An Overview of Patent Licensing
Patent Licensing is an agreement made between the Patent holder (licensor) and the company or person that wants to use and avail benefit from the licensee. It allows the licensee to sell or make the product, technology, or design in the Patent. Then the Patent creates income for both the licensee and the licensor through royalties & returns for the duration of the Patent Licensing period.
A Patent owner or holder can give away or transfer their interest in a patent to a third party or person. The licensor gives away their rights on the invented, patented Intellectual Property for a period of time over a mutual agreement. In this period, the licensee can extract benefits & have rights on the interest on the Patent. They may make and use the licensed design and also gain some profits during the licensed period.
What are the Different Types of Patent Licensing?
Following are the different types of Patent Licensing:
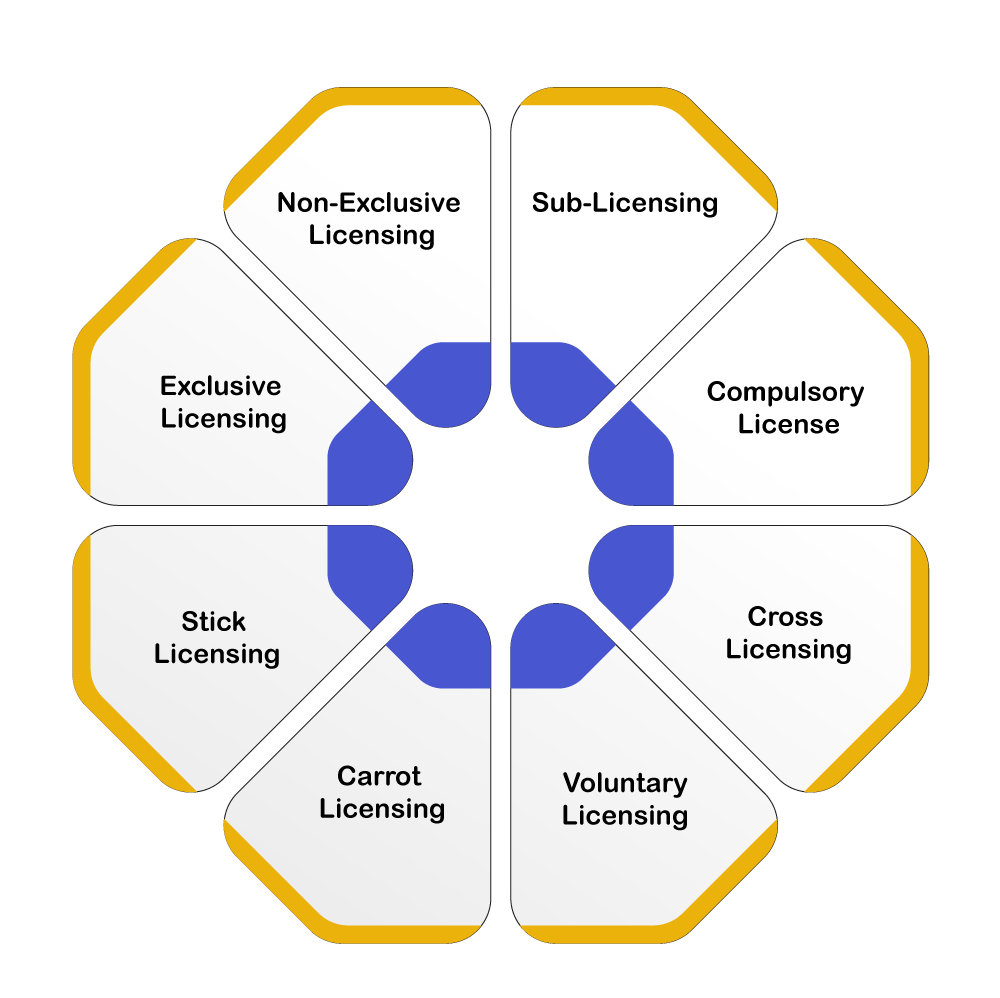
- Exclusive Licensing: This licensing is one in which all the Patent rights is transferred to the licensee. In this case, the licensee has all the rights as of the Patent holder except for transferring the Patent to another person. This restriction is because in such a license, even with the transfer of all other rights, the Patent right over the title still rests with the Patent holder. It is wholly granted to a particular party and hence cannot be further transferred. In this type of Patent Licensing, the possibility of the Patent getting infringed is negligible as the Patent rights are less being exploited, and the licensee has a monopoly over the market.
