addressed to the “CGM” (Chief General Manager) of the Department of Banking Regulation, RBI.
An EAC or External Advisory Committee consists of distinguished professionals, such as CAs (Chartered Accountants), Finance Professionals, Bankers, etc.
The EAC or External Advisory Committee shall assess the applications for Payments Bank License.
Yes, EAC or External Advisory Committee may call for additional information and can have negotiations and deliberations with applicants as well.
The Business Plan must address the aims, purpose, targets, and modes of achieving targets of the proposed payments bank.
Yes, it is mandatory for the applicants to furnish Business Plans and Project Reports with the application for Payments Bank License.
Yes, it is advisable to consult an expert who is having a prior banking experience to obtain a Payments Bank License in India.
Yes, as per the guidelines issued by the Apex Bank, a Payments Bank can undertake non-risk government services, such as Aadhar Enrolment.
Yes, a Payments Bank can connect to the NUUP or National Unified USSD Platform.
Yes, a Payments Bank can issue PPIs or Prepaid Payment Instruments.
Yes, a Payments Bank can pay utility bills for its customer.
The Capital Adequacy Leverage Ratio or CAL Ratio must not be less than 3%.
A Payments Bank must maintain at least 15% of its Total Risk-weighted Assets.
No, a Payments Bank can't offer a loan.
No, a Payments Bank cannot offer service of VISA Administrations.
Yes, a Payments Bank can handle Cross-Border Remittance Transactions.