Overview of Issue of Debentures
One of the biggest challenges for a company during its initial days is raising funds. Though there are various options available like Angel Investors, Bank Loans, Venture Capitals and Personal Investment, raising funds from Issue of Debentures to the public is considered the best option for a new company. Debentures are long-term instruments issued by companies to borrow funds at a fixed rate of interest. This interest is known as the Debenture Interest, and the person holding debentures is called the debenture holder.
As per the Companies Act, 2013, debentures are debt instrument issued by companies, whether secured or unsecured. Further, debentures represent the company's debt, which includes the details like Rate of Interest, Loan Amount, and Maturity Date. Moreover, a company can also transfer debentures according to its AOA (Article of Association).
Advantages of Issue of Debentures
The advantages of the Issue of Debenture can be summarised as:
- Issue of Debentures does not alter the company’s share capital and voting right pattern;
- The stamp duty payable on the issue of debentures is 0.05%, which is less than the amount of stamp duty payable on the shareholder loan;
- The company pays interest yearly;
- There is no statutory limit provided for the conversion/ redemption of unsecured debentures;
- At the time of winding-up, debenture holders are given priority over shareholders;
- Issue of debenture is a cheaper form of finance as compared to other borrowings;
Key Features of Debentures
The key features of debentures are as follows:
- Debentures do not carry voting rights;
- Debentures represent the debt of the company;
- Debentures can be secured or unsecured;
- Debentures can be convertible or non-convertible;
- Debentures may be redeemable or irredeemable;
- Debentures carry interest at a fixed rate;
- Debentures can also carry a zero rate of interest;
- The Issuer company needs to create a DRR (Debenture Redemption Reserve) account out of the profits available for the payment of dividends. Further, the company cannot use the amount credited to this account except for the redemption of debentures;