- Non-Exclusive Licensing: This Licensing involves giving license to more than one company, which means that one licensee may exploit the innovation, but along with them, others who have been given the license for the same Patent may be entitled to equal exploitation. The licensor also remains free to exploit the same IP (Intellectual Property).
- Sub-Licensing: It's a type of license issued by the licensee to different companies or organisations to make the products. This license can be said to be granting certain licensed rights on a product to a third party by the licensee.
- Compulsory License: When the Government gives permission to any persons or organisations to sell, make or use a patented design/product, irrespective of the Patent owner's will, for the public benefit, it is referred to as a Compulsory License. This license is generally seen granted in the pharmaceutical products and the products which fulfil the criteria as described in Section 84 of the Patents Act, 1970.
- Cross Licensing: This is a process when there could be an exchange of licenses between various creators & organisations. This is required when the innovation requires the support of other products to make its position in the market.
- Voluntary Licensing: This license is also applicable for pharmaceutical Patents; Voluntary Licenses are an act of goodwill towards society. In this case, Patent owners may, at their discretion, license to other parties, on an exclusive or non-exclusive basis, the right to import, manufacture, and/or distribute a pharmaceutical product. Depending on the license terms, the license may act completely or effectively as an agent of the Patent owner; or the licensee may be free to set the terms of distribution & sale within a prescribed market or markets, contingent royalty payment. Either option or arrangements in between would permit considerable price reductions.
- Carrot Licensing: This Patent Licensing approach is appropriate when the potential licensee is not in the practice of the patented invention and doesn’t come under any obligation to take a license. This type of license is a marketing method where the Patent owner gives the licensee a sight of what could be achieved by obtaining a license for their Patent.
- Stick Licensing: This Patent Licensing is an absolute contrast to Carrot Licensing. This licensing can be used when the potential licensee is already in use of your patented technology and thereby violating your Patent. The proposition of value states that “go for the license or else… Once actually should take care that the Carrot License is really a stick license in the cover-up.
Advantages of Patent Licensing
Following are some advantages of Patent Licensing:
- International Market: It becomes hard for many companies to have a bunch production of a product separately. Patent Licensing comes to help in overcoming this difficulty as it allows other companies or organisations to produce the Patent products & thereby help in a huge production. Patent Licensing can aid in introducing one invention in the international market.
- Competitive Benefit: If the Patent is licensed to an already established company with a huge customer base, the Patent product or item will have a bigger market to capture in comparison to other Patents, giving it a reasonable edge over other Patents.
- Transfer of Risks: Production & manufacture of design/products have a lot many risks involved. With Patent Licensing, the Patent holder can transfer such risks involved in the production of Patent Design or product to the licensee.
- Limited Period: Because the licensing is done for a limited period, the Patent owner gets back their exclusive rights over their invention as and when the duration of the license expires.
Disadvantages of Patent Licensing
Following are some disadvantages of Patent Licensing:
- Loss of Control: For the license period, the Patent holder transfers their rights to the licensee. The outcome of which is they losses their control, either partially or completely, on their own invention.
- Trouble in Determining Licensee: It takes lots of time & effort to find out the suitable licensee for the innovation. It is vital to obtain a potential licensee and have a structured agreement in order to have the greatest possibilities of success.
