An Overview of Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP)
An Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) is a benefit plan for the employee that gives workers ownership interest and this interest takes the form of shares of stock. The company’s shares are given to the employees of the company at discounted rates. Any companies other than the listed companies must have ESOP as per the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 & Companies (Share Capital & Debentures) Rules, 2014. For the listed companies, they must issue as per the SEBI (Securities & Exchange Board of India) Employee Stock Scheme Guidelines.
Employee Stock Option Plan benefits both the company and its employees and it benefits the start-ups where employees can be rewarded once the company goes public. Any employee of the company can be provided ESOP if they fit the criteria. ESOPs are often issued as profit-sharing plans, direct or bonuses stocks which would be availed by employees who are chosen at the decision of the employer.
How does ESOP Work?
- An ESOP (Employee Stock Ownership Plan) is set up as a trust fund in which companies may place freshly issued shares, borrow money to purchase company shares or fund/give money to the trust with cash to buy shares of the company.
- Meanwhile, employees can accumulate a growing number of shares, an amount that can increase over time depending on their employment term and these shares are intended to be sold only at or after the retirement or termination, and the employee has remunerated the cash value of their shares.
Importance of Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP)
- ESOPs are a tax-favoured strategy that provides fair value for shareholders;
- Employee Stock Ownership Plans are beneficial for those who play a productive role & remain in the company for a long time;
- The ESOP creates & preserves a legacy;
- ESOP allows for a slow & low ownership transition.
Advantages of Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP)
- Attract Top Talent: You may not be able to match their current salary, but an offer of shares in your company will be enough to attract the best talent.
- Build Motivation: The better your business performs, the better your most talented employees will get paid. There's no better way to motivate them.
- Keep Them Longer: The employees to whom shares have been allocated are almost certain to complete the two to three years you have defined as the vesting period.
List of Employees whom Company Issue ESOP
According to the Rule 12(1) of Companies (Share Capital & Debentures) Rules, 2014 following is the list of employees who can issue ESOP:
- A permanent director or employee of a subsidiary company in India or outside India or an associate company or holding company;
- A company’s permanent employee who is working in India or outside India;
- A company's director includes a part-time or whole-time director but not an independent director of the company.
Following are the employees to whom a company cannot issue ESOP (Employee Stock Ownership Plan):
- A director who either himself or via any corporate or through their relative holds more than 10% of the outstanding equity shares of the company;
- An employee of the company who belongs to the promoter group or is a company's promoter.
Note: These above 2 conditions are not for Start-up Companies for 10 years of the time period from the date of its incorporation
Who is Eligible for ESOP?
As per the Indian Revenue Service, the maximum age of an employer can impose to be eligible for an ESOP is 21 years. And he or she must be eligible for the Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) in the year of joining the company. An employer can restrict the eligibility to employees with 2 years of service but only if the plan has immediate vesting.
Requirements for Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP)
- There must be CC (Compensation Committee) and it shall be a committee of board directors including the majority of independent directors;
- Filing of Form-PAS-3;
- Disclosure in DR (Director Report);
- The date & members of the compensation committee must be included in the board meeting;
- Approval of shareholders by the separate resolution;
- Maintenance of ESOP Register in SH-6 at the registered office of the company or such other place as the board may decide;
- Entities in the ESOP register shall be certified by the CS or any other individual certified by the board;
- Hold a general meeting for the approval of shareholders by way of ordinary resolution. Moreover, including the authorisation for the issue of shares under the Employee Stock Ownership Plan & the formation of a compensation committee.
- General meeting notice including the number of Employee Stock Ownership Plan to be granted.
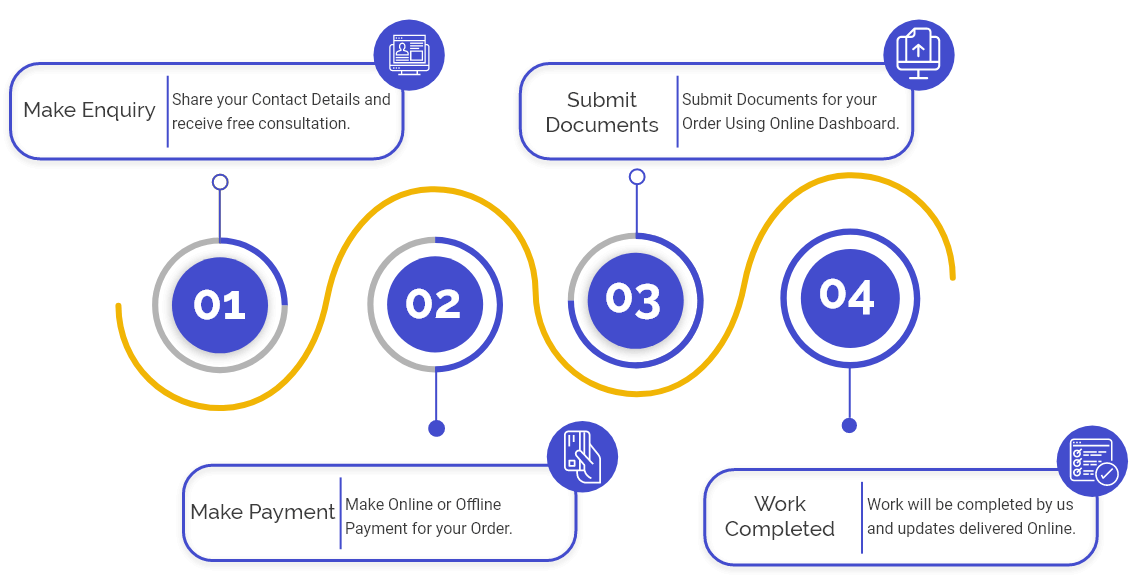
Procedure for the Issuance of Employee Stock Ownership Plan
Following is the procedure for the issuance of an Employee Stock Ownership Plan by a company:
- First, the company prepare the draft of ESOP as per the Companies Act, 2013 & Rules;
- After that, prepare the notice for the Board Meeting along with the Draft Resolution to be passed in the Bard Meeting;
- Once the notice of the Board Meeting is prepared, send the same to all the directors at least 7 days before the meeting;
- Then pass the resolution for the issuance of shares via ESOP, find out the price of shares to be issued pursuant to ESOP & fix the date & time and approve for conducting the general to pass a special resolution for issuing ESOP.