- Rule 18 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014, provides a period of ten years for the redemption of secured debentures. However, there is no period prescribed for the redemption of unsecured debentures;
- During winding-up, debenture holders are given priority over shareholders;
- Debenture-holders are not the owners of the company;
- The Debenture bears a common seal of the company.
- Debentures promote both long-term funding and long-term planning;
- Issue of Debentures involves the least risk, as the company needs to pay interest even if it incurs losses also;
- Debenture interest is a tax-deductible expense.
Laws Relating to Issue of Debentures
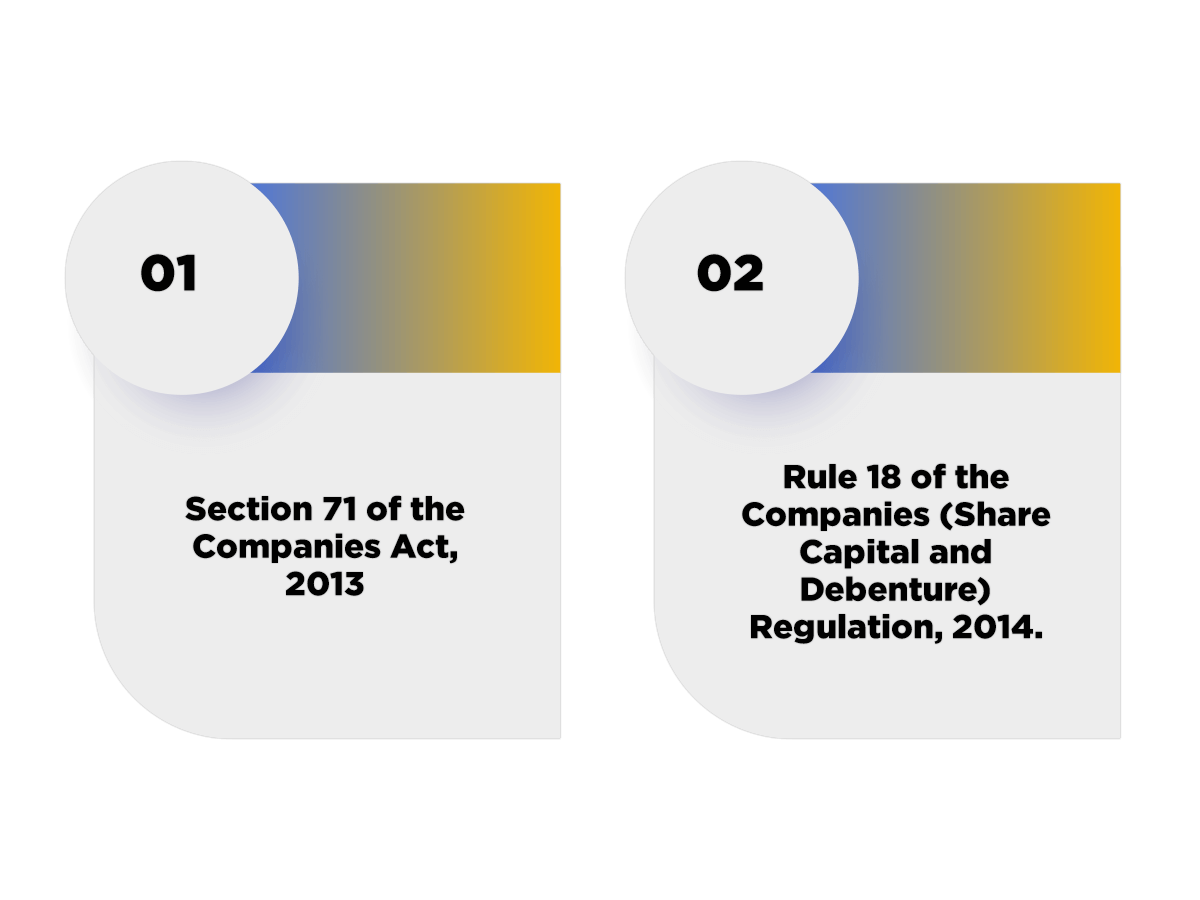
In India, the key legislation regulating the concept of Issue of Debentures are as follows:
- Section 71 of the Companies Act, 2013;
- Rule 18 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debenture) Regulation, 2014.
Types of Debentures in India
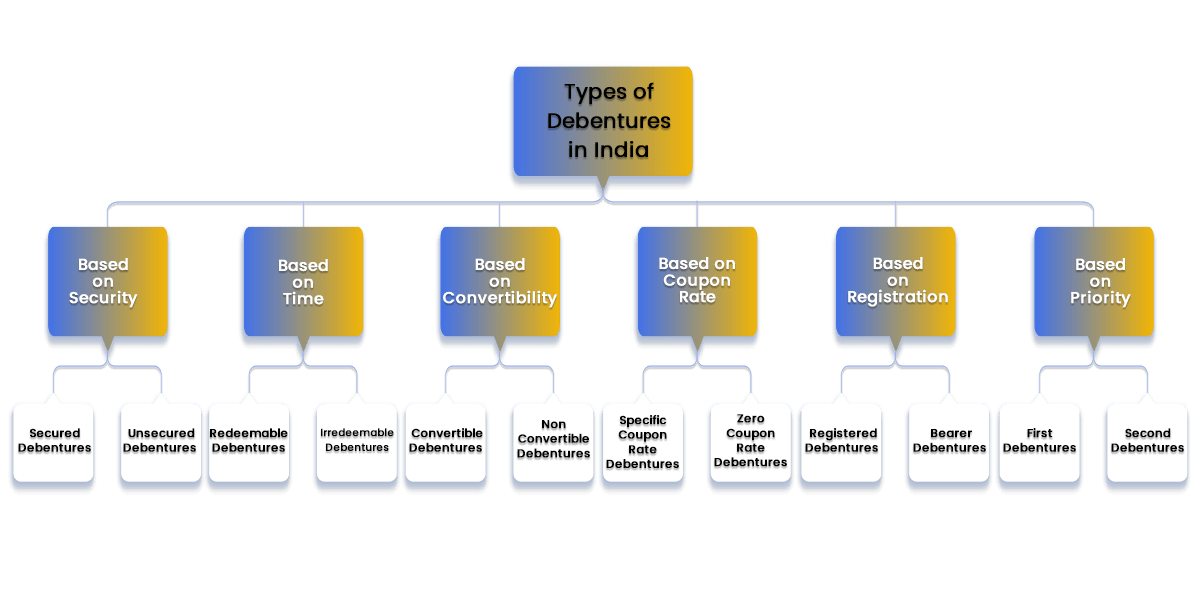
The different types of Debentures in India are as follows:
Based on Security
|
Secured Debentures |
|
|
Unsecured Debentures |
|
Based on Time
|
Redeemable Debentures |
|
|
Irredeemable Debentures |
|
Based on Convertibility
|
Convertible Debentures |
The debentures which are convertible into the equity shares after the expiry of a specified period are known as convertible debentures. |
|
Non-Convertible Debentures |
The debentures that cannot be converted into equity shares are known as non-convertible debentures. |
Based on Coupon Rate
|
Specific Coupon Rate Debentures |
|
|
Zero-Coupon Rate Debentures |
|
Based on Registration
|
Registered Debentures |
Registered Debentures means a company issuing debentures by recording the name of the holder in the made. |
|
Bearer Debentures |
When a company transfers debentures by mere delivery, they are known as Bearer Debentures. |
Based on Priority
|
First Debentures |
The Debentures that are given priority in repayment are called the First Debentures. |
| Second Debentures | The Debentures that are repaid after first debentures are known as Second Debentures. |
Different Ways for Issue of Debentures
When a company invites application from the public to apply for debentures, it can issue its debentures in either of the following ways:
- Issue of Debentures for Cash:
- Issue of Debentures at Par