- Risk of Licensee’s Ability: The Patent holder relies on the licensee's abilities & efficiency to efficiently commercialise the Patent product. The risk of poor quality management & strategy of which they lose their control, either completely or partially, on their own invention.
Common Mistakes People Committed During Patent Licensing
Following are some common mistakes committed during Patent Licensing:
- In the rapid growth, some inventors fail to determine to find the appropriate licensee for their product & end up granting license to some non-proficient party. This results in the invention's failure, which could have had increased in the international market had the owner opted for a competent licensee.
- The licensee tends to utilise the patented design/product before signing the Patent License Agreement outcome in Patent Infringement. The licensee should make sure that he or she signed the license agreement before using or selling the design or product so patented.
- Lack of awareness concerning the owner's liability also leads to loss for the licensee. The licensor is still the actual owner of the patented design or product, even during the license period. Hence, they can be held accountable for their invention even during the license period.
- Many Patent holders charge an advance in royalties, and many also ask for a minimum annual royalty.
- Filing an application for Patent Registration is difficult. Patent Licensing can be even more challenging. Hire a Patent Lawyer to do due diligence to safeguard your rights, and this can also aid you to increase your profits.
What is the Meaning of Patent Licensing Royalty Rate?
When an innovator licenses their Patent to any third person, they both enter into the license agreement wherein Patent rights are given to the licensee, and in return, the licensor receives a definite amount of money fixed in the agreement every time the product or item is sold. This fixed amount or fee is given to the licensor/inventor is called royalty, and the percentage of gross or net profit decided to be the royalty is referred to as Patent Licensing Royalty Rate. Usually, Patent Licensing Royalty Rate varies from 0.1% to 25% depending on the industry & invention type.
Difference Between Patent Licensing and Patent Assignment
Patent Assignment is an act of the Patent holder wherein the Patent owner transfers the exclusive rights of the Patent permanently. Such a transfer is noted in the official Patent record. In the Patent Assignment, the assignee has to pay the amount to the assignor in initial and can receive profits from the patented innovation later.
Whereas Patent Licensing is an act of the Patent holder where the owner grants permission to extract benefits on interest on the Patent to a third party for a limited time. Such transfer of Patent rights is temporary in nature. In a license, the licensee is required to pay the royalty to the licensor for the complete duration of the license period.
Risks and Limitations of Patent Licensing
- Dependent on the licensee’s skills – When you license your Patent, your dependability will depend on the licensee as you will be reliant on their sources, skills and efforts they put in to make your product or item available in the market. Therefore, it is vital to choose the correct licensee for getting your innovation to the market.
- Licensing could be less gainful, too – Patent Licensing can be less gainful, given that when you make the invention or innovation available in the market yourself, you can get a high amount of profits. Though investing capital is in danger, but profits will be more than your expectations.
- A Licensing Agreement can be Disadvantageous: If the working situation of the company goes well and the agreement doesn't state the royalty sharing & further processing, it will be a loss to the inventor. Hence, while making an agreement, all the terms & clauses should be evidently mentioned, and a second reading should be done so that subtractions/additions can be made.
- The extra requirement by the licensee- When you grant the Patent license to the licensee, in the beginning, he or she may not ask for anything, but in later development, they may ask for some contributions in case or even extra data, which may be time taken or may even take your funds. This will be a costly deal and a hindrance to innovation. So, it is vital that the agreement clearly states all the acts and the licensee don't ask anything from the licensor. These clauses should be evidently mentioned.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes you can, but not in all conditions.
Patent Licensing is an agreement made between the Patent holder (licensor) and the company or person that wants to use and avail benefit from the licensee.
Yes, sometimes the licensee can sub-license the Patent rights. The grant clause explains whether this is possible.
This license includes a Patent License and other rights. This permits the licensee to make use of IPR as much as possible.
This is an agreement where one company or assignor transfers all or part of their right, title & interest in a Patent to another company or the assignee.
No, you don’t need a Patent to license your idea. You can license the idea without the Patent.