- Send the draft of the Board Meeting to all the directors of the company within 15 days of and file the MGT-14 Form with the ROCs (Registrar of Companies) of passing the Board Resolution.
- Send the notice of the General Meeting to all the company’s directors, shareholders, auditors, and secretarial auditors for the company before 21 days of the meeting date.
- Pass the Special Resolution (SR) for the issuance of shares under the ESOP to the company's directors, officers, and employees in the general meeting;
- File MGT-14 Form with the ROCs within 30 days of passing the resolution in the general meeting;
- Send options to the Directors, Officers, and Employees for purchasing shares under Employee Stock Ownership Plan.
- Maintain a Register of ESO (Employee Stock Options) in Form SH-6 and enter the details of the ESOP issued to the directors, officers, or employees.
- If a Private Company wishes to issue Employee Stock Ownership Plan, then it should confirm that the AoA (Articles of Association) authorises the issuance of shares via ESOP. If the Articles of Association don't authorise, then the company should hold a general meeting to change the AoA to include the provisions of issuance of shares via ESOP & then proceed with holding the Board Meeting (BM) for the passing of the resolution & getting the shareholder's approval for ESOP Scheme.
Important Terms Focused During Issuance of Share via ESOP
- Grant: It means the issue of stocks to the employees, i.e., informing the employee of the company that he/she is eligible for ESOP. The company will have the freedom to find out the exercise price while giving the option of ESOP to the employees.
- Vest: It means the employees’ right to apply for the shared issued to them. There shall be a minimum of 1 year between the grant of opting & vesting for the ESOP Scheme.
- Exercise: The period for exercise is where the employees can exercise the option of buying the shares. The company have the liberty to specify the lock-in period for the shares issued after the exercise of the option. The employees will not have the right to get any dividend or to vote or enjoy the benefits of a shareholder concerning the ESOP granted to them until the shares are issued on exercise of their option.
Some Mandatory Disclosures
The company should make some disclosures in the explanatory statement annexed to the notice for passing the resolution for the issuance of the Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP):
- Requirements of vesting period of ESOP;
- Exercise prices & process;
- The lock-in period, if any;
- Methods used by the proposed company to value its options;
- Total number of stock options which is granted;
- Maximum period within which the options can be vested;
- The conditions of ending of the options besting in employees;
- A statement that the company will follow the applicable accounting standards;
- The identified class of employees who can participate in the ESOP.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, the employee stock option plan includes both the existing and future employees.
Yes, a Step down subsidiary company is considered as a subsidiary to the extent permitted by law. Also, an Indian Company can grant Employee Stock Option Plans to the employees of its Subsidiary Company, whether located in India or outside India.
No, a company is not allowed to set the exercise price below the face value of its shares.
Yes, a listed company can set the exercise price of the ESOPs below the current market price.
Yes, a company has the right to issue ESOPs at a different exercise price for each employee or class of employee.
Yes, a company can issue any type of shares as ESOPs. The term “any type” includes Equity Shares, Shares with Differential Voting Rights, and Preference Shares.
No, a share given in the Employee Stock Option Plan must carry a voting right, which needs to be same as the voting right given to the existing or differential shareholders.
The steps included in the process to issue ESOPs are Grant Notice, Option Plan, Allotment and Documentation, Options Agreement, and Business Valuation.
Normally, a period of 30 business working days is required to complete the process of Employee Stock Option Plan.
The benefits of ESOP are Attract Top Talent, Build Motivation, and Longer Vesting Period.
The term “Employee Stock Option Plan” simply means a plan where the company grants options or shares to its employees.
Only a company whose shares has been listed in the recognised stock exchange can undergo the process of ESOP.
No. ESOPs or Employee Stock Option Plans are valid only till the expiry of the exercise period.
No, ESOPs are not eligible to be converted into shares after the expiry of the exercise period.
Yes, a holding company has a right to issue ESOPs to the employees of its subsidiary company. However, the same is possible only if the same has been provided in the provisions of AOA (Articles of Association).
SEBI, Companies Act 2013, and Income Tax Act, governs the provisions and process of ESOPs in India.
No, mere grant of ESOP does not make an individual a shareholder of the issuing company.
Yes, the option of ESOP is legal in India.
Yes, a company can change or modify its regulations with regard to ESOP after its grant and acceptance by employees.
No, a promoter is not allowed to participate in the process of ESOP.