When the issue price and face value of a debenture are equal, it is known as the issue of Debenture at Par. In this case, the long-term borrowings in the liabilities section equals the cash in the balance sheet's assets side.
- Issue of Debenture at Discount
It means the issue price of a debenture is below its face value.
- Issue of Debenture at Premium
When a company issues its debenture at a price more than its face value, it is known as the Issue of Debenture at Premium.
- Issue of Debenture as Collateral
At times, debentures can also act as collateral security to the lenders. It happens when the lenders demand additional assets as security besides the primary security. If the lenders were not able to realise the amount of loan from the sale of primary assets, they can realise the same from the additional assets. Hence, many companies issue debentures to the lenders, together with the physical assets already pledged.
- Issue of Debenture for the Consideration other than Cash
Normally, companies follow this method with their vendors/ sellers. In this case, instead of paying the cash, a company issues its debentures for consideration apart from cash for the assets bought from the vendor. Moreover, a company can also issue debentures at par, premium or discount and are also accounted for in a similar fashion.
- Over Subscription of Debentures
Over Subscription of Debenture means when a company invites the public to subscribe to its debenture and the applications received are more than the number of debentures offered. In this case, a company cannot issue more debentures than it had initially invited the public for. Therefore, the company needs to refund the application money to the applicants to whom it does not allot debentures.
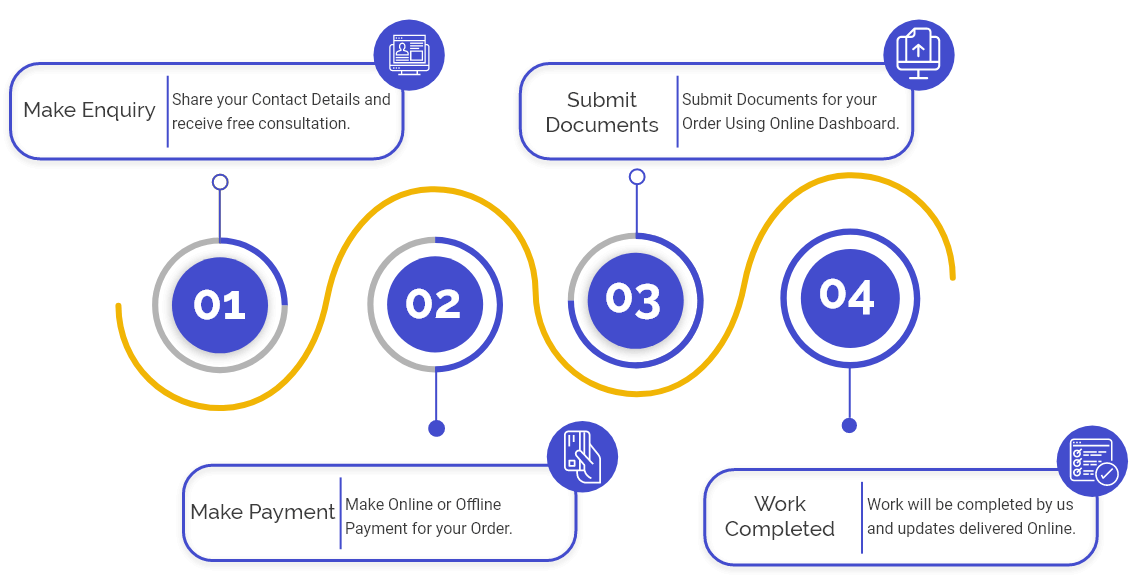
Process for the Issue of Debentures

The steps involved in the process for Issue of Debentures in India are as follows:
- Hold a Board Meeting
A company needs to hold a Board Meeting to take into account and pass resolutions for the following items:
- Issue of Debentures;
- Approving the Offer Letter;
- Approving Private Placement of shares;
- Debenture Subscription Agreement;
- Opening of a bank account; and
- Calling of the EGM (Extraordinary General Meeting).
- Call an EGM
The company also requires to call an EGM (Extraordinary General Meeting) to consider and pass a special resolution for the following items:
- Increment in the borrowing capacity of the company;
- Issue of the Non-Convertible Debentures.
- File MGT-14 with ROC
The company needs to file MGT-14 with the ROC (Registrar of Company), within thirty days of passing Special Resolution in the EGM.
- Maximum Limit
The company needs to restrict the offer letter to a maximum of 200 investors in any financial year;
- Investment Size
The investment size for each investor should not be less than Rs. 20000.
- Letter of Offer
The company needs to dispatch the letter of offer to the investors and open a bank account.
- File Offer Letter with ROC
The directors of the company need to file the offer letter with the ROC and Form GNL-2, PAS 4, and PAS 5.
- Receive Money from Investors
The directors then collect application money from the investors for the allotment of debentures.
- Convene a Board Meeting
The company requires to hold another board meeting after the closure of offer to discuss the agendas given below:
- To allot its debentures within sixty days starting from the date of receiving application money;
- To approve the agreement for charge creation;
- To approve the debenture trust deed.
- File CHG-9
Within thirty days of creating a charge on assets, the company needs to file Form CHG-9 with the ROC (Registrar of Companies).
- Restriction on using Application Money
The issuer company cannot use the funds collected until it allots its debentures to all the investors.
- File Return of Allotment
The director of the issuer company needs to file the Return of Allotment in Form PAS 3 with the Registrar of Companies within fifteen days of allotment.
- File the Corporate Action
The issuer company needs to file its Corporate Action within two working days of allotment.
Difference between Debentures and Shares
|
Point of Difference |
SHARE |
DEBENTURE |
|
Ownership |
A share is a part of the company’s share capital. |
A debenture is a part of the company’s borrowed capital. |
|
Return |
The return on shareholdings is known as Dividend. |
The return on debentures is known as Interest. |
|
Charge v. Appropriation |
The payment of dividends is an appropriation out of profits. |
The payment of interest is a charge. It means the company needs to pay the interest even if it incurs losses also. |
|
Priority |
Shareholders are not given preference at the time of liquidation. |
Debenture Holders are given priority over Shareholders. |
|
Security |
Shares are not secured, i.e., does carry any charge on assets. |
Debentures are usually secured, i.e., carry a fixed or a floating charge over the assets. |
|
Convertibility |
Shareholders cannot convert their shares into debentures. |
Debentures Holders can convert their debentures into shares. |
|
Voting Rights |
Shareholders are given voting rights. |
Debenture holders are not given any voting rights. |
|
Owner v. Creditor |
Shareholders are known as owners of a company. |
Debenture holders are known as creditors of a company. |
Issue of Debentures FAQs
The laws regulating the issue of debentures are section 71 of the Companies Act 2013 and Rule 18 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debenture) Regulation 2014.
Discount on the issue of debenture is considered as a Capital Loss to the company. Hence, it should be shown on the Assets Side of the Balance Sheet as the "Miscellaneous Expenditure” as a Fictitious Asset.
The different types of Debentures are Secured Debenture, Unsecured Debenture, Redeemable Debenture, Irredeemable Debenture, Convertible Debentures, Non-Convertible Debentures, Specific Coupon Rates Debentures, Zero-Coupon Rate Debentures, Registered Debentures, Bearer Debentures, First Debentures, and Second Debentures.
No, the debentures do not carry voting rights.
The Debentures represent the debt of the company.
Yes, the Interest Rate is fixed on Debentures.
Yes, the Debentures can carry a zero rate of interest.
Yes, Debentures bear a Common Seal of the Company.
The interest charged on Debentures is a Tax-deductible expense.
No, debenture holders are not the owner of the company.
The debenture holders are given priority over shareholders at the time of Winding up.
The different ways to issue debentures in India are the Oversubscription of Shares, Issue of Debentures for Cash, Issue of Debentures for the Consideration other than Cash, and Issue of Debentures as Collateral.
The steps involved in the process for issue of debentures are Hold a Board Meeting, Call an EGM, File MGT-14 with ROC, Maximum Limit, Investment Size, Letter of Offer, File Offer Letter with ROC, Receive Money from Investors, Convene a Board Meeting, File CHG-9, Restriction on using Application Money, File Return of Allotment, and File the Corporate Action.
Yes, there is a need to create a DRR (Debenture Redemption Reserve) account out of the profits available for the payment of dividends.
The company needs to file MGT-14 with the ROC (Registrar of Company) within 30 days of passing Special Resolution in the EGM.
The company needs to restrict the offer letter to a maximum of 200 investors in any financial year.
The debentures on the basis of security are Secured and Unsecured Debentures.
The debentures on the basis of time are Redeemable and Irremediable Debenture.
The debentures on the basis of Convertibility are Convertible Debentures and Non-Convertible Debentures.
The debentures on the basis of Coupon Rate are Specific Coupon Rate Debentures and Zero-coupon Rate Debentures.
The debentures on the basis of Registration are Registered Debentures and Bearer Debentures.
The debentures on the basis of Priority are First Debentures and Second Debentures.
The debentures that are repayable by the company after a specified period are known as Redeemable Debentures.
The debentures that carry a charge on the assets are known as secured debentures.
The debentures that are repayable during the existence of the company are known as Irredeemable Debentures.
The debentures that do not carry any charge on the assets are known as unsecured debentures.
The debentures which are convertible into the equity shares after the expiry of a specified period are known as Convertible Debentures.
The debentures that cannot be converted into equity shares are known as non-convertible debentures.
When a company issues debenture with a specific rate of interest, they are called Coupon Rate Debentures.
The debentures that do not carry a Specific Rate of Interest are known as Zero Coupon Rate Debentures.
Registered Debentures means a company issuing debentures by recording the name of the holder in the made.
When a company transfers debentures by mere delivery, they are known as Bearer Debentures.
The Debentures that are given priority in repayment are called the First Debentures.
The Debentures that are repaid after the first debentures are known as Second Debentures.
It means the issue price of a debenture is below its face value.
When a company issues its debenture at a price more than its face value, it is known as the Issue of Debenture at Premium.
When the issue price and face value of a debenture are equal, it is known as the issue of Debenture at Par.
Yes, debentures can act as collateral security to the lenders.
The term “collateral” means the debenture given or the assets pledged as a security to acquire a loan.
When instead of paying the cash, a company issues its debentures for consideration apart from cash for the assets bought from the vendor.
Yes, companies can Issue Debenture at Par for Consideration other than Cash.
Yes, companies can Issue Debenture at Premium for Consideration other than Cash.
Yes, companies can Issue Debenture at Discount for Consideration other than Cash.
Over Subscription of Debenture means when a company invites the public to subscribe to its debenture and the applications received are more than the number of debentures offered.
The Return on Debentures is known as Interest.
The payment of interest is a charge. It means the company needs to pay the interest even if it incurs losses also.
Debentures Holders can convert their debentures into shares.
No, Debenture holders do not have a Voting Right.
Debenture Holders are the Creditors of the Company.
Rule 18 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debenture) Regulation 2014 governs the Issue of Debentures.
The stamp duty payable on the Issue of Debenture is payable at 0.05%, which is less than the amount of stamp duty payable on the shareholder loan.